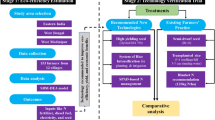
Abstract
In Japan, rice production is undergoing a transition from acreage reduction to an improvement in efficiency and competitiveness. Owing to the global warming, irrigation management is increasingly important in maintaining soil temperature and fertility for rice productivity. This chapter aimed to measure the production efficiency of rice yield, using a two-stage DEA like the former chapter. The data comprised of 122 paddy fields of Koshihikari, one of the most popular Japanese rice varieties. The data was sampled from a large-scale farm located in the Hokuriku Region of Japan in 2015.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, D., & Ali, S. (2014). Influence of subsurface drainage on the productivity of poorly drained paddy fields. European Journal of Agronomy, 56, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2014.02.003.
Aigner, D., Lovell, C., & Schmidt, P. (1977). Formulation and estimation of stochastic frontier production function models. Journal of Econometrics, 6, 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4076(77)90052-5.
Allen, R. G., Pereira, L. S., Raes, D., & Smith, M. (1998). Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements, United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56). Rome, 95–97, 103–109. https://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/40878584/Allen_FAO1998.pdf.
Asaoka, M., Okuno, K., Sugimoto, T., & Fuwa, H. (1985). Developmental changes in the structure of endosperm starch of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 49, 1973–1978. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.49.1973.
Audibert, M., Mathonnat, J., & Henry, M. C. (2003). Social and health determinants of the efficiency of cotton farmers in Northern Côte d’Ivoire. Social Science and Medicine, 56, 1705–1717.
Barrett, C. B., Bellemare, M. F., & Hou, J. Y. (2010). Reconsidering conventional explanations of the inverse productivity-size relationship. World Development, 38(1), 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2009.06.002.
Bouman, B. A. M., & Tuong, T. P. (2001). Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice. Agricultural Water Management, 49, 11–30.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. European Journal of Operations Research, 2, 429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8.
Choudhury, B. U., & Singh, A. K. (2016). Estimation of crop coefficient of irrigated transplanted puddled rice by field scale water balance in the semi-arid Indo-Gangetic Plains, India. Agricultural Water Management, 176, 142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.05.027.
Coelli, T. J., Prasada, R. D. S., Christopher, J. O., & George, E. B. (2005). An introduction to efficiency and productivity analysis (2nd ed., pp. 161–179, 211–213, 261). New York: Springer.
Farrell, M. J. (1957). The measurement of productive efficiency. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 120, 253–290.
Goto, Y., Nitta, Y., & Nakamura, S. (2000). Crops I: Paddy cultivation (pp. 120, 137–142, 195, 210–211). Tokyo: Japan Agricultural Development and Extension Association (JADEA) (in Japanese).
Hirai, Y., Saruta, K., & Hamagami, K. (2012). Evaluation of an analytical method to identify determinants of rice yield component and protein content. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 83, 77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2012.02.001.
Komenet. (2020). Information on production of rice in Japan. https://www.komenet.jp/data/jukyuudb/jukyuudb2/ (in Japanese).
Kozak, M., Singh, P. K., Verma, M. R., & Hore, D. K. (2007). Causal mechanism for determination of grain yield and milling quality of lowland rice. Field Crop Research, 102, 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.03.010.
Li, D., Nanseki, T., Chomei, Y., Sasaki, T., & Butta, T. (2017). Technical efficiency and the effects of water management on rice production in Japan: two-stage DEA on 122 paddy fields of a large-scale farm. In Proceedings of annual symposium of the farm management society of Japan (FMSJ).
Li, D., Nanseki, T., Chomei, Y., & Yokota, S. (2018). Production efficiency and effect of water management on rice yield in Japan: Two-stage DEA analysis on 110 paddy fields of a large-scale farm. Paddy and Water Environment, 16, 643–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-018-0652-0.
Li, D., Nanseki, T., Matsue, Y., Chomei, Y., & Shuichi, Y. (2016). Determinants of paddy yield of individual fields measured by IT combine: Empirical analysis from the perspective of large-scale farm management in Japan. Agricultural Information Research, 25(1), 39–46.
MAFF. (2016a). Statistics on the paddy yield of Japan in 2014. http://www.maff.go.jp/j/tokei/kouhyou/sakumotu/sakkyou_kome/pdf/syukaku_suiriku_14.pdf (in Japanese).
MAFF. (2016b). Statistics on agricultural production costs of Japan. http://www.maff.go.jp/j/tokei/sihyo/data/12-2.html (in Japanese).
Matsue, Y. (2016). Rice production technology for yield and quality improvement of high temperature during the ripening period. In Proceedings of the annual symposium of the Japanese Agricultural Systems Society (JASS) (in Japanese).
Nanseki, T. (Ed.). (2019). Smart agriculture practice in rice-farming and perspective of farm in next-generation (pp. 166, 363). Tokyo: Yokendo (in Japanese).
Nanseki, T., Chomei, Y., & Matsue, Y. (Ed.). (2016). Rice farm management innovation and smart agriculture in TPP era: Farming technology package and ICT applications (pp. 2–22, 168–178, 198–237). Tokyo, Japan: Yokendo (in Japanese).
NRCS (National Resources Conservation Services, USDA). (2017). Water Management—NRCS National Ag Water Management (AGWAM) Team. Retrieved November 20, 2017, from https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/water/manage/.
Roel, A., Mutters, R. G., Eckert, J. W., & Plant, R. E. (2005). Effect of low water temperature on rice yield in California. Agronomy Journal, 97, 943–948. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2004.0129.
Saga, K., Imou, K., Yokoyama, S., & Minowa, T. (2010). Net energy analysis of bioethanol production system from high-yield rice plant in Japan. Applied Energy, 87, 2164–2168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.12.014.
Sellamuthua, R., Liu, G., Ranganathan, C. B., & Serraj, R. (2011). Genetic analysis and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with reproductive-growth traits and grain yield under drought stress in a doubled haploid line population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Field Crops Research, 124, 46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.06.002.
Tao, Y., Zhang, Y., Jin, X., Saiz, G., Jing, R., Guo, L., et al. (2015). More rice with less water: evaluation of yield and resource use efficiency in ground cover rice production system with transplanting. European Journal of Agronomy, 68, 13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.04.002.
Tsujimoto, Y., Horie, T., Randriamihary, H., Shiraiwa, T., & Homma, K. (2009). Soil management: The key factors for higher productivity in the fields utilizing the system of rice intensification (SRI) in the central highland of Madagascar. Agricultural Systems, 100, 61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2009.01.001.
Wang, Z., Zhang, W., Beebout, S., Zhang, H., Liu, L., & Zhang, J. (2016). Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crop Research, 193, 54–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Li, D., Nanseki, T., Chomei, Y. (2021). Two-Stage DEA of 122 Paddy Fields in Hokuriku Region. In: Li, D., Nanseki, T. (eds) Empirical Analyses on Rice Yield Determinants of Smart Farming in Japan. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6256-7_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6256-7_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-6255-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-6256-7
eBook Packages: Economics and FinanceEconomics and Finance (R0)