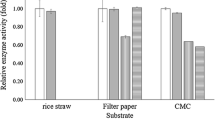
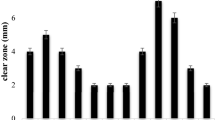
Abstract
Lignocellulose is found in nature as an alternative source of energy and can be used for the production of bioethanol. Cellulose, one of the most abundant components of lignocellulose can be hydrolyzed using enzymes cellulase to produce glucose, which can be used for the production of ethanol. Cellulase production from cellulolytic bacteria is challenging. Hence, research has been focused on isolation and identification of efficient cellulolytic bacteria for their use in bioethanol production. In the present investigation, the most potent screened bacterial strain was subjected to optimization of its cellulase production by using response surface methodology taking four independent variables such as substrate concentration, pH, temperature, and incubation time. The optimization result showed that the bacteria had a maximum production of cellulase enzyme of 617.71 U/mL in an optimized condition at an incubation time of 42 h, pH 9, carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC) concentration of 15 gm/L, and temperature of 37.5 °C. The strain, SCB9, was identified as Bacillus albus based on the 16S rRNA sequencing and phylogeny analysis. Overall results from this study indicate that the cellulolytic bacteria SCB9 is a potent candidate for cellulase production, which can be exploited for bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass through adaptation of further appropriate biotechnological approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aneja KR (2007) Experiments in microbiology, plant pathology and biotechnology new age international 1-602
Ballesteros I, Negro MJ, Oliva JM, Cabañas A, Manzanares P, Ballesteros M (2006) Ethanol production from steam-explosion pretreated wheat straw. Appl Biochem Biotechnol Spring 129–132:496–508
Doddapaneni KK, Tatineni R, Potumarthi R, Mangamoori LN (2007) Optimization of media constituents through response surface methodology for improved production of alkaline proteases by Serratia rubidea. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82(8):721–729
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Lynch JM, Slater JH, Jacqueline A, Bennett SH (1981) Cellulase activities of some aerobic microorganisms isolated from soil. J Gen Microbiol 127:231–236
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):538–542
Muhammad I, Asma S, Quratulain S, Muhammad N (2012) Isolation and screening of cellulolytic bacteria from soil and optimization of cellulase production and activity. Tur J Biochem 37(3):287–293
Saravanan P, Muthuvelayudham R, Kannan RR, Viruthagiri T (2012) Optimization of cellulase production using Trichoderma reesei by RSM and comparison with genetic algorithm. Front Chem Sci Eng 6:443–452
Shajahan S, Muthu GMI, Natesan S, Gopal S (2016) Statistical modeling and optimization of cellulase production by Bacillus licheniformis NCIM 5556 isolated from the hot spring, Maharashtra, India. J King Saud Univ Sci 29
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This chapter does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Collection of soil sample from the buffer areas of Similipal Biosphere Reserve, Odisha with a condition that no plants and animals would be disturbed and following all the provision of Biodiversity Act has been permitted by Odisha Forest and Environment Department, Government of Odisha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Paul, M., Meher, S.R., Giri, S., Thatoi, H. (2021). Isolation, Screening, and Evaluation of Cellulase-Producing Bacteria from the Soil of Similipal Biosphere Reserve for Biofuel Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass. In: Ramkrishna, D., Sengupta, S., Dey Bandyopadhyay, S., Ghosh, A. (eds) Advances in Bioprocess Engineering and Technology . Lecture Notes in Bioengineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7409-2_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7409-2_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-7408-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-7409-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)