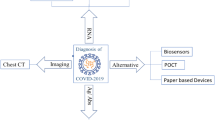
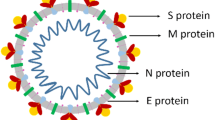
Abstract
COVID-19 is a new strain of coronavirus that had affected nations at a global scale. With an unprecedented high infection and mortality rate, the World Health Organization had declared this novel virus as a pandemic phenomenon in March 2020. Due to the seriousness of this situation, efforts to control and surveillance of this emerging disease are currently of global interest. This chapter will focus on analytical performance of biosensor and artificial intelligent (AI) technologies for the development of robust sensor to detect COVID-19. The future outlooks of biosensor and AI to be employed remotely for COVID-19 detection and diagnosis will also be discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott laboratories (2020) Website at https://www.abbott.com/coronavirus.html
Ahmed SR, Kang SW, Oh S, Lee J, Neethirajan S (2018) Chiral zirconium quantum dots: a new class of nanocrystals for optical detection of coronavirus. Heliyon, e007
Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, Tao Q, Sun Z, Xia L (2020) Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology 296:E32–E40
Allam Z, Jones DS (2020) On the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak and the smart city network: universal data sharing standards coupled with artificial intelligence (AI) to benefit urban health monitoring and management. Healthcare 8(1):46
Bai X, Hsieh B, Xiong Z, Halsey K, Choi JW, Tran T, Pan I, Shi L, Wang D, Mei J, Jiang X, Zeng Q, Egglin T, Hu P, Agarwal S, Xie F, Li S, Healey T, Atalay M, Liao W (2020) Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from viral pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology 296:E46–E54
Bezinge L, Suea-Ngam A, deMello AJ, Shih CJ (2020) Nanomaterials for molecular signal amplification in electrochemical nucleic acid biosensing: recent advances and future prospects for point-of-care diagnostics. Mol Syst Des Eng 5:49–66
Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R (2020) Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing
Chen S-H, Chuang Y-C, Lu YC, Lin H-C, Yang YL, Lin CS (2009) A method of layer-by-layer gold nanoparticle hybridization in a quartz crystal microbalance DNA sensing system used to detect dengue virus. Nanotechnology 20:215501
Chen S, Yang J, Yang W, Wang C, Bärnighausen T (2020) COVID-19 control in China during mass population movements at new year. Lancet 395(10226):764–766
Cooper MA (ed) (2009) Label-free biosensors: techniques and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York
Dong E, Du H, Gardner L (2020) An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet 20:533–534
Draz MS, Shafiee H (2018) Applications of gold nanoparticles in virus detection. Theranostics 8:1985–2017. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.23856
Du S, Wang J, Zhang H, Cui W, Kang Z, Yang T, Lou B, Chi Y, Long H, Ma M, Yuan Q, Zhang S, Zhang D, Xin J, Zheng N (2020) Predicting COVID-19 Using Hybrid AI Model. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3555202
Elfiky AA, Mahdy SM, Elshemey WM (2017) Quantitative structure-activity relationship and molecular docking revealed a potency of anti-hepatitis C virus drugs against human corona viruses. J Med Virol 89:1040–1047
Esteban C, Hyland S, Ratsch G (2017) Time series generation with recurrent conditional GANs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02633
Fahmiin MA, Lim TH (2020) Evaluating the effectiveness of wrapper feature selection methods with artificial neural network classifier for diabetes prediction. Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social informatics and telecommunications engineering, vol 309. Springer, Cham.
Generalov VM, Naumova OV, Fomin BI, P’Yankov SA, Khlistun IV, Safatov AS, Aseev AL (2019) Detection of Ebola virus VP40 protein using a nanowire SOI biosensor. Optoelectron Instrum Data Process 55:618–622. https://doi.org/10.3103/s875669901906013x
Gozes O, Frid-Adar M, Greenspan H, Browning PD, Zhang H, Ji W, Bernheim A, Siegel E (2020) Rapid AI development cycle for the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning CT image analysis. arXiv:2003.05037
Heymann DL, Shindo N (2020) COVID-19: what is next for public health? Lancet 395(10224):542–545
Huang JC, Chang YF, Chen KH, Su LC, Lee CW, Chen CC, … Chou C (2009) Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus nucleocapsid protein in human serum using a localized surface plasmon coupled fluorescence fiber-optic biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 25:320–325
Imran A, Posokhova I, Qureshi HN, Masood U, Riaz S, Ali K, John C, Nabeel M (2020) AI4COVID-19: AI enabled preliminary diagnosis for COVID-19 from cough samples via an app. arXiv:2004.01275
Ishikawa FN, Chang HK, Curreli M, Liao HI, Olson CA, Chen PC, … Zhou C (2009) Label-free, electrical detection of the SARS virus N-protein with nanowire Biosensors utilizing antibody mimics as capture probes. ACS Nano 3:1219–1224. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900086c
Jumper J, Tunyasuvunakool K, Kohli P, Hassabis D, AlphaFold Team (2020) Computational predictions of protein structures associated with COVID-19. DeepMind website. 2: https://deepmind.com/research/open-source/computational-predictions-of-protein-structures-associated-with-COVID-19
Kadioglu O, Saeed M, Johannes G, Efferth T (2020) Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning. Bull World Health Organ. E-pub
Kaya SI, Karadurmus L, Ozcelikay G, Bakirhan NK, Ozkan SA (2020) Electrochemical virus detections with nanobiosensors. In: Nanosensors for smart cities. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 303–326
Kim H, Park M, Hwang J, Kim JH, Chung DR, Lee KS, Kang M (2019) Development of label-free colorimetric assay for MERS-CoV using gold nanoparticles. ACS Sens 4:1306–1312. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00175
Li L, Zhang Q, Wang X, Zhang J, Wang T, Gao TL, Duan W, Tsoi KK, Wang FY (2020) Characterizing the propagation of situational information in social media during COVID-19 epidemic: a case study on Weibo. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 7:56–562
Lim SA, Ahmed MU (2016) Electrochemical immunosensors and their recent nanomaterial-based signal amplification strategies: a review. RSC Adv 6:24995–25014
Lim SA, Ahmed MU (2019) Chapter 1: Introduction to Immunosensors. In: Immunosensors. Royal Society of Chemistry, London, pp 1–20
Lopez CE, Vasu M, Gallemore C (2020) Understanding the perception of COVID-19 policies by mining a multilanguage Twitter dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10359
Mahapatra S, Chandra P (2020) Clinically practiced and commercially viable nanobio engineered analytical methods for COVID-19 diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 2020(165):112361
Mao K, Zhang H, Yang Z (2020) Can a paper-based device trace COVID-19 sources with wastewater-based epidemiology? Environ Sci Technol 2020(54):3733–3735
Monosik R, Streansky M, Surdik E (2012) Biosensors-classification, characterization and new trends. Acta Chim Slov 5:109–120
Ng M, Lee YP, Yang J, Yang F, Li X, Wang H, Lui M, Lo S, Leung B, Khong PL, Hui KM, Yuen K, Kuo MD (2020) Imaging profile of the COVID-19 infection: radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging 2:1
Pirouz B, Shaffiee Haghshenas S, Piro P (2020) Investigating a serious challenge in the sustainable development process: analysis of confirmed cases of COVID-19 (new type of coronavirus) through a binary classification using artificial intelligence and regression analysis. Sustainability 12:2427
Qiu G, Gai Z, Tao Y, Schmitt J, Kullak-Ublick GA, Wang J (2020) Dual-functional plasmonic photothermal biosensors for highly accurate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detection. ACS nano
Reza SM, Najarian K (2016) Transforming big data into computational models for personalized medicine and health care. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 18:339–343
Rinken T, Kivirand K (2019) Biosensors for environmental monitoring
Rothan HA, Byrareddy SN (2020) The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J Autoimmun 109:102433
Saurabh B, Sougat R (2020) Going viral – Covid-19 impact assessment: a perspective beyond clinical practice. J Mar Med Soc 22(1):9–12
Saylan Y, Erdem Ö, Ünal S, Denizli A (2019) An alternative medical diagnosis method: Biosensors for virus detection. Biosensors 9:65
Senior A, Evans R, Jumper J et al (2019) Protein structure prediction using multiple deep neural networks in the 13th critical assessment of protein structure prediction (CASP13). Proteins 87:1141–1148
Senior A, Evans R, Jumper J, Kirkpatrick J, Sifre L, Green T, Qin C, Žídek A, Nelson A, Bridgland A, Penedones H, Petersen S, Simonyan K, Crossan S, Kohli P, Jones D, Silver D, Kavukcuoglu K, Hassabis D (2020) Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning. Nature 7792:706–710
Seo G, Lee G, Kim MJ, Baek SH, Choi M, Ku KB, Kim SJ (2020) Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS nano
Shi L, Sun Q, He JA, Xu H, Liu C, Zhao C, … Long J (2015) Development of SPR biosensor for simultaneous detection of multiplex respiratory viruses. Biomed Mater Eng 26(s1):S2207–S2216
Shi F, Wang J, Shi J, Wu Z, Wang Q, Tang Z, He K, Shi Y, Shen D (2020) Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 1
Soures N, Chambers D, Carmichael Z, Daram A, Shah DP, Clark K, Potte L, Kudithipudi D (2020) SIRNET: understanding social distancing measures with hybrid neural network model for COVID-19 infectious spread, arXiv:2004.10376
Stebbing J, Phelan A, Griffin I, Tucker C, Oechsle O, Smith D, Richardson P (2020) COVID-19: combining antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatments. Lancet Infect Dis 20-4:400–402
Steinmetz M, Lima D, Viana AG, Fujiwara ST, Pessôa CA, Etto RM, Wohnrath K (2019) A sensitive label-free impedimetric DNA biosensor based on silsesquioxane-functionalized gold nanoparticles for Zika virus detection. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111351
Stroock AD (2008) Microfluidics. In: Optical biosensors. Elsevier, pp 659–681. Ligler FS, Taitt CR (eds) (2011). Optical biosensors: today and tomorrow. Elsevier
Takhistov P (2005) Biosensor technology for food processing. Saf Packag. https://doi.org/10.1201/b15995-143
Tam PD, Hieu NV, Chien ND, Le A-T, Tuan MA (2009) DNA sensor development based on multi-wall carbon nanotubes for label-free influenza virus (type a) detection. J Immunol Methods 350(1–2):118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2009.08.002
Teengam P, Siangproh W, Tuantranont A, Vilaivan T, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2017) Multiplex paper-based colorimetric DNA sensor using pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acid-induced AgNPs aggregation for detecting MERS-CoV, MTB, and HPV oligonucleotides. Anal Chem 89(10):5428–5435
Ting DSW, Carin L, Dzau V, Wong TY (2020) Digital technology and COVID-19. Nat Med 26:459–461
Tuena C, Semonella M, Fernández-Álvarez J, Colombo D, Cipresso P (2019) Predictive precision medicine: towards the computational challenge. In: Pravettoni G, Triberti S (eds) P5 eHealth: an agenda for the health technologies of the future. Springer
Wei G (2019) Protein structure prediction beyond AlphaFold. Nat Mach Intell 1:336–337
Weng X, Neethirajan S (2018) Immunosensor based on antibody-functionalized MoS 2 for rapid detection of avian coronavirus on cotton thread. IEEE Sensors J 18:4358–4363
World Health Organization (2020) Accessed 17 Apr 2020 at 8.28 pm, https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
Wu A, Khan WS (eds) (2020) Nanobiosensors: from design to applications. Wiley, Weinheim
Wynants L, Van Calster B, Bonten M, Collins GS, Debray T, De Vos M, Haller M, Heinze G, Moons K, Riley R, Schuit E, Smits L, Snell K, Steyerberg W, Wallisch C, Smeden M (2020) Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of covid-19 infection: systematic review and critical appraisal. Br Med J 369:m1328
Zhang C, Zheng W, Huang X, Bell E, Zhou X, Zhang Y (2020) Protein structure and sequence reanalysis of 2019-nCoV genome refutes snakes as its intermediate host and the unique similarity between its spike protein insertions and HIV-1. J Proteome Res 19:1351–1360
Zhao CT, Daubinger P (2019) Nanobiosensors. Johnson Matthey Technol Rev 63:205–207
Zhavoronkov A, Aladinskiy V, Zhebrak A, Zagribelnyy B, Terentiev V, Bezrukov D, Polykovskiy D, Shayakhmetov R, Filimonov A, Orekhov P, Yan Y, Popova O, Vanhaelen Q, Aliper A, Ivanenkov Y (2020) Potential COVID-2019 3C-like protease inhibitors designed using generative deep learning approaches. Chemrvix website, https://chemrxiv.org/articles/Potential_2019-nCoV_3C-like_Protease_Inhibitors_Designed_Using_Generative_Deep_Learning_Approaches/11829102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lim, S.A., Lim, T.H., Ahmad, A.N. (2020). The Applications of Biosensing and Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Rapid Detection and Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Remote Setting. In: Chandra, P., Roy, S. (eds) Diagnostic Strategies for COVID-19 and other Coronaviruses. Medical Virology: From Pathogenesis to Disease Control. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6006-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6006-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-6005-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-6006-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)