Abstract
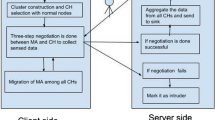
In wireless sensor network, mobile agent (MA) paradigm is the substitute which has many advantages over client–server paradigm. As energy consumption is the major issue for research in WSNs, MA-based paradigm has been a boon in resolving this. In spite of sending data from all nodes to sink, mobile agent itself migrates to all the sensor nodes and collects data which results in minimized energy and bandwidth consumption. But for better efficiency, it is required to plan the itinerary in a best way so that MA can collect data from source nodes efficiently. Many algorithms have been given by researchers which consider all sensor nodes to be visited by MA which is incompetent, and none of the algorithm considers the detection of malicious node and preventing mobile agent to migrate to malicious nodes. Proposed algorithm, first stores the device signature of all intended participating sensor nodes, cluster formation, and eventually by authenticating the nodes based on fingerprints an itinerary for MA will be designed. Cluster head nodes are traversed excluding MNs in CHs itinerary, and data will be aggregated from benign nodes only.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jayram BG, Ashoka DV (2013) Merits and demerits of existing energy efficient data gathering techniques for wireless sensor networks. Int J Comput Appl 66(9)
Cheng C-T, Tse Chi K, Francis CM, Lau (2010) A delay-aware data collection network structure for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens J 11(3):699–710
Vukasinovic I, Babovic Z, Rakocevic G (2012) A survey on the use of mobile agents in wireless sensor networks. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on industrial technology 2012. IEEE, Greece, pp 271–277
Chen X, Makki K, Yen K, Pissinou N (2009) Sensor network security: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 11(2):52–73
Kumar U, Gambhir S (2018) Device fingerprint and Mobile agent based authentication technique in wireless networks. Int J Fut Gen Comm Netw 11(3): 33–48
Mei X, Liu D, Sun K, Xu D (2013) On feasibility of fingerprinting wireless sensor nodes using physical properties. In: 2013 IEEE 27th international symposium on parallel and distributed processing. IEEE, pp 1112–1121
Akyildiz IF, Melodia T, Chowdury KR (2007) Wireless multimedia sensor networks: a survey. IEEE Wirel Commun 14(6):32–39
Chen M, Kwon T, Yuan Y, Leung VC (2006) Mobile agent based wireless sensor networks. J Comput 1(1):4–21
Akkaya K, Younis M (2005) A survey on routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Ad hoc Netw 3(3):325–349
Qi H, Wang F (2001) Optimal itinerary analysis for mobile agents in ad hoc wireless sensor networks. Proc IEEE 18(5):147–153
Chen M, Kwon T, Yuan Y, Choi Y, Leung VC (2006) Mobile agent-based directed diffusion in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2007, 1–13
Wu Q., Rao NS, Barhen J, Iyenger SS, Vaishnavi VK, Qi H, Chakrabarty K (2004) On computing mobile agent routes for data fusion in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 16(6):740–753
Konstantopoulos C, Mpitziopoulos A, Gavalas D, Pantziou G (2009) Effective determination of mobile agent itineraries for data aggregation on sensor networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(12):1679–1693
Venetis IE, Gavalas D, Pantziou GE, Konstantopoulos C (2018) Mobile agents-based data aggregation in WSNs: benchmarking itinerary planning approaches. Wirel Netw 24(6):2111–2132
Qadori HQ, Zulkarnain ZA, Hanapi ZM, Subramaniam S (2017) Multi-mobile agent itinerary planning algorithms for data gathering in wireless sensor networks: a review paper. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 13(1):1550147716684841
El Fissaoui M, Beni-Hssane A, Saadi M (2018) Multi-mobile agent itinerary planning-based energy and fault aware data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 92(1)
Gupta GP, Misra M, Garg K (2014) Energy and trust aware mobile agent migration protocol for data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. J Netw Comput Appl 41:300–311
Lohani D, Varma S (2015) Dynamic mobile agent itinerary planning for collaborative processing in wireless sensor networks. In: 2015 annual IEEE India conference (INDICON). IEEE, pp 1–5
Brar RS, Arora H (2013) Mobile agent security issue in wireless sensor networks. Int J 3(1)
Alrajeh N, Bashir A, Shams MB (2013) Localization techniques in wireless sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 9(6):304628
Chen M, Gonzalez S, Zhang Y, Leung VC (2009) Multi-agent itinerary planning for wireless sensor networks. In: International conference on heterogeneous networking for quality, reliability, security and robustness. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 584–597
Chen M, Cai W, Gonzalez S, Leung VC (2010) Balanced itinerary planning for multiple mobile agents in wireless sensor networks. In: International conference on ad hoc networks. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 416–428
Aşçı M, İleri CU, Dağdeviren O (2017) An energy-efficient capacitated minimum spanning tree algorithm for topology control in wireless sensor networks. In: 2017 25th signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU). IEEE, pp. 1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chaudhary, S., Kumar, U., Gambhir, S. (2021). Energy-Efficient and Secured Mobile Agent Itinerary Approach in Wireless Sensor Network. In: Favorskaya, M.N., Mekhilef, S., Pandey, R.K., Singh, N. (eds) Innovations in Electrical and Electronic Engineering. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 661. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4692-1_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4692-1_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4691-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4692-1
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)