Abstract
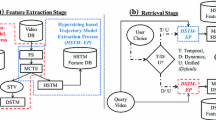
This paper presents VIDeo Content Analysis and Retrieval (VIDCAR), an unsupervised framework for Content-Based Video Retrieval (CBVR) using representation of the dynamics in the spatio-temporal model extracted from video shots. We propose Dynamic Multi Spectro Temporal-Curvature Scale Space (DMST-CSS), an improved feature descriptor for enhancing the performance of CBVR task. Our primary contribution is in representation of the dynamics of the evolution of the MST-CSS surface. Unlike the earlier MST-CSS descriptor [22], which extracts geometric features after the evolving MST-CSS surface converges to a final formation, this DMST-CSS captures the dynamics of the evolution (formation) of the surface and is thus more robust. We have represented the dynamics of MST-CSS surface as a multivariate time series to obtain a DMST-CSS descriptor. A global kernel alignment technique has been adapted to compute a match cost between query and model DMST-CSS descriptor. In our experiments, VIDCAR was shown to have greater precision recall than the competitors on five datasets.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal G, Chowdhury A, Chellappa R (2004) A system identification approach for video-based face recognition. In: ICPR, pp 175–178
Auguste R, El Ghini A, Bilasco M, Ihaddadene N, Djeraba C (2010) Motion similarity measure between video sequences using multivariate time series modeling. In: ICMWI, pp 292–296
Babu RV, Ramakrishnan KR (2007) Compressed domain video retrieval using object and global motion descriptors. MTA 32(1):93–113
Barnich O, Droogenbroeck MV (2011) ViBe: a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE TIP 20(6):1709–1724
Basharat A, Zhai Y, Shah M (2008) Content based video matching using spatiotemporal volumes. CVIU 110(3):360–377
Bashir FI, Member S, Khokhar AA, Member S, Schonfeld D, Member S (2007) Real-time motion trajectory-based indexing and retrieval of video sequences. IEEE TM 9:58–65
Bissacco A, Chiuso A, Ma Y, Soatto S (2001) Recognition of human gaits. CVPR 2:52–57
Brendel W, Todorovic S (2010) Activities as time series of human postures. In: ECCV, pp 721–734
Chattopadhyay C, Das S (2013) STAR: a content based video retrieval system for moving camera video shots. In: NCVPRIPG, pp 1–4
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G (1997) Geodesic active contours. IJCV 22(1):61–79
Chattopadhyay C, Das S (2012) A novel hyperstring based descriptor for an improved representation of motion trajectory and retrieval of similar video shots with static camera. In: EAIT, pp 174–177
Chattopadhyay C, Das S (2012) Enhancing the MST-CSS representation using robust geometric features, for efficient content based video retrieval (CBVR). In: ISM, pp 352–355
Chattopadhyay C, Maurya AK (2013) Multivariate time series modeling of geometric features of spatio-temporal volumes for content based video retrieval. IJMIR 3:15–28
Chellappa R, Sankaranarayanan AC, Veeraraghavan A, Turaga P (2010) Statistical methods and models for video-based tracking, modeling, and recognition. Found Trends Signal Process 3:1–151
Chen PY, Chen ALP (2003) Video retrieval based on video motion tracks of moving objects. Proc SPIE 5307:550–558
Chorley RJ, Morley LSD (1959) A simplified approximation for the hypsometric integral. J Geol, pp 566–571
Cui B, Zhao Z, Tok WH (2012) A framework for similarity search of time series cliques with natural relations. IEEE TKDE 24(3):385–398
Cuturi M (2011) Fast global alignment kernels. In: ICML, pp 929–936
Deng Y, Mukherjee D, Manjunath BS (1998) NeTra-V: toward an object-based video representation. IEEE TCSVT 8:616–627
Doretto G, Chiuso A, Wu YN, Soatto S (2003) Dynamic textures. IJCV 51(2):91–109
Dyana A, Das S (2009) Trajectory representation using Gabor features for motion-based video retrieval. Pattern Recogn Lett 30(10):877–892
Dyana A, Das S (2010) MST-CSS (Multi-Spectro-Temporal Curvature Scale Space), a novel spatio-temporal representation for content-based video retrieval. IEEE TCSVT 20(8):1080–1094
Elliot JK (1989) An investigation of the change in surface roughness through time on the foreland of austre okstindbreen, North Norway. Comput Geosci 15:209–217
Erol B, Kossentini F (2005) Shape-based retrieval of video objects. IEEE TM 7(1):179–182
Fiedler M (1973) Algebraic connectivity of graphs. Czechoslov Math J 23(98):298–305
Florez OU, Lim S (2009) Discovery of time series in video data through distribution of spatiotemporal gradients. In: SAC, pp 1816–1820
Gao HP, Yang ZQ (2010) Content based video retrieval using spatiotemporal salient objects. In: IPTC, pp 689–692
Ghosh A, Boyd S (2006) Upper bounds on algebraic connectivity via convex optimization. Linear Algebra Appl
Giga Y (2006) Surface evolution equations: a level set approach, 1st edn. Springer
Gorelick L, Blank M, Shechtman E, Irani M, Basri R (2007) Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE TPAMI 29(12):2247–2253
Hou S, Zhou S, Siddique M (2013) A compressed sensing approach for query by example video retrieval. MTA 72(3):3031–3044
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J (2012) Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE TPAMI 34(7):1409–1422
Kolmogorov V, Zabih R (2004) What energy functions can be minimized via graph cuts. IEEE TPAMI 26:65–81
Laxman S, Sastry P (2006) A survey of temporal data mining. Sadhana 31(2):173–198
Lee SL, Chun SJ, Kim DH, Lee JH, Chung CW (2000) Similarity search for multidimensional data sequences. In: ICDE, pp 599–608
Liang B, Xiao W, Liu X (2012) Design of video retrieval system using MPEG-7 descriptors. In: Procedia engineering, pp 2578–2582
Lin J, Li Y (2009) Finding structural similarity in time series data using bag-of-patterns representation. In: SSDBM, pp 461–477
Ma Y, Zhang H (2002) Motion texture: a new motion based video representation. In: ICPR, pp 548–551
Madokoro H, Tsukada M, Sato K (2013) Unsupervised and self-mapping category formation and semantic object recognition for mobile robot vision used in an actual environment. Pattern Recogn Phys 1(1):63–74
O’Neill B (1997) Elementary differential geometry, 2nd edn. Academic Press
Peyre G (2011) The numerical tours of signal processing. Comput Sci Eng 13(4):94–97
Popivanov I, Miller RJ (2002) Similarity search over time series data using wavelets. In: ICDE, pp 212–221
Poullot S, Buisson O, Crucianu M (2010) Scaling content-based video copy detection to very large databases. Multimed Tools Appl 47(2):279–306
Reddy KK, Shah M (2012) Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. MVA 24(5):971–981
Richard JC, Morley LSD (2005) Measurement of DEM roughness using the local fractal dimension. Geomorphologie, pp 327–338
Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B (2004) Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: ICPR, pp 32–36
Sellier D, Plank MJ, Harrington JJ (2011) A mathematical framework for modelling cambial surface evolution using a level set method. An Bot 108:1001–1011
Singh O, Sarangi A, Sharma C (2008) Hypsometric integral estimation methods and its relevance on erosion status of north-western lesser himalayan watersheds. Water Resour Manag, pp. 1545–1560
Turaga PK, Veeraraghavan A, Srivastava A, Chellappa R (2011) Statistical computations on Grassmann and Stiefel manifolds for image and video-based recognition. IEEE TPAMI 33(11):2273–2286
Vaduva C, Costachioiu T, Patrascu C, Gavat I, Lazarescu V, Datcu M (2013) A latent analysis of earth surface dynamic evolution using change map time series. IEEE TGRS 51(4):2105–2118
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang MH (2013) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: CVPR
Yilmaz A, Shah M (2008) A differential geometric approach to representing the human actions. CVIU 109(3):335–351
Zhang D, Zuo W, Zhang D, Zhang H (2010) Time series classification using support vector machine with Gaussian elastic metric kernel. In: ICPR, pp 29–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chattopadhyay, C. VIDCAR: an unsupervised CBVR framework for identifying similar videos with prominent object motion. Int J Multimed Info Retr 4, 59–72 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-014-0070-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-014-0070-z