Abstract
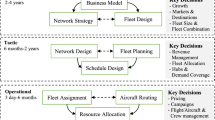
The airline fleet assignment problem consists of assigning an aircraft type to each flight leg of a flight schedule in order to maximize the airline expected profit. Most existing fleet assignment models (FAMs) use an estimation of the revenues per flight leg that neglects the interdependency between the flight legs and poorly approximates the spill and recapture of the passengers. To overcome this difficulty, Dumas et al. (Transp Res Part B 43(4):466–475, 2009) have introduced an iterative solution method that solves at each iteration a FAM and a passenger flow model (PFM). A solution to the PFM provides the expected number of passengers on each leg, taking into account spill and recapture. These numbers are then used to better estimate the revenues per flight leg for the next iteration. Compared to solving a FAM once, this method yields better quality solutions but requires much larger computational times (by a factor 10 or more). In this paper, we aim at reducing these computational times while preserving solution quality. To do so, we propose to reevaluate periodically the flight leg revenues via the PFM while solving the FAM with a heuristic branch-and-bound algorithm. Computational results obtained for a large-scale real-life network and various demand levels show that the proposed method can reduce the average computational time by a factor of 2–3 to obtain solutions of similar quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja R, Goodstein KJ, Mukherjee A, Orlin JB, Sharma D (2002) A very large-scale neighborhood search algorithm for the combined through-fleet-assignment model. INFORMS J Comput 19(3): 416–428
Air Canada (2012) Annual Report 2012. http://www.aircanada.com/en/about/investor/documents/2012_ar.pdf
Barnhart C, Boland NL, Clarke LW, Johnson EL, Nemhauser GL, Shenoi RG (1998) Flight string models for aircraft fleeting and routing. Transp Sci 32(3):208–220
Barnhart C, Farahat A, Lohatepanont M (2009) Airline fleet assignment with enhanced revenue. Oper Res 57(1): 231–244
Barnhart C, Kniker T, Lohatepanont M (2002) Itinerary-based airline fleet assignment. Transp Sci 36(2):199–217
Bélanger N, Desaulniers G, Soumis F, Desrosiers J (2006a) Periodic airline fleet assignment with time windows, spacing constraints, and time dependent revenues. Eur J Oper Res 175(3):1754–1766
Bélanger N, Desaulniers G, Soumis F, Desrosiers J, Lavigne J (2006b) Weekly airline fleet assignment with homogeneity. Transp Res Part B: Methodol 40(4):306–318
Burden RL, Faires JD (2011) Numerical analysis, 9th edn. Brooks/Cole Cengage Learning, Boston
Clarke L, Hane C, Johnson E, Nemhauser G (1996) Maintenance and crew considerations in fleet assignment. Transp Sci 30(3):249–260
Desaulniers G, Desrosiers J, Dumas Y, Solomon MM, Soumis F (1997) Daily aircraft routing and scheduling. Manag Sci 43(6):841–855
Dumas J, Aithnard F, Soumis F (2009) Improving the objective function of the fleet assignment problem. Transp Res Part B 43(4):466–475
Dumas J, Soumis F (2008) Passenger flow model for airline networks. Transp Sci 42(2):197–207
Farkas A (1996) The influence of network effects and yield management on airline fleet assignment decisions. Doctoral thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Hane CA, Barnhart C, Johnson EL, Marsten RE, Nemhauser GL, Sigismondi G (1995) The fleet assignment problem: solving a large-scale integer program. Math Program 70(2):211–232
Ioachim I, Desrosiers J, Soumis F, Bélanger N (1999) Fleet assignment and routing with schedule synchronization constraints. Eur J Oper Res 119(1):75–90
Jacobs TL, Smith BC, Johnson EL (2008) Incorporating network flow effects into the airline fleet assignment process. Transp Sci 42(4):514–529
Klabjan D (2005) Large-scale models in the airline industry. In: Desaulniers G, Desrosiers J, Solomon MM (eds) Column generation. Springer, New York, pp 163–195
Rexing B, Barnhart C, Kniker T, Jarrah A, Krishnamurthy N (2000) Airline fleet assignment with time windows. Transp Sci 34(1):1–20
Sherali HD, Bish EK, Zhu X (2006) Airline fleet assignment concepts, models, and algorithms. Eur J Oper Res 172(1):1–30
Sherali HD, Bae K-H, Haouari M (2009) Integrated airline schedule design and fleet assignment: polyhedral analysis and Benders decomposition approach. INFORMS J Comput 22(4):500–513
Smith BC, Johnson EL (2006) Robust airline fleet assignment: imposing station purity using station decomposition. Transp Sci 40(4):497–516
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasalle Ialongo, D., Desaulniers, G. Airline fleet assignment with internal passenger flow reevaluations. EURO J Transp Logist 3, 121–142 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13676-013-0038-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13676-013-0038-9