Abstract
Background
Osteosarcoma is a malignant bone cancer of which the survival rate is still low. One reason for this low survival rate is drug resistance. In the past, it has been shown that microRNAs may play critical roles in osteosarcoma development and drug resistance. The mechanisms by which osteosarcoma cells acquire this resistance have, however, remained largely unknown. Here, we aimed at assessing the role of microRNA-488 in the acquisition of drug resistance by osteosarcoma cells.
Methods
Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure the expression of microRNA-488 in primary osteosarcoma samples and in osteosarcoma-derived cells, whereas microRNA-488 mimics and inhibitors were used to modify its expression in these cells. Luciferase reporter, Western blotting, cell viability, apoptosis and ChIP assays were used to assess the various effects of modified microRNA-488 expression in osteosarcoma-derived cells.
Results
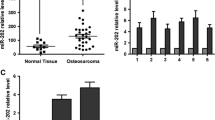
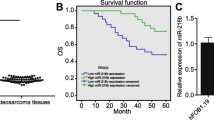
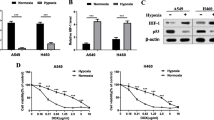
We found that microRNA-488 is over-expressed in primary osteosarcoma tissues and osteosarcoma-derived cells and that hypoxia can induce microRNA-488 expression via binding to the hypoxia response element (HRE) in its promoter. We also found that exogenous over-expression of microRNA-488 promotes the proliferation, reduces the apoptosis and decreases the sensitivity to chemotherapy (doxorubicin) of osteosarcoma cells via direct targeting of the tumor suppressor Bim, which is a mediator of apoptosis. In contrast, we found that transfection of a microRNA-488 inhibitor resulted in an increase in both apoptosis and drug sensitivity, and a decrease in proliferation.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that miRNA-488 may serve as a predictor of response to chemotherapy and as a therapeutic target in human osteosarcomas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. S. Geller, R. Gorlick, Osteosarcoma: a review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 8, 705–718 (2010)
W. S. Ferguson, A. M. Goorin, Current treatment of osteosarcoma. Cancer Investig. 19, 292–315 (2001)
A. Luetke, P. A. Meyers, I. Lewis, H. Juergens, Osteosarcoma treatment - where do we stand? A state of the art review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 40, 523–532 (2014)
Z. Wei, L. Cui, Z. Mei, M. Liu, D. Zhang, miR-181a mediates metabolic shift in colon cancer cells via the PTEN/AKT pathway. FEBS Lett. 588, 1773–1779 (2014)
R. Mitra, J. Sun, Z. Zhao, microRNA regulation in cancer: One arm or two arms? Int. J. Cancer 137, 1516-1518 (2015)
E. Prodromaki, A. Korpetinou, E. Giannopoulou, E. Vlotinou, M. Chatziathanasiadou, N. I. Papachristou, C. D. Scopa, H. Papadaki, H. P. Kalofonos, D. J. Papachristou, Expression of the microRNA regulators Drosha, dicer and Ago2 in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cell. Oncol. 38, 307–317 (2015)
Y. S. Lee, A. Dutta, MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 4, 199–227 (2009)
C. Salazar, R. Nagadia, P. Pandit, J. Cooper-White, N. Baneriee, N. Dimitrova, W. B. Coman, C. Punyadeera, A novel saliva-based microRNA biomarker panel to detect head and neck cancers. Cell. Oncol. 37, 331–338 (2014)
L. Rask, E. Balslev, R. Sokilde, E. Hogdall, H. Flyger, J. Eriksen, T. Litman, Differential expression of miR-139, miR-486 and miR-21 in breast cancer patients sub-classified according to lymph node status. Cell. Oncol. 37, 215–227 (2014)
C. Yu, M. Wang, Z. Li, J. Xiao, F. Peng, X. Guo, Y. Deng, J. Jiang, C. Sun, MicroRNA-138-5p regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth through targeting FOXC1. Cell. Oncol. 38, 173–181. (2015)
I. Fkih M'hamed, M. Privat, F. Ponelle, F. Penault-Llorca, A. Kenani, Y. J. Bignon, Identification of miR-10b, miR-26a, miR-146a and miR-153 as potential triple-negative breast cancer biomarkers. Cell. Oncol. 38, 433–442 (2015)
D. Zhang, Z. Shi, M. Li, J. Mi, Hypoxia-induced miR-424 decreases tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy by inhibiting apoptosis. Cell. Death Dis. 5, e1301 (2014)
Y. Zhang, G. Talmon, J. Wang, MicroRNA-587 antagonizes 5-FU-induced apoptosis and confers drug resistance by regulating PPP2R1B expression in colorectal cancer. Cell. Death. Dis. 6, e1845 (2015)
M. E. Fiori, C. Barbini, T. L. Haas, N. Marroncelli, M. Patrizii, M. Biffoni, R. De Maria, Antitumor effect of miR-197 targeting in p53 wild-type lung cancer. Cell. Death Differ. 21, 774–782 (2014)
K. Jain, A. Basu, The multifunctional protein kinase C-epsilon in cancer development and progression. Cancers (Basel) 6, 860–878 (2014)
J. G. Zhang, J. F. Guo, D. L. Liu, Q. Liu, J. J. Wang, MicroRNA-101 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in non-small cell lung cancer through directly targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2. J. Thorac. Oncol. 6, 671–678 (2011)
J. Song, D. Kim, C.H. Lee, M.S. Lee, C.H. Chun, E.J. Jin, MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J. Biomed. Sci. 20, 20–31 (2013)
M. Muinos-Gimeno, Y. Espinosa-Parrilla, M. Guidi, B. Kagerbauer, T. Sipila, E. Maron, K. Pettai, L. Kananen, R. Navines, R. Martin-Santos, M. Gratacos, A. Metspalu, I. Hovatta, X. Estivilla, Human microRNAs miR-22, miR-138-2, miR-148a, and miR-488 are associated with panic disorder and regulate several anxiety candidate genes and related pathways. Biol. Psychiatry 69, 526–533 (2011)
K. Sikand, J.E. Slaibi, R. Singh, S.D. Singh, G.C. Shukla, miR 488* inhibits androgen receptor expression in prostate carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 129, 810–819 (2011)
D. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Shi, J. Liu, P. Sun, X. Hou, J. Zhang, S. Zhao, B. P. Zhou, J. Mi, Metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts by IDH3alpha downregulation. Cell. Rep. 10, 1335–1348 (2015)
Q. Li, D. Zhang, Y. Wang, P. Sun, X. Hou, J. Larner, W. Xiong, J. Mi, MiR-21/Smad 7 signaling determines TGF-beta1-induced CAF formation. Sci. Rep. 3, 2038 (2013)
A. J. Chou, R. Gorlick, Chemotherapy resistance in osteosarcoma: current challenges and future directions. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 6, 1075–1085 (2006)
S. W. Lowe, A. W. Lin, Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 21, 485–495 (2000)
Y. Wang, C. G. Lee, MicroRNA and cancer--focus on apoptosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 13, 12–23 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (81,372,869).
Ethical standard
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All patients provided informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Tan, W., Lv, H. et al. Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-488 regulates apoptosis by targeting Bim in osteosarcoma. Cell Oncol. 39, 463–471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0288-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0288-2