Abstract
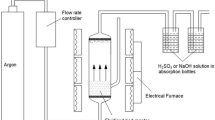
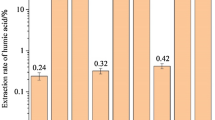
The pretreatment of low rank coal with nitric acid oxidation can promote its bio-liquefaction. However, the detailed mechanism of which remains an unresolved problem. In the present work, the characteristics of Fushun coal before and after oxidation by nitric acid were investigated combined with elemental composition, pore volume and pore size, Zeta potential, FT-IR, and 13C solid NMR spectrum analysis. The results show that the inorganic substance inlaid in coal are dissolved by nitric acid, which results in the decrease of coal ash content and increase of pore volume and pore size. Furthermore, there exist obvious chemical reactions between nitric acid and the functional groups of coal including aromatic ring carboxylation, side chain alkyl of aromatic ring oxidation and aromatic ring nitration. Among these reactions, some led to the increase in content of carboxyl, aliphatic carbon connected with O and humic acid carbon, while others caused the reduction of aromaticity, methyl carbon, substituted aryl carbon and side chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catcheside D E A, Mallett K J, 1991. Solubilization of Australian lignites by fungi and other microorganisms. Energy & Fuels, 5(1): 141–145.
Hofrichter M, Bublitz F, Fritsche W, 1997. Fungal attack on coal II: solubilization of low-rank coal by filamentous fungi. Fuel Processing Technology, 52(1–3): 55–64.
Machnikowska H, Pawelec K, Anna P, 2002. Microbial degradation of low rank coals. Fuel Processing Technology, 77–78: 17–23.
Maka A, Srivastava V, Kllbane J, Akin C, 1989. Biological solubilization of untreated north dakota lignite by a mixed bacterial and a mixed bacterial/fungal culture. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 20–21(1): 715–729.
Ni X Z, Xu Z H, Zeng P J, 1996. The Research of preparing nitrohumic acid from low rank coal oxidized with nitric acid. Coal Conversion, 19(2): 80–86.
Selvi A V, Banerjee R, Ram L C, Singh G, 2009. Biodepolymerization studies of low rank Indian coals. World Journal of Microbiology and biotechnology, 25(10): 1713–1720.
Shi K Y, Tao X X, Yin S D, Yin W X, 2007. Bio-solubilization of Fushun lignite. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 36(3): 339–342.
Solum M. S, Pugmire R J, Grant D M, 1989. Carbon-13 solid-state NMR of Argonne-premium coals. Energy & Fuels, 3 (2): 187–193.
Wang Y J, 2008. Study on screening of high efficient strains for Shenfu coal bioconversion. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology.
Wang Y, Wang L, Wang X M, 2006. Analysis of biosolubilization coal products. Hydrometallurgy of China, 25(3): 165–168.
Wang Z H, Gao J S, Xu Z, Chen S R, 1991. The chemical depolymerization of coal II depolymerization of coal with nitric acid. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 119(2): 164–169.
Wong D, 2009. Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 157(2): 174–209.
Zhang M X, Wang L G, Ou Z S, Shen G J, 2007. Selection of several degradation lignin funguns and the experimental study of their cooperation to biodegradation of coal. Journal of China Coal Sociey, 32(6): 634–638.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50874107); the Guizhou Science and Technology Fund (Qiankehe J zi [2012]2306); the Guizhou High-level Talent Special Assistant Fund (TZJF-2011-04); the Guizhou Research Laboratory Platform of Clean and Efficient Use of Coal Resources (Qianke Platform [2011] 4003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Ky., Tao, Xx., Hong, Ff. et al. Mechanism of oxidation of low rank coal by nitric acid. J Coal Sci Eng China 18, 396–399 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-012-0411-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-012-0411-6