Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of a fludarabine-based individualized regimen in elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
Methods
Sixteen patients were treated with the individual regimen of fludarabine combined with rituximab. Adverse reactions and efficacy of treatment were observed.
Results
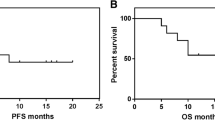
Sixteen patients received a total of 69 courses of immunochemotherapy, with an average administration of 275 mg fludarabine per person. The overall response rate was 81.3% (13/16), in which seven cases (43.8%) achieved complete remission, six cases (37.5%) achieved partial remission, two cases (12.5%) had stable disease, and one case (6.3%) developed disease progression. The most frequent side effect was myelosuppression. Two patients experienced grade 3–4 cytopenia, one case developed a grade 3 infection, and no treatment-related death was observed.
Conclusion
The individual regimen of fludarabine combined with rituximab demonstrated marked clinical efficacy and acceptable toxicity in elderly patients with CLL/SLL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin TS. What is the optimal initial treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia? Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21:1641–1649.
Guo B, Zhu H-L, Li S-X, et al. Individualized liposomal doxorubicin-based treatment in elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Oncologie. 2011;34:184–188.
Ferrajoli A, O’Brien S, Wierda W, et al. Treatment of patients with CLL 70 years old and older: a single center experience of 142 patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46:S86.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IWCLL) updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group (NCI-WG) 1996 guidelines. Blood. 2008;111:5446–5456.
Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, et al. Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1750–1757.
Schulz H, Klein SK, Rehwald U, et al. Phase 2 study of a combined immunochemotherapy using rituximab and fludarabine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2002;100:3115–3120.
Tam CS, O’Brien S, Wierda W, et al. Long-term results of the fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab regimen as initial therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2008;112:975–980.
Robak T, Dmoszynska A, Solal-Celigny P, et al. Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide prolongs progression-free survival compared with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide alone in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1756–1765.
Foon KA, Boyiadzis M, Land SR, Pietragallo L, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with low-dose fludarabine and cyclophosphamide and high-dose rituximab in previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:498–503.
Eichhorst BF, Busch R, Hopfinger G, et al. Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide versus fludarabine alone in first-line therapy of younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2006;107:885–891.
Woyach JA, Ruppert AS, Heerema NA, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine and rituximab produces extended overall survival and progression-free survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: long-term follow-up of CALGB study 9712. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1349–1355.
Zhu H-L, Fan H, Yao S. A case study of fludarabine treatment of prolymphocytic leukemia in elderly. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2000;39:351–353.
Liu Y, Zhu H-L, Lu X-C. The treatment of fludarabine combined with CD antibody and amifostine of elderly chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chinese Laboratory Journal of Hematology. 2007;15:989–992.
Keating M, O’Brien S, Albitar M, et al. Early results of a chemoimmunotherapy regimen of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as initial therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4079–4088.
Del Poeta G, Del Principe MI, Irno Consalvo MA, et al. The addition of rituximab to fludarabine improves clinical outcome in untreated patients with ZAP-70 negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 2005;104:2743–2752.
Byrd JC, Rai K, Peterson BL, et a1. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine may prolong progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an updated retrospective comparative analysis of CALGB 9712 and CALGB 9011. Blood. 2005;105:49–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
To view enhanced content go to www.advancesintherapy.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Zhu, HL., Fan, H. et al. Individualized Fludarabine-Based Regimen in Elderly Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Adv Therapy 29, 178–186 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-011-0097-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-011-0097-y