Abstract
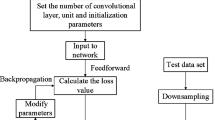
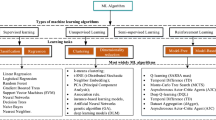
The mechanical and physical properties of spun yarns and fabrics depend not only on properties of constituent fibers, but also the yarn structure characterized by geometrical arrangement of fibers in the yarn body. Although there are many studies related to analyzing the migratory properties of spun yarns, there are no studies available about predicting yarn migration parameters. Therefore, the main aim of this research is to introduce a new approach to predict migratory properties of different kinds of spun yarns, namely siro, solo, compact and conventional ring-spun yarns. To achieve the objectives of the research, general physical and mechanical properties of spun yarns together with existing standards were thoroughly studied. Spun yarn migratory properties were predicted using intelligent technique of artificial neural network (ANN). Results signified that the ANN models can predict precisely the yarn migratory properties on the basis of a series of yarn physical and mechanical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. E. Morton and K. C. Yen, J. Text. Inst., 43, 60 (1952).
H. Wu, M. Chen, W. Wang, K. Lai, and B. Ma, Text. Res. J., 79, 810 (2009).
W. E. Morton, Text. Res. J., 26, 325 (1956).
J. W. S. Hearle, B. S. Gupta, and V. B. Merchant, Text. Res. J., 35, 329 (1965).
Y. Huh, Y. R. Kim, and W. Y. Ryu, Text. Res. J., 71, 81 (2001).
G. Riding, J. Text. Inst., 55, 9 (1964).
B. S. Gupta and J. W. S. Hearle, Text. Res. J., 35, 788 (1965).
G. Basal, Ph. D., Dissertation, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, 2003.
D. Yilmaz, F. Goktepe, O. Goktepe, and D. Kremenakova, Text. Res. J., 77, 661 (2007).
M. C. Ramesh, R. Rajamanickam, and S. Jayaraman, J. Text. Inst., 86, 459 (1995).
A. Guha, R. Chattopadhyay, and B. Jayadeva, J. Text. Inst., 92, 139 (2001).
P. K. Majumdar and A. Majumdar, Text. Res. J., 74, 652 (2004).
Y. C. Zeng, K. F. Wang, and C. W. Yu, Text. Res. J., 74, 689 (2004).
A. A. Gharehaghaji, M. Shanbeh, and M. Palhang, Text. Res. J., 77, 565 (2007).
G. Yao, J. Guo, and Y. Zhou, Text. Res. J., 75, 274 (2005).
S. Ertugrul and N. Ucar, Text. Res. J., 70, 845 (2000).
D. Semnani, M. Vadood, Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., 23, 217 (2010).
M. Vadood, D. Semnani, and M. Morshed, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 120, 735 (2011).
P. Soltani and M. S. Johari, J. Text. Inst., 103, 622 (2012).
R. D. Anandjiwala, J. D. Bargeron, C. K. Bragg, and B. C. Goswami, Text. Res. J., 69, 129 (1999).
A. Ghosh, S. M. Ishtiaque, and R. S. Rengasamy, Text. Res. J., 75, 731 (2005).
P. Soltani and M. S. Johari, J. Text. Inst., available online (04 Nov. 2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltani, P., Vadood, M. & Johari, M.S. Modeling spun yarns migratory properties using artificial neural network. Fibers Polym 13, 1190–1195 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-1190-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-1190-9