Abstract
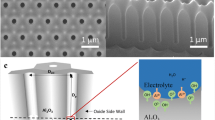
The present work demonstrates a simple method to prepare nanostructured Ni films with different morphologies with the assistance of porous anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) membranes. A great distinction is observed as the Ni films deposited onto the top and bottom sides of AAO membranes. The wetting properties of as-prepared membranes are investigated by measuring the contact angles of water on the surfaces. Results show that the static water contact angle changes dramatically from 124°±1° to 45°±1° on different Ni films, implying a change of the wettability from hydrophobicity to hydrophilicity affected by the surface patterns. This versatile approach can be conducted on various materials with potential applications in a broad range of fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ko H, Zhang Z X, Chueh Y L, Ho J C, Lee J, Fearing R S, Javey A. Wet and dry adhesion properties of self-selective nanowire connectors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(19): 3098–3102
Lu J G, Chang P C, Fan Z Y. Quasi-one-dimensional metal oxide materials — synthesis, properties and applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2006, 52(1–3): 49–91
Hurst S J, Payne E K, Qin L D, Mirkin C A. Multisegmented one-dimensional nanorods prepared by hard-template synthetic methods. Angewandte Chemie, 2006, 45(17): 2672–2692
Martin C R. Nanomaterials: a membrane-based synthetic approach. Science, 1994, 266(5193): 1961–1966
Li D, Jiang C, Jiang J, Lu J G. Self-assembly of periodic serrated nanostructures. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(2): 253–258
Li D, Thompson R S, Bergmann G, Lu J G. Template-based synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt nanotube arrays. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(23): 4575–4578
Liu ZW, Chang P C, Chang C C, Galaktionov E, Bergmann G, Lu J G. Shape anisotropy and magnetization modulation in hexagonal cobalt nanowires. Advanced Functional Materials, 2008, 18(10): 1573–1578
Qu M, Zhao G Y, Wang Q, Cao X P, Zhang J. Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces by a Pt nanowire array on Ti/Si substrates. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(19): 055707
Taberna P L, Mitra S, Poizot P, Simon P, Tarascon J-M. High rate capabilities Fe3O4-based Cu nano-architectured electrodes for lithium-ion battery applications. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(7): 567–573
Ding G Q, Shen W Z, Zheng M J, Xu W L, He Y L, Guo Q X. Fabrication of highly ordered nanocrystalline Si:H nanodots for the application of nanodevice arrays. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 283(3–4): 339–345
Lei Y, Chim W K, Weissmuller J, Wilde G, Sun H P, Pan X Q. Ordered arrays of highly oriented single-crystal semiconductor nanoparticles on silicon substrates. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16(9): 1892–1898
Li A P, Müller F, Birner A, Nielsch K, Gösele U. Hexagonal pore arrays with a 50–420 nm interpore distance formed by selforganization in anodic alumina. Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 84(11): 6023–6026
Lee W, Ji R, Gösele U, Nielsch K. Fast fabrication of long-range ordered porous alumina membranes by hard anodization. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(9): 741–747
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta, 1997, 202(1): 1–8
Parkin I P, Palgrave R G. Self-cleaning coatings. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 15(17): 1689–1695
Zorba V, Stratakis E, Barberoglou M, Spanakis E, Tzanetakis P, Anastasiadis S H, Fotakis C. Biomimetic artificial surfaces quantitatively reproduce the water repellency of a lotus leaf. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(21): 4049–4054
Blossey R. Self-cleaning surfaces — virtual realities. Nature Materials, 2003, 2(5): 301–306
Callies M, Quere D. On water repellency. Soft Matter, 2005, 1(1): 55–61
Nakajima A, Hashimoto K, Watanabe T. Recent studies on superhydrophobic films. Monatshefte Fur Chemie, 2001, 132(1): 31–41
Hsu S H, Sigmund W M. Artificial hairy surfaces with a nearly perfect hydrophobic response. Langmuir, 2010, 26(3): 1504–1506
Wenzel R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28: 988–994
Cassie A B D, Baxter S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1944, 40: 0546–0550
Krupenkin T N, Taylor J A, Schneider T M, Yang S. From rolling ball to complete wetting: the dynamic tuning of liquids on nanostructured surfaces. Langmuir, 2004, 20(10): 3824–3827
Dorrer C, Ruhe J. Wetting of silicon nanograss: from superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic surfaces. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(1): 159–163
Furstner R, Barthlott W, Neinhuis C, Walzel P. Wetting and selfcleaning properties of artificial superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir, 2005, 21(3): 956–961
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Jiang, C., Zhou, J. et al. Tunable wettability of metallic films with assistance of porous anodic aluminum oxide. Front. Optoelectron. China 3, 317–320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-010-0104-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-010-0104-y