Abstract
Introduction
Bone marrow-derived cells (BMCs) include stem cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into a variety of cell types. Administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) induces the circulation of BMCs in the peripheral blood. A phase II prospective trial was carried out for evaluation of BMC mobilization induced by multiple courses of G-CSF in cirrhotic patients.
Patients and methods
Fifteen patients with advanced liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh score ≥6 points) were enrolled and treated with a 3-day G-CSF course, administered at 3-month intervals for a total of four courses. BMC mobilization was assessed by evaluating CD34+ve cells using flow cytometry. Expressions of multiple hepatic and stem markers were assessed on mobilized CD34+ve cells. Feasibility and safety were explored; clinical and adverse events were compared to those of a control group. Telomere length was monitored to rule out early cell aging caused by G-CSF.
Results
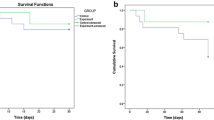
A significant increase in G-CSF-induced circulating CD34+ve cells was consistently observed, although a progressive reduction of peak values was documented from cycle I to IV (p < 0.005). Mobilized CD34+ve cells expressed both stem and multiple hepatocyte markers, including mRNA of albumin and CYP2B6 (cytochrome P2 B6). Treatment was well tolerated, with no severe adverse events and no significant telomere length shortening following G-CSF. The procedure was safe. Overall, ten patients had either improved or had stable liver function tests (such as the Child-Pugh score), whereas five worsened and died from liver-related causes.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that G-CSF can be safely administrated up to four times over a 1-year period in decompensated cirrhotic patients. The repeated BMC mobilization favors the circulation of stem cells coexpressing hepatic markers and mRNA of liver-related genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMC:
-
Bone marrow-derived cells
- G-CSF:
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- TL:
-
Telomere length
- PB:
-
Peripheral blood
- BM:
-
Bone marrow
- MELD:
-
Model for end-stage liver disease
- CFU-GM:
-
Colony-forming unit-granulocyte–macrophage
- SDF-1:
-
Stromal derived factor-1
- SCF:
-
Stem cell factor
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- ALB_1:
-
Albumin 1
- AFP-1:
-
Alpha-feto protein 1
- HNF4A-1:
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4A
- CYP2B6_2:
-
Cytochrome P2 B6
- RT-PCR:
-
Real time polymerase chain reaction
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- CP:
-
Child-Pugh
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
- c-Met:
-
Hepatocyte growth-factor receptor
References
Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L, Jiang Y, Blackstad M, Lund T, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest 2002;109:1291–1302
Haga J, Wakabayashi G, Shimazu M, Tanabe M, Takahara T, Azuma T, et al. In vivo visualization and portally repeated transplantation of bone marrow cells in rats with liver damage. Stem Cells Dev 2007;16:319–328
Ng IO, Chan KL, Shek WH, Lee JM, Fong DY, Lo CM, et al. High frequency of chimerism in transplanted livers. Hepatology 2003;38:989–998
Gaia S, Cappia S, Smedile A, Bacillo E, Gaia E, Gubetta L, et al. Epithelial microchimerism: consistent finding in human liver transplants. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21:1801–1806
Herencia C, Rodriguez-Ariza A, Canalejo A, Naranjo A, Briceno FJ, Lopez-Cillero P, et al. Differential bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells mobilization in hepatectomized patients. J Gastrointest Surg 2011;15:1459–1467
Tarella C, Ferrero D, Bregni M, Siena S, Gallo E, Pileri A, et al. Peripheral blood expansion of early progenitor cells after high-dose cyclophosphamide and rhGM-CSF. Eur J Cancer 1991;27:22–27
Levesque JP, Winkler IG. Mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells: state of the art. Curr Opin Organ Transpl 2008;13:53–58
Spahr L, Lambert JF, Rubbia-Brandt L, Chalandon Y, Frossard JL, Giostra E, et al. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor induces proliferation of hepatic progenitors in alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized trial. Hepatology 2008;48:221–229
Gaia S, Smedile A, Omede P, Olivero A, Sanavio F, Balzola F, et al. Feasibility and safety of G-CSF administration to induce bone marrow-derived cells mobilization in patients with end stage liver disease. J Hepatol 2006;45:13–19
Jin SZ, Meng XW, Sun X, Han MZ, Liu BR, Wang XH, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances bone marrow mononuclear cell homing to the liver in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:2805–13
Li N, Zhang L, Fang B. Human CD34+ cells mobilized by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor ameliorate radiation-induced liver damage in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther 2010;1:22. doi:10.1186/scrt22.
Garg V, Garg H, Khan A, Trehanpati N, Kumar A, Sharma BC, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes CD34(+) cells and improves survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gastroenterology 2012;142(505–512):e501
Dar A, Goichberg P, Shinder V, Kalinkovich A, Kollet O, Netzer N, et al. Chemokine receptor CXCR4-dependent internalization and resecretion of functional chemokine SDF-1 by bone marrow endothelial and stromal cells. Nat Immunol 2005;6:1038–1046.
Corradini P, Tarella C, Olivieri A, Gianni AM, Voena C, Zallio F, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by allografting of hematopoietic cells can produce clinical and molecular remissions in patients with poor-risk hematologic malignancies. Blood 2002;99:75–82
Tarella C, Rutella S, Gualandi F, Melazzini M, Scime R, Petrini M, et al. Consistent bone marrow-derived cell mobilization following repeated short courses of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: results from a multicenter prospective trial. Cytotherapy 2010;12:50–59
Ruella M, Rocci A, Ricca I, Carniti C, Bodoni CL, Ladetto M, et al. Comparative assessment of telomere length before and after hematopoietic SCT: role of grafted cells in determining post-transplant telomere status. Bone Marrow Transpl 2010;45:505–512
Rocci A, Ricca I, Dellacasa C, Longoni P, Compagno M, Francese R, et al. Long-term lymphoma survivors following high-dose chemotherapy and autograft: evidence of permanent telomere shortening in myeloid cells, associated with marked reduction of bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell reservoir. Exp Hematol 2007;35:673–681
Gianni AM, Siena S, Bregni M, Tarella C, Stern AC, Pileri A, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to harvest circulating haemopoietic stem cells for autotransplantation. Lancet 1989;2:580–585
Couto BG, Goldenberg RC, da Fonseca LM, Thomas J, Gutfilen B, Resende CM, et al. Bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for patients with cirrhosis: a phase 1 study. Liver Int 2011;31:391–400
Lorenzini S, Isidori A, Catani L, Gramenzi A, Talarico S, Bonifazi F, et al. Stem cell mobilization and collection in patients with liver cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2008;27(10):932–939
Panasiuk A, Kemona A. Bone marrow failure and hematological abnormalities in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst 2001;46:100–105
Pozotrigo M, Adel N, Landau H, Lesokhin A, Lendvai N, Chung DJ, et al. Factors impacting stem cell mobilization failure rate and efficiency in multiple myeloma in the era of novel therapies: experience at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. Bone Marrow Transpl 2013;. doi:10.1038/bmt.2012.281.
Chow S, Lazo-Langner A, Ormond G, Howson-Jan K, Xenocostas A. Predictors of unsuccessful mobilization with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor alone in patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Clin Apher 2013;. doi:10.1002/jca.21252.
Akard LP, Wiemann M, Thompson JM, Swinney M, Lynn K, Hanks S, Jansen J. Impaired stem cell collection by consecutive courses of high-dose mobilizing chemotherapy using cyclophosphamide, etoposide, and G-CSF. J Hematother 1996;5:271–277
Tarella C, Caracciolo D, Gavarotti P, Bondesan P, Cherasco C, Omede P, Bregni M, et al. Circulating progenitors following high-dose sequential (HDS) chemotherapy with G-CSF: short intervals between drug courses severely impair progenitor mobilization. Bone Marrow Transpl 1995;16:223–238
Wan Z, You S, Rong Y, Zhu B, Zhang A, Zang H, Xiao L, et al. CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells mobilization, paralleled with multiple cytokines elevated in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Dig Dis Sci 2013;58:448–457
Gehling UM, Willems M, Schlagner K, Benndorf RA, Dandri M, Petersen J, et al. Mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:217–224
Zocco MA, Piscaglia AC, Giuliante F, Arena V, Novi M, Rinninella E, Tortora A, et al. CD133+ stem cell mobilization after partial hepatectomy depends on resection extent and underlying disease. Dig Liver Dis 2010;43:147–154
Swenson ES, Kuwahara R, Krause DS, Theise ND. Physiological variations of stem cell factor and stromal-derived factor-1 in murine models of liver injury and regeneration. Liver Int 2008;28:308–318
Hu B, Colletti LM. Stem cell factor and c-kit are involved in hepatic recovery after acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008;295:G45–G53
Lei Y, Liu Z, Han Q, Kang W, Zhang L, Lou S. G-CSF enhanced SDF-1 gradient between bone marrow and liver associated with mobilization of peripheral blood CD34+ cells in rats with acute liver failure. Dig Dis Sci 2009;55:285–291
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by grants from the Ministero Italiano Università e Ricerca (MIUR) (PRIN 2006 and Ricerca locale), Rome, Italy; Regione Piemonte (Ricerca Sanitaria Finalizzata and Ricerca Scientifica Applicata), Torino, Italy. G-CSF Lenograstim (rHu G-CSF) (Myelostim®, Italfarmaco) was kindly provided by Azienda Ospedaliero—Universitaria Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino (ex San Giovanni Battista of Torino). Study sponsors approved the design and protocol but had no involvement in the study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation, or in the writing of the report or the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Conflict of interest
Silvia Gaia, Antonella Olivero, Antonina Smedile, Marco Ruella, Maria Lorena Abate, Maurizio Fadda, Emanuela Rolle, Paola Omedè, Paola Bondesan, Roberto Passera, Alessandra Risso, Manuela Aragno, Alfredo Marzano, Alessia Ciancio, Mario Rizzetto and Corrado Tarella declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with Ethical Requirements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. No identifying information about patients is included in the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaia, S., Olivero, A., Smedile, A. et al. Multiple courses of G-CSF in patients with decompensated cirrhosis: consistent mobilization of immature cells expressing hepatocyte markers and exploratory clinical evaluation. Hepatol Int 7, 1075–1083 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9473-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-013-9473-9