Abstract
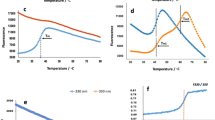
It is the common feature of α-amylases that calcium ion is required for their structural integrity and thermal stability. All amylases have at least one Ca2+ per molecule; therefore amino acids involved in calcium binding are specific and conserved. In this study, sequence analysis revealed the presence of EF-hand-like motif in calcium-binding loop of Bacillus megaterium WHO (BMW)-amylase that was previously isolated from BMW. The EF-hand motif and its variants (EF-hand-like motif) are the most common calcium-binding motifs found in a large number of protein families. To investigate the effect of calcium ion on the thermal stability and activity of BMW-amylase, we used site-directed mutagenesis to replace histidine 58 with Asp (D), Ile (I), Tyr (Y), Phe (F), and Arg (R) at the seventh position of EF-hand-like motif. Upon the addition of an extra DX unit to the calcium-binding loop in H58D variant, thermal stability, catalytic activity, and chelating power of the enzyme improved due to higher affinity toward calcium. H58D variant demonstrated calcium independency compared to the wild type and other created mutants. Conformational changes in the presence and absence of Ca2+ were monitored using fluorescence technique.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMW:
-
Bacillus megaterium WHO
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacryl amide gel electrophoresis
- DNS:
-
Dinitrosalicylic acid
References
Smith, R. J. (1995). Calcium and bacteria. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 37, 83–133.
Vallee, B. L., Stein, E. A., Sumerwell, W. N., & Fischer, E. H. (1959). Metal content of alpha-amylases of various origins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 234, 2901–2905.
Janecek, S., Svensson, B., & MacGregor, E. A. (2003). Relation between domain evolution, specificity, and taxonomy of the α-amylase family members containing a C-terminal starch-binding domain. European Journal of Biochemistry, 270, 635–645.
Declerck, N., Machius, M., Joyet, P., Wiegand, G., Huber, R., & Gaillardin, C. (2003). Engineering the thermostability of Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase. Protein Engineering, 16, 287–293.
Torrance, J. W., MacArthur, M. W., & Thornton, J. M. (2008). Evolution of binding sites for zinc and calcium ions playing structural roles. Proteins, 71, 813–830.
Ghollasi, M., Khajeh, K., Naderi-Manesh, H., & Ghasemi, A. (2010). Engineering of a bacillus α-amylase with improved thermostability and calcium independency. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 444–459.
Spurway, T. D., Morland, C., Cooper, A., Sumner, I., Hazlewood, G. P., O’Donnell, A. G., et al. (1997). Calcium protects a mesophilic xylanase from proteinase inactivation and thermal unfolding. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 17523–17530.
Zhou, Y., Yang, W., Kirberger, M., Lee, H. W., Ayalasomayajula, G., & Yang, J. J. (2006). Prediction of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins and analysis of bacterial EF-hand proteins. Proteins, 65, 643–655.
Liu, T., & Altman, R. B. (2009). Prediction of calcium-binding sites by combining loop-modeling with machine learning. BMC Structural Biology, 9, 72.
Rigden, D. J., Woodhead, D. D., Wong, P. W., & Galperin, M. Y. (2011). New structural and functional contexts of the Dx[DN]xDG linear motif: Insights into evolution of calcium-binding proteins. PLoS One, 6(6), e21507.
Rigden, D. J., & Galperin, M. Y. (2004). The DxDxDG motif for calcium binding: multiple structural contexts and implications for evolution. Journal of Molecular Biology, 343, 971–984.
Fisher, C. L., & Pei, G. K. (1997). Modification of a PCR-based site-directed mutagenesis method. BioTechniques, 23(570–1), 574.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed.). New York: Cold Spring Harbor.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Raser, K. J., Buroker-Kilgore, M., & Wang, K. K. (1996). Binding and aggregation of human mu-calpain by terbium ion. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1292, 9–14.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Krieg, P., Schuppler, M., Koesters, R., Mincheva, A., Lichter, P., & Marks, F. (1997). Repetin (Rptn), a new member of the “fused gene” subgroup within the S100 gene family encoding a murine epidermal differentiation protein. Genomics, 43, 339–348.
Nordberg Karlsson, E., Labes, A., Turner, P., Fridjohnsson, O. H., Wennerberg, C., Pozzo, T., et al. (2008). Differences and similarities in enzymes from the neopullulanase subfamily isolated from thermophilic species. Biologia, 63, 1006–1014.
Rigden, D. J., Jedrzejas, M. J., Moroz, O. V., & Galperin, M. Y. (2003). Structural diversity of calcium-binding proteins in bacteria: single handed EF-hands? Trends in Microbiology, 11, 295–297.
Vyas, N. K., Vyas, M. N., & Quiocho, F. A. (1987). A novel calcium binding site in the galactose-binding protein of bacterial transport and chemotaxis. Nature, 327, 635–638.
Tanaka, A., & Hoshino, E. (2002). Calcium-binding parameter of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase determined by inactivation kinetics. Biochemical Journal, 15, 635–639.
D’Amico, S., Gerday, C., & Feller, G. (2003). Temperature adaptation of proteins: Engineering mesophilic-like activity and stability in a cold-adapted alpha-amylase. Journal of Molecular Biology, 332(5), 981–988.
Hsiu, J., Fischer, E. H., & Stein, E. A. (1964). Alpha amylase as calcium-metalloenzymes II. Calcium and the catalytic activity. Biochemistry, 3, 61–66.
Yang, K. (2001). Prokaryotic calmodulins: Recent developments and evolutionary implications. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 3, 457–459.
Michalet, X., Weiss, S., & Jäger, M. (2006). Single-molecule fluorescence studies of protein folding and conformational dynamics. Chemical Reviews, 106, 1785–1813.
Royer, C. A. (2006). Probing protein folding and conformational transitions with fluorescence. Chemical Reviews, 106, 1769–1784.
Babor, M., Greenblatt, H. M., Edelman, M., & Sobolev, V. (2005). Flexibility of metal binding sites in proteins on a database scale. Proteins, 59, 221–230.
Fitter, J. (2005). Structural and dynamical features contributing to thermostability in alpha-amylases. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 62, 1925–1937.
Danson, M. J., Hough, D. W., Russell, R. J., Taylor, G. L., & Pearl, L. (1996). Enzyme thermostability and thermoactivity. Protein Engineering, 9, 629–630.
Lin, L. L., Huang, C. C., & Lo, H. F. (2008). Engineering of a truncated alpha-amylase of Bacillus sp. TS-23 for the simultaneous improvement of thermal and oxidative stabilities, and mutational analysis of the proposed calcium-binding aspartates. Process Biochemistry, 43, 559–565.
Liu, Y., Shen, W., Shi, G. Y., & Wang, Z. X. (2010). Role of the calcium-binding residues Asp231, Asp233, and Asp438 in alpha-amylase of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as revealed by mutational analysis. Current Microbiology, 60(3), 162–166.
Gether, U., Lin, S., Ghanouni, P., Ballesteros, J. A., Weinstein, H., & Kobilka, B. K. (1997). Agonists induce conformational changes in transmembrane domains III and VI of the adrenoceptor. EMBO Journal, 16, 6737–6747.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, L., Khajeh, K., Mollania, N. et al. Extra EF Hand Unit (DX) Mediated Stabilization and Calcium Independency of α-Amylase. Mol Biotechnol 53, 270–277 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9523-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9523-x