Abstract
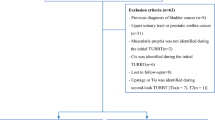
The objective of this study was to compare surgical treatments for non-invasive bladder tumor. Hundred and forty patients with non-invasive bladder tumor were studied. Seventy-three patients were treated by transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) and Repeated-Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (R-TURBT), while 67 by partial cystectomy. Operation time, blood loss, postoperative complications, and postoperative recurrence rate were better in the TURBT+R-TURBT group compared with the partial cystectomy group. Further, TURBT+R-TURBT offers advantages, such as simple surgical manipulation, less trauma, faster recovery, repeatedly performable procedure, and safety. In conclusion, this is an optimal therapy for treatment of non-invasive bladder tumor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TURBT:
-
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor
- R-TURBT:
-
Repeated-Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor
- THP:
-
Therarubicin Pirarubicin
References
Xu, B., & Hua, L. (2007). Epidemiology of bladder cancer. International Urology and Nephrology, 27, 469–476.
Paul, R., Kübler, H., van Randenborgh, H., & Hartung, R. (2002). Prognostic significance of the TNM-Staging-System of 1987 and 1997 as compared to the Robson-classification for renal cell cancer. Actuellement Urology, 33, 531–539.
Pellucchi, F., Freschi, M., Ibrahim, B., Rocchini, L., Maccagnano, C., Briganti, A., et al. (2011). Clinical reliability of the 2004 WHO histological classification system compared with the 1973 WHO system for Ta primary bladder tumors. Journal of Urology, 186, 2194–2199.
Hollenbeck, B. K., Miller, D. C., Taub, D., Dunn, R. L., Khuri, S. F., Henderson, W. G., et al. (2006). Risk factors for adverse outcomes after transurethral resection of bladder tumors. Cancer, 106, 1527–1535.
Barnes, R. V. (1996). Treatment of superficial bladder tumors with transurethral resection clinical analzsis of 505 cases. Journal of Urology, 97, 864.
Zhou, R. (1996). Bladder Surgery. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. in Chinese.
Manoharan, M., & Soloway, M. S. (2005). Optimal management of the T1G3 bladder cancer. Urologic Clinics of North America, 32, 133–145.
Masood, S., Sriprasad, S., Palmer, J. H., & Mufti, G. R. (2004). T1G3 bladder cancer: Indications for early cystectomy. International Urology and Nephrology, 36, 41–44.
Wu, T., Zhang, J., & Wang, F. (2006). Prevention and treatment of recurrence of superficial bladder cancer by postoperative intravital instillation of pirarubicin (report of 109 cases). Journal of Southeast University, 25, 113–115. in Chinese.
Wu, X., Lu, S., & Cai, L. (2005). Application of multidrug resistance of bladder tumor cell in the treatment of invasive bladder tumor. Journal of Southeast University, 24, 374–376. in Chinese.
Wu, J. (2004). Wu Jie-Ping’s Urology. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press. in Chinese.
Kriegmair, M., Zaak, D., Rothenberger, K. H., Rassweiler, J., Jocham, D., Eisenberger, F., et al. (2002). Transurethral resection for bladder cancer using 5-aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence endoscopy versus white light endoscopy. Journal of Urology, 168, 475–478.
Acknowledgments
Conghui Han, Zhenduo SHI, and Xujun Xuan contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Ch., Shi, Z., Xuan, X. et al. Re-Transurethral Resection Treatment for Non-invasive Bladder Tumor. Cell Biochem Biophys 69, 589–592 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9837-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9837-3