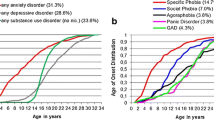
Abstract
The debate regarding the possible existence of prepubertal bipolar illness has surfaced at various points in history. In its most recent incarnation, proponents of a childhood bipolar diagnosis argue that there is an early-onset form of bipolar illness that is highly comorbid and characterized by simultaneous irritability and depression. Others have suggested that childhood manic symptoms are more likely a nonspecific indicator of risk, or may be the result of symptom overlap with various other forms of childhood pathology. This article briefly reviews pertinent findings from epidemiologic, developmental, family, and treatment studies that shed light on the etiology, phenomenology, and developmental significance of manic symptoms in young people.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Goodwin FK, Jamison KR: Manic Depressive Illness. New York: Oxford University Press; 1990:56–69.
Kraepelin E: Manic Depressive Insanity and Paranoia. Edinburgh: Livingstone; 1921.
Leonhard K: Aufteilung der Endogenen Psychosen edn 1. Berlin: Akademie-Verlag; 1957; The Classification of Endogenous Psychoses edn 5. Edited by Robins E. Translated by Russell Berman. New York: Irvington; 1979.
Winokur G, Clayton P, Reich T: Manic Depressive Illness. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 1969.
Anthony EJ, Scott P: Manic-depressive psychosis in childhood. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1960, 1:53–72.
Weinberg WA, Brumbach RA: Mania in childhood: case studies and literature review. Am J Dis Child 1975, 130:380–385.
Biederman J: Resolved: mania is mistaken for ADHD in prepubertal children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1998, 37:1091–1096. This article and the one by Klein et al. [8] provide opposing, but equally informed, viewpoints regarding the diagnosis of childhood bipolar disorder. Both articles address important issues in this debate, including comorbidity (with an emphasis on the relationship between ADHD and mania), phenomenology, prevalence, and validity.
Klein RG, Pine DS, Klein DF: Resolved: mania is mistaken for ADHD in prepubertal children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1998, 37:1091–1096; discussion 1096–1099. This article and the one by Biederman [7] provide opposing, but equally informed, viewpoints regarding the diagnosis of childhood bipolar disorder. Both articles address important issues in this debate, including comorbidity (with an emphasis on the relationship between ADHD and mania), phenomenology, prevalence, and validity.
Carlson GA: Child and adolescent mania: diagnostic considerations. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1990, 31:331–341.
Biederman J, Faraone S, Mick E, et al.: Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and juvenile mania: an overlooked comorbidity? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:997–1008.
Wozniak J, Biederman J, Kiely K, et al.: Mania-like symptoms suggestive of childhood-onset bipolar disorder in clinically referred children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1995, 34:867–876.
Biederman J, Faraone SV, Hatch M, et al.: Conduct disorder with and without mania in a referred sample of ADHD children. J Affect Disord 1997, 44:177–188.
Wozniak J, Biederman J, Faraone SV, et al.: Mania in children with pervasive developmental disorder revisited. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1997, 36:1552–1559.
Lewinsohn PM, Klein DN, Seeley JR: Bipolar disorder in community sample of older adolescents: prevalence, phenomenology, comorbidity and course. J Amer Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1995, 34:454–463.
Lewinsohn PM, Rohde P, Klein DN, Seeley JR: Natural course of adolescent major depressive disorder: I. Continuity into young adulthood. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:56–63.
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zhao S, et al.: Lifetime and 12 month prevalence of DSM III R psychiatric disorders among persons aged 15–64 in the United States: results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1994, 51:8–19.
Carlson GA, Loney J, Salisbury H, Volpe RJ: Young referred boys with DICA-P manic symptoms vs. two comparison groups. J Affect Disord 1998, 51:113–121.
Carlson GA, Kelly KL: Manic symptoms in psychiatrically hospitalized children - what do they mean? J Affect Disord 1998, 51:123–135.
Hilty DM, Brady KT, Hales RE: A review of bipolar disorder among adults. Psychiatr Serv 1999, 50:201–213.
Kessler RC, Rubinow DR, Holmes C, et al.: The epidemiology of DSM-III-R bipolar I disorder in a general population survey. Psychol Med 1997, 27:1079–1089.
Klein DN, Lewinsohn PM, Seeley JR: Hypomanic personality traits in a community sample of adolescents. J Affect Disord 1996, 38:135–143.
Kerbeshian J, Burd L, Klug MG: Comorbid Tourette’s disorder and bipolar disorder: an etiologic perspective. Am J Psychiatry 1995, 152:1646–1651.
Wozniak J, Crawford MH, Biederman J, et al.: Antecedents and complications of trauma in boys with ADHD: findings from a longitudinal study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:48–55.
Papolos DF, Faedda GL, Veit S, et al.: Bipolar spectrum disorders in patients diagnosed with velo-cardio-facial syndrome: does a hemizygous deletion of chromosome 22q11 result in bipolar affective disorder? Am J Psychiatry 1996, 153:1541–1547.
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Wozniak J, et al.: Is comorbidity with ADHD a marker for juvenile-onset mania? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1997, 36:1046–1055.
Rasanen P, Tiihonen J, Hakko H: The incidence and onset-age of hospitalized bipolar affective disorder in Finland. J Affect Disord 1998, 48:63–68.
Reddy YC, Girimaji S, Srinath S: Clinical profile of mania in children and adolescents from the Indian subcontinent. Can J Psychiatry - Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie 1997, 42:841–846.
Srinath S, Janardhan Reddy YC, et al.: A prospective study of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents from India. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1998, 98:437–442.
Carlson GA, Bromet EJ, Sievers SB: Phenomenology and outcome of youth and adult onset subjects with psychotic mania. Am J Psychiatry 2000, 157:213–219 This article outlines many of the critical issues that need to be addressed in the study of psychiatrically ill populations, such as determining age of onset, comorbidity, sample selection, and the importance of long-term follow-up. Findings highlight differences between individuals with early- and late-onset bipolar disorder with regard to developmental history, symptom presentation, and course of illness.
Guth C, Jones P, Murray R: Familial psychiatric illness and obstetric complications in early-onset affective disorder. A case-control study. Br J Psychiatry 1993, 163:492–498.
Sigurdsson E, Fombonne E, Sayal K, Checkley S: Neurodevelopmental antecedents of early-onset bipolar affective disorder. Br J Psychiatry 1999, 174:121–127.
Kinney DK, Yurgelun-Todd DA, Levy DL, et al.: Obstetrical complications in patients with bipolar disorder and their siblings. Psychiatry Res 1993, 48:47–56.
Marcelis M, van Os J, Sham P, et al.: Obstetric complications and familial morbid risk of psychiatric disorders. Am J Med Genet 1998, 81:29–36.
van Os J, Takei N, Castle DJ, et al.: Premorbid abnormalities in mania, schizomania, acute schizophrenia, and chronic schizophrenia. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 1995; 30:274–278.
Weissman MM, Wolk S, Wickramaratne P, et al.: Children with prepubertal-onset maor depressive disorder and anxiety grown up. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999, 56:794–801.
Kovacs M: Presentation and course of major depressive disorder during childhood and later years of the life span. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:705–715.
Geller B, Fox LW, Clark KA: Rate and predictors of prepubertal bipolarity during follow-up of 6-to 12-year-old depressed children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1994, 33:461–468.
Strober M, Lampert C, Schmidt S, Morrell W: The course of major depressive disorder in adolescents: recovery and risk of manic switching in a 24-month prospective, naturalistic follow-up of psychotic and non-psychotic subtypes. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1993, 32:34–42.
Strober M: Mixed mania associated with tricyclic antidepressant therapy in prepubertal delusional depression: three cases. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1998, 8:181–185.
Kat H: More on SSRI-induced mania. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:975.
Levy D, Kimhi R, Barak Y, et al.: Antidepressant-associated mania: a study of anxiety disorders patients. Psychopharmacology 1998, 136:243–246.
Damore J, Stine J., Brody L: Medication-induced hypomania in Asperger’s disorder [letter]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1998, 37:248–249.
Go FS, Malley EE, Birmaher B, Rosenberg DR: Manic behaviors associated with fluoxetine in three 12-to 18-year-olds with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1998, 8:73–80.
Diler RS, Avci A: SSRI-induced mania in obsessive-compulsive disorder [6]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:6–7.
Horrigan JP, Barnhill LJ: Guanfacine and secondary mania in children. J Affect Disord 1999, 54:309–314.
Bond AJ: Drug induced behavioral disinhibition: incidence, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs 1998, 9:41–57.
Amsterdam JD, Garcia-Espana F, Fawcett J, et al.: Efficacy and safety of fluoxetine in treating bipolar II major depressive episode. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1998, 18:435–440.
Geller B, Fox LW, Fletcher M: Effect of tricyclic antidepressants on switching to mania and on the onset of bipolarity in depressed 6–12 year olds. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1993, 32:43–50.
Lapalme M, Hodgins S, LaRoche C: Children of parents with bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis of risk for mental disorders. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry - Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie 1997, 42:623–631.
Todd RD, Reich W, Petti TA, et al.: Psychiatric diagnoses in the child and adolescent members of extended families identified through adult bipolar affective disorder probands. J Am Academy Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:664–671.
Todd RD, Geller B, Neuman R, et al.: Increased prevalence of alcoholism in relatives of depressed and bipolar children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:716–724.
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Mennin D, et al.: Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with bipolar disorder: a familial subtype? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1997, 36:1378–1387.
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Mennin D, Russell R: Bipolar and antisocial disorders among relatives of ADHD children: parsing familial subtypes of illness. Am J Med Genet 1998, 81:108–116.
Biederman J, Faraone SV, Chu MP, Wozniak J: Further evidence of a bidirectional overlap between juvenile mania and conduct disorder in children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:468–476.
Gershon ES, Berrettini WH, Nurnberger JI, Goldin LR: Genetic studies of affective illness. In Models of Depressive Disorders: Psychological, Biological, and Genetic Perspectives vol 2. Edited by Mann JJ. New York: Plenum Press; 1989:109–142.
Strober M, DeAntonio M, Schmidt-Lackner S, et al.: Early childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder predicts poorer response to acute lithium therapy in adolescent mania. J Affect Disord 1998, 51:145–151.
Kafantaris V, Coletti DJ, Dicker R, et al.: Are childhood psychiatric histories of bipolar adolescents associated with family history, psychosis, and response to lithium treatment? J Affect Disord 1998, 51:153–164.
Geller B, Cooper TB, Sun K, et al.: Double-blind and placebocontrolled study of lithium for adolescent bipolar disorders with secondary substance dependency. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1998, 37:171–178.
Carlson GA, Bromet EJ, Lavelle J: Medication treatment in adolescents vs adults with psychotic mania. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1999, 9:221–231.
Duffy A, Alda M, Kutcher S, et al.: Psychiatric symptoms and syndromes among adolescent children of parents with lithium-responsive or lithium-nonresponsive bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1998, 155:431–433. This paper elegantly illustrates the importance of studying homogeneous subgroups. The authors compared long-term psychiatric outcomes of children of lithium-responsive bipolar parents with children of lithium nonresponders, and found parental lithium response to be associated with a less complicated course in offspring affective disorder.
Hagino OR, Weller EB, Weller RA, Fristad MA: Comparison of lithium dosage methods for preschool- and early school-age children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1998, 37:60–65.
Hagino OR, Weller EB, Weller RA, et al.: Untoward effects of lithium treatment in children aged four through six years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1995, 34:1584–1590.
Papatheodorou G, Kutcher SP, Katic M, Szalai JP: The efficacy and safety of divalproex sodium in the treatment of acute mania in adolescents and young adults: an open clinical trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1995, 15:110–116.
Deltito AJ, Levitan J, Damore J, et al.: Naturalistic experience with the use of divalproex sodium on an in-patient unit for adolescent psychiatric patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1998, 97:236–240.
Donovan SJ, Nunes EV: Treatment of comorbid affective and substance use disorders. Therapeutic potential of anticonvulsants. Am J Addictions 1998, 7:210–220.
Isojarvi JIT, Ratrya J, Myllyla W, et al.: Valproate, lamotrigine and insulin-mediated risks in women with epilepsy. Ann Neurol 1998, 43:446–451.
Garland EJ, Behr R: Hormonal effects of valproic acid? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1996, 35:1424–1425.
Johnston HF: More on valproate and polycystic ovaries [2]. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:354.
Frazier JA, Meyer MC, Biederman J, et al.: Risperidone treatment for juvenile bipolar disorder: A retrospective chart review. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:960–965.
Schaller JL, Behar D: Quetiapine for refractory mania in a child. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:498–499.
Schreier HA: Risperidone for young children with mood disorders and aggressive behavior. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1998, 8:49–59.
Woolston JL: Case study: carbamazepine treatment of juvenile-onset bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1999, 38:335–338.
Kastner T, Friedman DL: Verapamil and valproic acid treatment of prolonged mania. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1992, 31:271–275.
Davanzo PA, Krah N, Kleiner J, McCracken J: Nimodipine treatment of an adolescent with ultradian cycling bipolar affective illness. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1999, 9:51–61.
Soutullo CA, Casuto LS, Keck PE Jr: Gabapentin in the treatment of adolescent mania: a case report. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 1998, 8:81–85.
Robertson JM, Tanguay PE: Case study: the use of melatonin in a boy with refractory bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1997, 36:822–825.
Rey JM, Walter G: Half a century of ECT use in young people. Am J Psychiatry 1997, 154:595–602.
Walter G, Rey JM, Mitchell PB: Practioner review: electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1999, 40:325–334. Although not specifically about bipolar disorder, this review of ECT use in young people is important reading for clinicians treating seriously disturbed adolescents.
Carlson GA, Bromet EJ, Jandorf L: Conduct disorder and mania: what does it mean in adults? J Affect Disord 1998, 148:199–205.
Carlson GA: Bipolar disorder and attention deficit disordercomorbidity or confusion. J Affect Disord 1998, 51:177–189. This article is both a review and an attempt to put in perspective the conflicting opinions about what constitutes bipolar disorder in children.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlson, G.A., Meyer, S.E. Bipolar disorder in youth. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2, 90–94 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-000-0051-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-000-0051-1