Abstract
Purpose
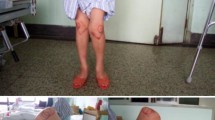
Congenital dislocation of the knee (CDK) is a relatively rare condition. It may occur as an isolated deformity, it may be associated with musculoskeletal anomalies such as developmental dysplasia of the hip and clubfoot, or it may occur as part of a syndrome such as arthrogryposis multiplex congenita or Larsen syndrome, or it may occur in paralytic conditions such as meningomyelocele. Treatment options include serial casting, percutaneous quadriceps recession (PQR) and V–Y quadricepsplasty (VYQ). The aim of this study is to evaluate the medium-term results of PQR and VYQ, and to set a protocol of management for CDK based on a modified grading system.
Methods
Eleven infants with 21 CDK were treated at our unit. Five knees were treated with serial casting, 12 knees with PQR and four knees with VYQ. Follow up averaged 41 months.
Results
Twelve knees achieved excellent results, seven knees achieved good results and two knees achieved fair results.
Conclusion
A modified grading system for CDK is introduced. Based on this, we recommend the following. Serial casting is performed in patients with GI CDK. In GII CDK in neonates (babies up to the age of 1 month) serial casting is started. A maximum of four weekly manipulations and castings are attempted. If a range of flexion >90° is achieved, serial casting is continued; if range of flexion remains <90° it is necessary to proceed to PQR. In babies older than 1 month when first seen; PQR is performed from the start. VYQ is indicated in patients with GIII CDK or in recurrent cases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobsen K, Vopalecky F (1985) Congenital dislocation of the knee. Acta Orthop Scand 56:1–7
Curtis BH, Fisher RL (1969) Congenital hyperextension with anterior subluxation of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 51:255–269
Johnson E, Audell R, Oppenheim WL (1987) Congenital dislocation of the knee. J Pediatr Orthop 7:194–200
Nogi J, MacEwen GD (1982) Congenital dislocation of the knee. J Pediatr Orthop 2:509–513
Haga N, Nakamura S, Sakaguchi R et al (1997) Congenital dislocation of the knee reduced spontaneously or with minimal treatment. J Pediatr Orthop 17:59–62
Katz MP, Grogono JS, Soper KC (1967) The etiology and treatment of congenital dislocation of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 49:112–120
Laurence M (1967) Genu recurvatum congenitum. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 49:121–134
Uhthoff HK, Ogata S (1994) Early intrauterine presence of congenital dislocation of the knee. J Pediatr Orthop 14:254–257
Ferris B, Aichroth P (1987) The treatment of congenital knee dislocation: a review of nineteen knees. Clin Orthop Rel Res 216:135–140
Leveuf J, Pais C (1946). Les dislocations congenitales du genou. Rev Chir Orthop 32:313–350 [Quoted from Bensahel H, Dal Monte A, Hjelmstedt, et al. (1989) Congenital dislocation of the knee. J Paediatr Orthop 9:174–177]
Finder JG (1964) Congenital hyperextension of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 46:783
Parsch K, Schulz R (1994) Ultrasonography in congenital dislocation of the knee. J Pediatr Orthop B 3(1):76–81
Roy DR, Crawford AH (1989) Percutaneous quadriceps recession: a technique for management of congenital hyperextension deformities of the knee in the neonate. J Pediatr Orthop 9:717–719
Ooishi T, Sugioka Y, Matsumoto S, Fujii T (1993) Congenital dislocation of the knee: its pathologic features and treatment. Clin Orthop Rel Res 287:187–192
Iwaya T, Sakaguchi R, Tsuyama N (1983) The treatment of congenital dislocation of the knee with the Pavlik harness. Int Orthop 7:25–30
Ko Y, Shih CH, Wenger DR (1999) Congenital dislocation of the knee. J Paediatr Orthop 19:252–259
Bensahel H, Dal Monte A, Hjelmstedt A et al (1989) Congenital dislocation of the knee. J Pediatr Orthop 9(2):174–177
Bell MJ, Atkins RM, Sharrard WJW (1987) Irreducible congenital knee dislocation. Aetiology and Management. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 69:403–406
Mehrafshan M, Rampal V, Seringe R, Wicart P (2010) Congenital dislocation of the knee: mid-term outcome and prognosis. J Child Orthop 4(suppl 1):S 22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelaziz, T.H., Samir, S. Congenital dislocation of the knee: a protocol for management based on degree of knee flexion. J Child Orthop 5, 143–149 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-011-0333-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-011-0333-7