Abstract
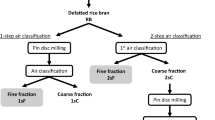
Commercially obtained defatted (DF), full-fat stabilized (FFS), and full-fat unstabilized (FFU) rice bran were processed by colloid milling and homogenization to affect bran breakdown and extraction of rice protein. Relative to unprocessed samples, there were moderate to slight increases in the amount of protein extracted from the various fractions of processed bran. Colloid milling and homogenizing slightly influenced the distribution of proteins in the various fractions obtained, with the FFU showing the greatest effect compared to DF and FFS protein fractions. The protein content of the supernatant fraction of FFU bran increased from 21.8 to 33.0% after colloid milling with a further increase to 38.2% after homogenizing, representing an overall increase of 75.2% in protein content. The supernatant fractions of DF bran increased from 13.9 to 14.7% after colloid milling, and to 16.5% after colloid milling and homogenizing, for an overall increase of 18.7%. Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed a molecular weight distribution ranging from 6.0 to 97.4 kDa. Few detectable differences between protein bands of unprocessed and processed DF and FFU bran were observed. However, FFS bran showed breakdown in size distribution of protein after colloid milling and homogenizing, because certain high molecular weight proteins shifted to lower molecular weight units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hammond, N.A., Method of Stabilizing Rice Bran, U.S. Patent 5,512,307 (1996).
Shih, F.F., E.T. Champagne, K. Daigle, and Z. Zarins, Use of Enzymes in the Processing of Protein Products from Rice Bran and Rice Flour, Die Nahrung 43:14–18 (1999).
Landers, P.S., and B.R. Hamaker, Antigenic Properties of Albumin, Globulin, and Protein Concentrate Fractions from Rice Bran, Cereal Chem. 71:409–411 (1994).
Gnanasambandam, R., and N.S. Hettiarachchy, Protein Concentrates from Unstabilized Rice Bran: Preparation and Properties, J. Food Sci. 60:1066–1069, 1074 (1995).
Hamada, J.S., Characterization of Protein Fractions of Rice Bran to Devise Effective Methods of Protein Solubilization, Cereal Chem. 74:662–668 (1997).
Prakash, J., and G. Ramanatham, Effect of Stabilization of Rice Bran on the Extractability and Recovery of Proteins, Die Nahrung 38:87–95 (1994).
Otterburn, M.S., Protein Crosslinking, in Protein Quality and the Effects of Processing, edited by R.D. Phillips and J.W. Finley, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1989, p. 247.
Ansharullah, J., A. Hourigan, and C.F. Chesterman, Application of Carbohydrases in Extracting Protein from Rice Bran, J. Sci. Food Agric. 74:141–146 (1997).
Chan, K.-Y., and B.P. Wasserman, Rapid Solid-Phse Determination of Cereal Protein Using Bicinchoninic Acid, Cereal Chem. 70:27–28 (1993).
Betschart, A.A., R.Y. Fong, and R.M. Saunders, Rice By-Products: Comparative Extraction and Precipitation of Nitrogen from U.S. and Spanish Bran and Germ, J. Food Sci. 42:1088–1093 (1977).
Sayre, R.N., R.M. Saunders, R.V. Enochain, W.G. Schultz, and E.C. Beagle, Review of Rice Bran Stabilization Systems with Emphasis on Extrusion Cooking, Cereal Foods World 27:317–322 (1982).
Hamada, J.S., Characterization and Functional Properties of Rice Bran Proteins Modified by Commercial Exoproteases and Endoproteases, J. Food Sci. 65:305–310 (2000).
Anderson, A.K., and P.K.W. Ng, Changes in Disulfide and Sulfhydryl Contents and Electrophoretic Patterns of Extruded Wheat Flour Proteins, Cereal Chem. 77:354–359 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, A.K., Guraya, H.S. Extractability of protein in physically processed rice bran. J Amer Oil Chem Soc 78, 969–972 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0373-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-001-0373-1