Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) has been our operation of choice for morbid obesity since 2003. The aim of this study was to review 5 years of LAGB procedures at a single institution in China.
Methods
All patients who underwent LAGB at our institution from June 2003 to November 2009 were analyzed retrospectively. A telephone survey of patients was conducted in 2010.
Results
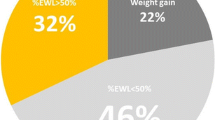
This study included 188 Chinese patients, of which 69.7 % were female and 8 (4.3 %) were super-obese (body mass index (BMI) >50 kg/m2). The mean age of patients was 27.2 ± 9.1 years (range, 14–55 years), mean weight was 106.8 ± 24.7 kg (range, 67–230 kg), and mean BMI was 37.5 ± 6.2 kg/m2 (range, 26.1–61.7 kg/m2). The mortality rate was 0 %. Six bands were removed (four for slippage). One operation was converted to an open procedure. Ninety-eight patients were surveyed by telephone. The mean weight loss was 17.6 ± 12.5 kg, and the mean follow-up time was 23.6 months. Percentage excess weight loss (%EWL) at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years was 27.8 ± 16.4, 39.0 ± 23.1, 44.1 ± 27.3, and 43.1 ± 28.4 %, respectively. The nonresponder rate (%EWL <30 %) at 2 years was 33.3 % (20/60). Weight regain of more than 10 kg from nadir was observed in 10 of the 98 patients (10.2 %).
Conclusions
LAGB is a relatively safe procedure with few major complications. However, a minority of morbidly obese patients did not benefit sufficiently from their surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fobi MA. Surgical treatment of obesity: a review. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004;96:61–75.
Favretti F, Ashton D, Busetto L, et al. The gastric band: first-choice procedure for obesity surgery. World J Surg. 2009;33:2039–48.
Buchwald H. Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity: health implications for patients, health professionals, and third-party payers. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;200:593–604.
Ji XR, Chen DL, Hu XG, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: analysis of 172 cases. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;12:551–3.
Ding D, Chen DL, Hu XG, et al. Outcomes after laparoscopic surgery for 219 patients with obesity. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;14:128–31.
Naef M, Mouton WG, Naef U, et al. Graft survival and complications after laparoscopic gastric banding for morbid obesity—lessons learned from a 12-year experience. Obes Surg. 2010;20:1206–14.
Weiner R, Blanco-Engert R, Weiner S, et al. Outcome after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding—8 years experience. Obes Surg. 2003;13:427–34.
Lomanto D, Lee WJ, Goel R, et al. Bariatric surgery in Asia in the last 5 years (2005–2009). Obes Surg. 2012;22(3):502–6.
Carelli AM, Youn HA, Kurian MS, et al. Safety of the laparoscopic adjustable gastric band: 7-year data from a U.S. center of excellence. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1819–23.
Oria HE, Carrasquilla C, Cunningham P, et al. Guidelines for weight calculations and follow-up in bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2005;1:67–8.
Lakdawala M, Bhasker A. Report: Asian consensus meeting on metabolic surgery. Recommendations for the use of bariatric and gastrointestinal metabolic surgery for treatment of obesity and type II diabetes mellitus in the Asian population: August 9th and 10th, 2008, Trivandrum, India. Obes Surg. 2010;20:929–36.
Expert Consultation WHO. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–63.
Thomusch O, Keck T, Dobschutz EV, et al. Risk factors for the intermediate outcome of morbid obesity after laparoscopically placed adjustable gastric banding. Am J Surg. 2005;189:214–8.
Acknowledgments
We thank John E. Woods (Emeritus Professor of Plastic Surgery, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, MN, USA) for careful reading of the manuscript and editorial help.
Conflicts of Interest
Qiaojun Han, Yue Chen, Jianbing Zhuge, Zhaolong Zhang, and Dajin Zou declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qiaojun Han and Yue Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Q., Chen, Y., Zhuge, J. et al. A 5-Year Experience of Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding in China. OBES SURG 23, 197–200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0771-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0771-4