Abstract
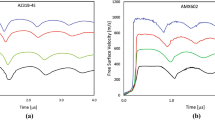
Recent development of a laser-based experimental platform allows loading materials to high pressures in the solid state while controlling both strain rate and peak pressure. The drive utilizes momentum transfer from a plasma generated by the introduction of a strong shock in a reservoir of low-Z material. This study looks at the response of a commercial aluminum alloy (6061-T6) subjected to pressures of 18 and 40 GPa at strain rates of 107/s and 5 × 107/s, respectively. It was found that the depth of the crater formed on the sample surface is a good indicator of the general yield behavior of the material and that a relatively simple strength model prevails under the loading conditions considered here. Metallographic examination of recovered samples showed no evidence of shear-band formation or significant melting due to plasma-surface interactions. Crystal plasticity-based calculations were used to assess the effects of material texture. Lack of shear-band formation during the laser-based drive is rationalized by considering the strain gradient as compared to grain size and texture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.H. Kalantar, B.A. Remington J.D. Colvin, D.M. Gold, K.O. Mikaelian, S.V. Weber, and L.G. Wiley: American Institute of Physics Conf. Proc., 2000, No. 505, Part 2, pp. 1193–97.
M.A. Meyers, F. Gregori, B.K. Kad, M.S. Schneider, D.H. Kalantar, B.A. Remington, G. Ravichandran, T. Boehly, and J.S. Wark: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, p. 1211.
J. Edwards, K.T. Lorenz, B.A. Remington, S. Pollaine, J. Colvin, D. Braun, B.F. Lasinski, D. Reisman, J.M. McNaney, J.A. Greenough, R. Wallace, H. Louis, and D. Kalantar: Phys. Rev. Let., 2004, in press.
J.F. Barnes, P.J. Blewett, R.G. McQueen, K.A. Meyer, and D. Venable: J. Appl. Phys. 1974, vol. 45 (2), p. 727.
A.I. Lebedev, P.N. Nizovtsev, and V.A. Rayevsky: in Proc. 4th Int. Workshop on the Physics of Compressible Turbulent Mixing, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1993.
A.I. Lebedev, P.N. Nizovtsev, V.A. Rayevsky, and V.P. Solov’ev: Dokl. Akad. Nauk, vol. 349 (MAIK Nauka/Interperiodica Publishing, Moscow, 1996); translation: Phys. Dokl., 1996, vol. 41, p. 328.
C.A. Hall: Phys. Plas., 2000, vol. 7 (5), p. 2069.
C.A. Hall, J.R. Asay, M.D. Knudson, W.A. Stygar, R.B. Spielman, T.D. Pointon, D.B. Reisman, A. Toor, and R.C. Cauble: Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2001, vol. 72 (9), p. 3587.
D.B. Reisman, A. Toor, R.C. Cauble, C.A. Hall, J.R. Asay, M.D. Knudson, and M.D. Furnish: J. App. Phys., 2001, vol. 89 (3), p. 1625.
Electron Backscatter Diffraction in Materials Science, A.J. Schwartz, M. Kumar, and B.L. Adams, eds., Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, NY, 2000.
B.A. Remington, G. Bazan, J. Belak, E. Bringa, M. Caturla, J.D. Colvin, M.J. Edwards, S.G. Glendinning, D.S. Ivanov, B. Kad, D.H. Kalantar, M. Kumar, B.F. Lasinski, K.T. Lorenz, J.M. McNaney, D.D. Meyerhofer, M.A. Meyers, S.M. Pollaine, D. Rowley, M. Schneider, J.S. Stölken, J.S. Wark, S.V. Weber, W.G. Wolfer, B. Yaakobi, and L.V. Zhigilei: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 2587–2607.
E. Dube, R. Neely, A. Nichols, R. Sharp, and R. Couch: Users Manual for ALE3D-An Arbitrary Lagrange/Eulerian 3-D Code System, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, 2001.
D. Peirce, R.J. Asaro, and A. Needleman: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30 (6), pp. 1087–1119.
R. Tipton, R. Managan, and P. Amala: Users Manual for CALE, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, 2002.
D.J. Steinberg, S.G. Cochran, and M.W. Guinan: J. Appl. Phys., 1980, vol. 51, p. 1496.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation given in the symposium “Dynamic Deformation: Constitutive Modeling, Grain Size, and Other Effects: In Honor of Prof. Ronald W. Armstrong,” March 2–6, 2003, at the 2003 TMS/ASM Annual Meeting, San Diego, California, under the auspices of the TMS/ASM Joint Mechanical Behavior of Materials Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McNaney, J.M., Edwards, M.J., Becker, R. et al. High-pressure, laser-driven deformation of an aluminum alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 35, 2625–2631 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0208-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0208-3