Abstract
Background
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the setting of cirrhosis is limited by tumor size/location and underlying liver disease. Radiofrequency ablation is utilized in selected patients; however, local recurrence remains a concern. Microwave ablation (MWA) delivers energy to tissue in a unique fashion, reducing local recurrence. A minimally invasive operative approach allows for mobilization/protection of adjacent structures, intra-operative ultrasound, and assessment of ablation progress.
Study Design
Retrospective review of operative MWA performed for HCC in patients with cirrhosis over a 4-year period at a single center. Complications were stratified by Clavien–Dindo classification. Incomplete ablation and local, regional, and metastatic recurrence was assessed on follow-up imaging. Survival was assessed in months.
Results
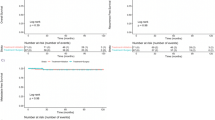
Fifty-four patients with 73 tumors underwent MWA. Median tumor size was 2.6 cm (range 0.5–8.5 cm). Cirrhosis was present in 92.6 % of patients, with a Child–Pugh score of B/C in 27.8 % and hepatitis C present in 59.3 %. A minimally invasive approach was used in 94.5 % of patients. There were no deaths within 30 days. Thirty-day morbidity was 28.9 %, with grade III complications present in 11.5 %. Delayed complications occurred in 7.8 % of patients, with a 5.6 % 90-day mortality. Incomplete ablation was identified in 5.9 % of tumors with local recurrence of 2.9 % at 9 months median follow-up. Regional and metastatic recurrence occurred in 27.5 and 11.8 % at 9 months median follow-up. Median survival was not reached at 11 months median follow-up. One- and 2-year survival was 72.3 and 58.8 %.
Conclusion
Operative, preferably minimally invasive, MWA can be performed in cirrhotic patients with HCC with acceptable morbidity and low recurrence rates. High regional and metastatic recurrence rates in these patients underscore the need for minimally invasive, low morbidity approaches to liver-directed therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- IOUS:
-
Intra-operative ultrasound
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- AFP:
-
alpha-Fetoprotein
- MELD:
-
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease
- AJCC:
-
American Joint Committee on Cancer
References
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. Jun 2007;132(7):2557–2576.
El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in USA. Hepatol Res. Sep 2007;37 Suppl 2:S88–94.
El-Serag HB, Mason AC. Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med. Mar 11 1999;340(10):745–750.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. Nov 2005;42(5):1208–1236.
Vauthey JN, Dixon E, Abdalla EK, et al. Pretreatment assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma: expert consensus statement. HPB (Oxford). Jun 2010;12(5):289–299.
Jarnagin W, Chapman WC, Curley S, et al. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: expert consensus statement. HPB (Oxford). Jun 2010;12(5):302–310.
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. Mar 2005;234(3):961–967.
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. Jan 2008;47(1):82–89.
N'Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. Nov 2009;50(5):1475–1483.
Tateishi R, Shiina S, Teratani T, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer. Mar 15 2005;103(6):1201–1209.
Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Ruers T, Marchal G, Michel L. Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation: multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg. Aug 2005;242(2):158–171.
Nahum Goldberg S, Dupuy DE. Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities—part I. J Vasc Interv Radiol. Sep 2001;12(9):1021–1032.
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR, Rosenthal DI. Radiofrequency tissue ablation: importance of local temperature along the electrode tip exposure in determining lesion shape and size. Acad Radiol. Mar 1996;3(3):212–218.
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR. Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: a unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. Feb 2000;174(2):323–331.
Patterson EJ, Scudamore CH, Owen DA, Nagy AG, Buczkowski AK. Radiofrequency ablation of porcine liver in vivo: effects of blood flow and treatment time on lesion size. Ann Surg. Apr 1998;227(4):559–565.
Schramm W, Yang D, Wood BJ, Rattay F, Haemmerich D. Contribution of direct heating, thermal conduction and perfusion during radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Open Biomed Eng J. 2007;1:47–52.
Chinn SB, Lee FT, Jr., Kennedy GD, et al. Effect of vascular occlusion on radiofrequency ablation of the liver: results in a porcine model. AJR Am J Roentgenol. Mar 2001;176(3):789–795.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW. Microwave ablation: principles and applications. Radiographics. Oct 2005;25 Suppl 1:S69–83.
Yu NC, Raman SS, Kim YJ, Lassman C, Chang X, Lu DS. Microwave liver ablation: influence of hepatic vein size on heat-sink effect in a porcine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. Jul 2008;19(7):1087–1092.
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF, Mahvi DM, Lee FT, Jr. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology. Jul 2005;236(1):132–139.
Brace CL. Microwave tissue ablation: biophysics, technology, and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;38(1):65–78.
Brace CL. Microwave ablation technology: what every user should know. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. Mar–Apr 2009;38(2):61–67.
Bhardwaj N, Strickland AD, Ahmad F, et al. Microwave ablation for unresectable hepatic tumours: clinical results using a novel microwave probe and generator. Eur J Surg Oncol. Mar 2010;36(3):264–268.
Iannitti DA, Martin RC, Simon CJ, et al. Hepatic tumor ablation with clustered microwave antennae: the US Phase II Trial. HPB (Oxford). 2007;9(2):120–124.
Martin RC, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM. Safety and efficacy of microwave ablation of hepatic tumors: a prospective review of a 5-year experience. Ann Surg Oncol. Jan 2010;17(1):171–178.
Liang P, Wang Y, Yu X, Dong B. Malignant liver tumors: treatment with percutaneous microwave ablation—complications among cohort of 1136 patients. Radiology. Jun 2009;251(3):933–940.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Iannitti DA, et al. Intraoperative triple antenna hepatic microwave ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. Oct 2006;187(4):W333–340.
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Zanus G. Complications of microwave ablation for liver tumors: results of a multicenter study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. Aug 11 2011;35(4):868–74.
Bertot LC, Sato M, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Koike K. Mortality and complication rates of percutaneous ablative techniques for the treatment of liver tumors: a systematic review. Eur Radiol. Dec 2011;21(12):2584–2596.
Lu MD, Xu HX, Xie XY, et al. Percutaneous microwave and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective comparative study. J Gastroenterol. Nov 2005;40(11):1054–1060.
Xu HX, Xie XY, Lu MD, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma using microwave and radiofrequency ablation. Clin Radiol. Jan 2004;59(1):53–61.
Yin XY, Xie XY, Lu MD, et al. Percutaneous thermal ablation of medium and large hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term outcome and prognostic factors. Cancer. May 1 2009;115(9):1914–1923.
Byrd JF, Agee N, McKillop IH, Sindram D, Martinie JB, Iannitti DA. Colour Doppler ultrasonography provides real-time microwave field visualisation in an ex vivo porcine model. HPB (Oxford). Jun 2011;13(6):400–403.
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, et al. The Clavien–Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg. Aug 2009;250(2):187–196.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. Dec 6 2003;362(9399):1907–1917.
Bruix J, Llovet JM. Two decades of advances in hepatocellular carcinoma research. Semin Liver Dis. Feb 2010;30(1):1–2.
Livraghi T. Single HCC smaller than 2 cm: surgery or ablation: interventional oncologist's perspective. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. Jul 2010;17(4):425–429.
Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. Mar 2006;243(3):321–328.
Huang J, Yan L, Cheng Z, et al. A randomized trial comparing radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for HCC conforming to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. Dec 2010;252(6):903–912.
Ong SL, Gravante G, Metcalfe MS, Strickland AD, Dennison AR, Lloyd DM. Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation for primary and secondary liver malignancies: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. Jun 2009;21(6):599–605.
Waki K, Aikata H, Katamura Y, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma: results and prognostic factors on long-term follow up. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. Mar 2010;25(3):597–604.
Shiina S, Tateishi R, Arano T, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. Apr 2012;107(4):569–577; quiz 578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
RZS and DS contributed equally as first author for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swan, R.Z., Sindram, D., Martinie, J.B. et al. Operative Microwave Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Complications, Recurrence, and Long-Term Outcomes. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 719–729 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2164-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2164-y