Abstract
Background, aim, and scope
The paper presents the complex approach to the assessment of the state of the environment in Southern Serbia, surroundings of Bujanovac, the region which is of great concern as being exposed to contamination by depleted uranium (DU) ammunition during the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) attacks in 1999. It includes studies on concentrations of radionuclides and heavy metals in different environmental samples 5 years after the military actions.
Materials and methods
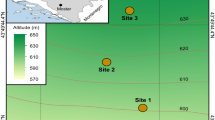
In October 2004, samples of soil, grass, lichen, moss, honey, and water were collected at two sites, in the immediate vicinity of the targeted area and 5 km away from it. Radionuclide (7Be, 40K, 137Cs, 210Pb, 226Ra, 232Th, 235U, 238U) activities in solid samples were determined by standard gamma spectrometry and total alpha and beta activity in water was determined by proportional alpha–beta counting. Concentrations of 35 elements were determined in the samples of soil, moss, grass, and lichen by instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA).
Results
The results are discussed in the context of a possible contamination by DU that reached the environment during the attacks as well as in the context of an environmental pollution by radionuclides and heavy metals in Southern Serbia. The results are compared to the state of environment in the region and other parts of the country both prior to and following the attacks.
Discussion
This is the first comprehensive study of the contents of radionuclides and heavy metals in Southern Serbia and consequently highly important for the assessment of the state of environment in this part of the country concerning possible effects of DU ammunition on the environment, as well as anthropogenic source of pollution by radionuclides and heavy metals and other elements. Also, the highly sensitive method of INAA was used for the first time to analyze the environmental samples from this area.
Conclusions
The results of the study of radionuclides in the samples of soils, leaves, grass, moss, lichen, honey, and water in Southern Serbia (Bujanovac) gave no evidence of the DU contamination of the environment 5 years after the military actions in 1999. Activities of radionuclides in soils were within the range of the values obtained in the other parts of the country and within the global average. The ratio of uranium isotopes confirmed the natural origin of uranium. In general, concentrations of heavy metals in the samples of soils, plant leaves, mosses, and lichen are found to be less or in the lower range of values found in other parts of the country, in spite of the differences in plant and moss species or soil characteristics. Possible sources of heavy metal contamination were identified as a power coal plant in the vicinity of the sampling sites and wood and waste burning processes.
Recommendations and perspectives
The collected data should provide a base for the health risk assessments on animals and humans in the near future. It should be emphasized that the sampling was carried out 5 years after the military action and that the number of samples was limited; therefore, the conclusions should be accepted only as observed tendencies and a detailed study should be recommended in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksic J, Lumić S, Jović S, Kovačević M, Vlaški M, Božić T, Popović D, Stevanović J (2004) Investigation of oxidative stress in sheep bred in areas exposed to DU ammunition. Yugoslav Physiol Pharmacol Acta 40:139–144
Anicic M (2006) Mosses as bioindicators of pollution by heavy metals and other elements in urban areas. MSc Thesis, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Belgrade
Anicic M, Frontasyeva M, Tomasevic M, Popovic A (2006) Assessment of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and other elements in Belgrade using the moss biomonitoring technique and neutron activation analysis. Environ Monit Assess 129:207–219
Barandovski L, Cekova M, Frontasyeva MV, Pavlov SS, Stafilov T, Steinnes E, Urumov V (2008) Air pollution studies in Macedonia using the moss biomonitoring technique, NAA, AAS and GIS technology. Environ Monitor Assess (in press)
Bernal M, Clemente R, Walker D (2007) The role of organic amendments in the bioremediation of heavy metal-polluted soils. In: Gore RW (Ed) Environmental research at the leading edge. Nova Science, New York, pp 1–58
Bikit I, Slivka J, Krmar M, Veskovic M, Conkic LJ, Varga E, Curcic M, Mrdja D (2001) Determination of DU at Novi Sad low level laboratory. Arch Oncol 9:241–243
Bikit I, Slivka J, Krmar M, Veskovic M, Conkic Lj, Varga E, Curcic M, Mrdja D (2002) Depleted uranium determination in soil samples. In: Proceedings of the VII Symposium on natural radiation environment et NRE-VII, Rhodes, Greece, pp. 205–206
Bozic T, Stefanovic J, Kovacevic-Filipovic M, Borozan S, Popovic D, Todorovic D (2003) Possible effects of depleted uranium (DU): I. Changes in cellular and biochemical values in peripheral blood of ruminants in exposed areas. Cent Eur J Occup Environ Med 9:267–272
Clinton GJ (2001) Depleted uranium—environmental and medical surveillance in the Balkans. Information paper 1-800-497-6261. Department of Defence, Arlington
Cothern CR, Lappenbuch WL (1983) Occurrence of uranium in drinking water in the US. Health Physiol 45:89–99
Di Lella L, Frati L, Loppi S, Protano G, Riccobono F (2003) Lichen as biomonitors of uranium and other trace elements in an area of Kosovo heavily shelled with depleted uranium rounds. Atmos Environ 37:5445–449
Di Lella L, Frati L, Loppi S, Protano G, Riccobono F (2004) Environmental distribution of uranium and other trace elements at selected Kosovo sites. Chemosphere 56:861–865
Djuric G, Popovic D (1988) Natural and man made radionuclides in meat. Veterinaria 37:513–520
Djuric G, Popovic D (1994) Radioactive contamination of plants. Ecologica I(2):19–24
Djuric G, Popovic D (1997) Gamma contamination food factor for milk powder and whey. Acta Vet 47:245–250
Djuric G, Popovic D (2000) Uranium in the environment. Chem Ind 54:50–52
Djuric G, Popovic D, Petrovic B (1987) Variations of the activity and concentration factors of Cs-137 in a ‘fish-water’ system. Intern Agrophys 3:41–44
Djuric G, Petrovic B, Smelcerovic M, Popovic D (1988a) Radioactive contamination in children summer resorts area on Tara and Divcibara in May, 1986. Veterinaria 37:555–560
Djuric G, Popovic D, Djujic I (1988b) The contents of radionuclides Ru-103 and Ru-106 in food. Radiation protection practice, vol. III. Pergamon, Sydney, pp. 1497–1500
Djuric G, Popovic D, Djujic I (1988c) The contents of some biologically significant radionuclides in meat. Trends in Food Science, Singapore Institute of Food Science and Technology 5:35–38
Djuric G, Smelcerovic M, Petrovic B, Popovic D (1988d) Radio contamination in a feed plant due to the nuclear accident at Chernobyl, 86. Veterinaria 37:561–566
Djuric G, Popovic D, Smelcerovic M, Petrovic B, Djujic I (1989) Radioactive contamination of food and forage in Serbia after the Chernobyl accident. Radiation Protection—Selected Topics, IBK Vinca, pp. 421–426
Djuric G, Popovic D, Mihaljev Z, Slivka J (1992a) Natural radionuclides in honey. Acta Vet 42:357–360
Djuric G, Popovic D, Vaupotic J, Krizman M, Sutej T, Kljajic R, Stegnar P, Kobal I (1992b) Indoor radon concentrations in kindergartens from different regions in Yugoslavia. Radiat Protect Dosim 45:487–493
Djuric G, Popovic D, Todorovic D (1996a) Activity variations and concentrations factors for natural radionuclides in a ‘soil–plant–honey’ system. Environ Int 22:361–363
Djuric G, Popovic D, Popeskovic D, Petrovic B (1998) The level of natural and fallout radionuclides in honey. Acta Vet 38:293–298
Feige GB, Niemann L, Jahnke S (1990) Lichen and mosses—silent chronics of the Chernobyl accident. Biblioth Lichenol 38:63–77
FM REPORT (2000) Consequences of NATO Bombing. Federal Ministry of Science and Environment, Belgrade
Frontasyeva MV, Pavlov SS (2000) Analytical investigations at the IBR-2 reactor in Dubna. JINR Preprint, E14-2000-177. JINR, Dubna
Frontasyeva MV, Grass F, Nazarov VM, Steinnes E (1995) Intercomparison of moss reference material by different multielement techniques. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 2:371–379
Frontasyeva MV, Galinskaya T, Krmar M, Matavuly M, Pavlov SS, Povtoreyko EA, Radnovic D, Steinnes E (2004) Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in northern Serbia and Bosnia-Herzegovina studied by moss biomonitoring, neutron activation analysis and GIS technology. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 259:141–147
Gadjanski-Omerovic G, Borozan S, Bozic T, Popovic D (2003) Possible effects of depleted uranium (DU): II. Damage of Liver and Kidney Malfunction in animals of exposed areas. Cent Eur J Occup Environ Med 9:273–278
Gao Y, Nelson ED, Field MP, Ding Q, Li H, Sherrell RM, Gigliotti CL,Van Ry DA, Glenn TR, Eisenreich SJ (2002) Characterization of atmospheric trace elements on PM2.5 particulate matter over the New York–New Jersey harbor estuary. Atmos Environ 36:1077–1086
Golubev AV, Golubeva VN, Krylov NG, Kuznetsova VF, Mavrin SV, Aleinikov A, Hoppes WG, Surano KA (2005) On monitoring anthropogenic airborne uranium concentrations and 235U/238U isotopic ratio by lichen-bio-indicator techniques. J Environ Radioact 84:333–342
Gramatica P, Battaini F, Giani E, Papa E, Jones AR, Preatoni D, Cenci MR (2006) Analysis of mosses and soils for quantifying heavy metal concentrations in Sicily: a multivariate and spatial analytical approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13(1):28–36
Herpin U, Siewers U, Markert B, Rosolen V, Breulmann G, Bernoux M (2004) Second German heavy-metal survey by means of mosses, and comparison of the first and second approach in Germany and other European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 11(1):57–66
Hofmann W, Attarpour N, Lettner H, Turk R (1993) 137Cs in lichen before and after the Chernobyl accident. Health Phys 64:70–73
IAEA (2000) A workbook of data analysis. Regional cooperative agreement. NAHRES-52. IAEA, Vienna
Jeran Z, Jacimovic R, Batic F, Smodlis B, Walterbeck H (1996) Atmospheric heavy metal pollution in Slovenia derived from results for epiphytic lichen. Fresenius J Anal Chem 354:681–687
Kestell D (2002) SRP scientific meeting, depleted uranium report. J Radiol Prot 22:215–217
Loppi S, Riccobono F, Zhang ZH, Savic S, Ivanov D, Pirinsos SA (2003) Lichens as biomonitors of uranium in the Balkan Area. Environ Pollut 125:277–280
Magnoni M, Bertino S, Bellotto B, Campi M (2001) Variations of the isotopic ratios of uranium in the environmental samples containing traces of depleted uranium: theoretical and experimental aspects. Radiat Protect Dosim 97:337–340
Manic G, Petrovic S, Manic V, Popovic D, Todorovic D (2006) Radon concentrations in a spa in Serbia. Environ Internat 32:533–537
Manoli E, Voutsa D, Samara C (2002) Chemical characterization and source identification/apportionment of fine and coarse air particles in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos Environ 36:949–961
Mason B (1996) Principles of geochemistry. Wiley, New York
Ministry of Mining and Energy (1992) Ore deposits database: mineral deposits of Serbia. Ministry of Mining and Energy report. Ministry of Mining and Energy, Republic of Serbia, Belgrade
Ostrovnaya TM, Nefedyeva LS, Nazarov VM, Borzakov SB, Strelkova LP (1993) Software for NAA on the basis of relative and absolute methods using nuclear data base. In: Activation analysis in environment protection. D-14-93-325, JINR, Dubna, pp. 319–326
Papastefanou C (2002) Depleted uranium in military conflicts and the impact on the environment. Health Phys 83:280–282
Petrovic B, Smelcerovic M, Djuric G, Popovic D (1989) Radiocontamination of agricultural workers due to nuclear accidents. In: Radiation protection—Selected topics. IBK Vinca, pp. 427–431
Popovic D, Djuric G (2001) Environment damage assessment by the use of DU ammunition on health and environment. Environmental impacts of the NATO war in Yugoslavia. An Independent Experts Group Report. Eco-Centre, Belgrade, pp. 103–115
Popovic D, Spasic-Jokic V (2006) Effects of the nuclear plant accident at Chernobyl on the territory of Serbia. Military Rev 63:481–487
Popovic D, Todorovic D (2006) Radon indoor concentrations and activity of radionuclides in building materials in Serbia. Facta Univer: Series Phys Chem Tech 4:11–20
Popovic D, Djuric G, Smelcerovic M, Maksimovic B (1989) Contribution of the short lived radionuclides in food to the total radiation burden of man after the nuclear accident in Chernobyl. Radiation protection—selected topics. IBK Vinca, Belgrade, pp. 416–420
Popovic D, Djuric G, Smelcerovic M (1995) Short-lived radionuclides in food and feed after the nuclear accident in Chernobyl. Acta Vet 45:337–340
Popovic D, Djuric G, Todorovic D (1996a) Chernobyl fallout radionuclides in soil, plant and honey of a mountain region. In: International Conference ‘A Decade After Chernobyl', Vienna, IAEA Tech. Reports No.964, vol. II, pp. 432–437
Popovic D, Djuric G, Todorovic D (1996b) Natural and fallout radionuclides in different types of honey. J Environ Biol 17:339–343
Popovic D, Djuric G, Todorovic D (1996c) Radionuclides in building materials and radon indoor concentrations. Radiat Protect Dosim 63:223–225
Popovic D, Todorovic D, Djuric G (1999) Activity of Cs-137 and Be-7 in surface air in Belgrade city area. Environ Internat 25:59–66
Popovic D, Djuric G, Todorovic D, Spasic V (2000) Radionuclides in building materials and radon in Belgrade dwellings. Cen Europ J Ocupp Environ Med 6:129–133
Popovic D, Djuric G, Todorovic D (2002) Possible impacts of depleted uranium on health and environment: the case of Yugoslavia. Cen Europ J Occupp Environ Med 8:227–233
RA Report (2002) Radioactivity in the environment in the Republic of Serbia in 2002. Ministry of the Environmental Protection of the Republic of Serbia, Belgrade
Radenkovic M, Cupac S, Joksic J, Todorovic D (2007) Depleted uranium mobility and fractionation in contaminated soil (Southern Serbia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 15(1):61–67
RSWG Summary (2002) Royal society working group on the health hazards of depleted uranium ammunition: A summary. J Radiol Prot 22:131–139
Sahoo SK, Fujimoto K, Celikovic J, Ujic P, Zunic Z (2004) Distribution of uranium, thorium and isotopic composition of uranium in soil samples of South Serbia: Evidence of depleted uranium. Nucl Tech Radiat Protect 19:26–30
Samecka-Cymerman A, Kolon K, Kempers A, Jansen J, Boonen B (2005) Bioaccumulation of elements in bryophytes from Serra da Estrela, Portugal and Veluwezoom, the Netherlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12(2):71–79
Schröder W, Pesch R (2005) Time series of metals in mosses and their correlation with selected sampling site-specific and ecoregional characteristics in Germany. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12(3):159–167
Steinnes E, Frontasyeva MV (1995) Epithermal neutron activation analysis of mosses used to monitor heavy metal deposition around an iron smelter complex. Analyst 120:1437–1440
Steinnes E, Hanssen JE, Rambæk JP, Vogt NB (1994) Atmospheric deposition of trace elements in Norway: temporal and spatial trend studied by moss analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 74:121–140
Stevanovic J, Kovacevic-Filipovic M, Vlaski M, Popovic D, Borozan S, Jovic S, Bozic T (2005) A study of oxidative stress and peripheral blood parameters of cows bred in the area exposed to DU ammunition. Acta Vet 55:269–278
Todorovic D, Popovic D, Djuric G (1994) Content of natural radionuclides in building materials. Ionizing radiation from the environment. INN Vinca, Belgrade, pp. 249–257
Todorovic D, Popovic D, Djuric G (1996) Activity of 137Cs in air before and after nuclear plant accident at Chernobyl. Vinca Bull (Belgrade) INS Vinca 2(Suppl 1):635–638
Todorović D, Popović D, Djuric G (2000) Concentration of Pb-210 in ground level air in Belgrade city area. Atmos Environ 34:3245–3248
Todorovic D, Radenkovic M, Popovic D, Ivanov S, Djuric G (2001) Contents of radionuclides in the region of Stara Planina. Chemistry and Environment. In: Proceedings of the IV Regional Symposium, Zrenjanin, pp. 431–33
Todorović D, Popović D, Djurić D, Radenković M (2002a) Transfer of 137Cs from soils to plants in different types of soils. Applied physics in Serbia. In: Koicki S, Konjevic N, Petrovic ZLj, Bek-Uzarov D (eds), SANU, XCVIII (2/1), Belgrade, pp. 259–262
Todorović D, Popović D, Radenković M, Djurić G (2002b) Concentrations of 7Be, 137Cs and 210Pb in ground level air in Belgrade area 1985–2001. Applied Physics in Serbia. In: Koicki S, Konjevic N, Petrovic ZLj, Bek-Uzarov D (eds) SANU, XCVIII (2/1), Belgrade, pp. 63–66
Todorovic D, Popovic D, Djuric G, Radenkovic M (2005a) 7Be to 210Pb concentration ratio in ground level air in Belgrade area. J Environ Radioact 79(3):297–307
Todorović D, Radenković M, Popović D, Tasić M, Rajšić S (2005b) Ground level air radioactivity monitoring in Belgrade urban area. Recent advances in multidisciplinary applied physics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 479
Tomasevic M, Rajsic S, Djordjevic D, Tasic M, Krstic J, Novakovic V (2004) Heavy metal accumulation in tree leaves from urban areas. Environ Chem Lett 2:151–154
UNCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. UNCEAR report to General Assembly, I. UN, New York
UNEP (2001) United Nations Environment Programme report: depleted uranium in Kosovo: post-conflict environmental assessment. United Nations Development Program, Geneva
UNEP (2002) United Nations Environment Programme report: post-conflict environmental assessment report on depleted uranium in Serbia and Montenegro. United Nations Development Program, Geneva
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Ministry of Science of the Republic of Serbia for the financial support under project no 141012 and Joint Institute for Nuclear Researches, Dubna, Russia, for fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popovic, D., Todorovic, D., Frontasyeva, M. et al. Radionuclides and heavy metals in Borovac, Southern Serbia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15, 509–520 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-008-0003-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-008-0003-6