Abstract
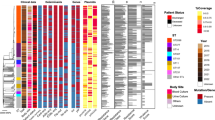
Aminoglycosides are key drugs for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. A total of 97 extensively drug-resistant (XDR) and 29 pan-susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Korean tuberculosis patients were analyzed to characterize mutations within the rrs, rpsL, gidB, eis and tlyA genes. Thirty (56.6 %) of the 53 streptomycin (STR)-resistant strains had a rpsL mutation and eight strains (15.1 %) had a rrs (514 or 908 site) mutation, whereas 11 (20.8 %) of the 53 STR-resistant strains had a gidB mutation without rpsL or either rrs mutation. Most of the gidB mutations conferred low-level STR resistance, and 22 of these mutations were novel. Mutation at position 1401 in rrs lead to resistance to kanamycin (80/95 = 84.2 %; KAN), amikacin (80/87 = 92.0 %; AMK), and capreomycin (74/86 = 86.0 %; CAP). In this study, 13.7 % (13/95) of KAN-resistant strains showed eis mutations, including 4 kinds of novel mutations. Isolates with eis structural gene mutations were cross-resistant to STR, KAN, CAP, and AMK. Here, 5.8 % (5/86) of the CAP-resistant strains harbored a tlyA mutation that included 3 different novel point mutations. Detection of the A1401G mutation appeared to be 100 % specific for the detection of resistance to KAN and AMK. These data establish the presence of phenotypic XDR strains using molecular profiling and are helpful to understanding of aminoglycoside resistance at the molecular level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen BW, Mitchison DA, Chan YC, Yew WW, Allan WG, Girling DJ (1983) Amikacin in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle 64:111–118
Campbell PJ, Morlock GP, Sikes RD, Dalton TL, Metchock B, Starks AM, Hooks DP, Cowan LS, Plikaytis BB, Posey JE (2011) Molecular detection of mutations associated with first- and second-line drug resistance compared with conventional drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:2032–2041
Cooksey RC, Morlock GP, McQueen A, Glickman SE, Crawford JT (1996) Characterization of streptomycin resistance mechanism among Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from patients in New York City. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:1186–1188
Douglass J, Steyn LM (1993) A ribosomal gene mutation in streptomycin resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. J Infect Dis 167:1505–1506
Engström A, Perskvist N, Werngren J, Hoffner SE, Juréen P (2011) Comparison of clinical isolates and in vitro selected mutants reveals that tlyA is not a sensitive genetic marker for capreomycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:1247–1254
Feuerriegel S, Cox HS, Zarkua N, Karimovich HA, Braker K, Rüsch-Gerdes S, Niemann S (2009) Sequence analyses of just four genes to detect extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in multi drug-resistant tuberculosis patients undergoing treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:3353–3356
Finken M, Kirschner P, Meier A, Wrede A, Bo¨ttger EC (1993) Molecular basis of streptomycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: alterations of the ribosomal protein S12 gene and point mutations within a functional 16S ribosomal RNA pseudoknot. Mol Microbiol 9:1239–1246
Georghiou SB, Magana M, Garfein RS, Catanzaro DG, Catanzaro A, Rodwell TC (2012) Evaluation of genetic mutations associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to amikacin, kanamycin and capreomycin: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 7:e33275
Jugheli L, Bzekalava N, de Rijk P, Fissette K, Portaels F, Rigouts L (2009) High level of cross-resistance between kanamycin, amikacin, and capreomycin among Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Georgia and a close relation with mutations in the rrs gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:5064–5068
Katsukawa C, Tamaru A, Miyata Y, Abe C, Makino M, Suzuki Y (1997) Characterization of the rpsL and rrs genes of streptomycin-resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Japan. J Appl Microbiol 83:634–640
Kim SJ, Bai GH, Hong YP (1997) Drug-resistant tuberculosis in Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 1:302–308
Maus CE, Plikaytis BB, Shinnick TM (2005a) Molecular analysis of cross-resistance to capreomycin, kanamycin, amikacin, and viomycin in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:3192–3197
Maus CE, Plikaytis BB, Shinnick TM (2005b) Mutation of tlyA confers capreomycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:571–577
Meier A, Kirschner P, Bange FC, Vogel U, Bo¨ttger EC (1994) Genetic alterations in streptomycin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: mapping of mutations conferring resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:228–233
Nair D, Capoor MR, Rawat D, Srivastava L, Aggarwal P (2009) Standardization of first and second-line antitubercular susceptibility testing using BacT Alert 3D system: a report from a tertiary care centre in India. Braz J Infect Dis 13:422–426
Nhu NT, Lan NT, Phuong NT, Chau Nv, Farrar J, Caws M (2012) Association of streptomycin resistance mutations with level of drug resistance and Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotypes. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16:527–531
Nishimura K, Hosaka T, Tokuyama S, Okamoto S, Ochi K (2007) Mutations in rsmG, encoding a 16S rRNA methyltransferase, result in low level streptomycin resistance and antibiotic overproduction in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 189:3876–3883
Noller HF (1984) Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem 53:119–162
Okamoto S, Tamaru AC, Nakajima C, Nishimura K, Tanaka Y, Tokuyama S, Suzuki Y, Ochi K (2007) Loss of a conserved 7-methylguanosine modification in 16S rRNA confers low-level streptomycin resistance in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 63:1096–1106
Ramaswamy SV, Dou SJ, Rendon A, Yang Z, Cave MD, Graviss EA (2004) Genotype analysis of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Monterrey, Mexico. J Med Microbiol 53:107–113
Sander P, Prammananan T, Böttger EC (1996) Introducing mutations into a chromosomal rRNA gene using a genetically modified eubacterial host with a single rRNA operon. Mol Microbiol 22:841–848
Sirgel FA, Tait M, Warren RM, Streicher EM, Böttger EC, van Helden PD, Gey van Pittius NC, Coetzee G, Hoosain EY, Chabula-Nxiweni M, Hayes C, Victor TC, Trollip A (2012) Mutations in the rrs A1401G gene and phenotypic resistance to amikacin and capreomycin in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microb Drug Resist 18:193–197
Spies FS, da Silva PE, Ribeiro MO, Rossetti ML, Zaha A (2008) Identification of mutations related to streptomycin resistance in clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and possible involvement of efflux mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:2947–2949
Sreevatsan S, Pan X, Stockbauer KE, Williams DL, Kreiswirth BN, Musser JM (1996) Characterization of rpsL and rrs mutations in streptomycin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from diverse geographic localities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:1024–1026
Suzuki Y, Katsukawa C, Tamaru A, Abe C, Makino M, Mizuguchi Y, Taniguchi H (1998) Detection of kanamycin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by identifying mutations in the 16S rRNA gene. J Clin Microbiol 36:1220–1225
Via LE, Cho SN, Hwang S, Bang H, Park SK, Kang HS, Jeon D, Min SY, Oh T, Kim Y, Kim YM, Rajan V, Wong SY, Shamputa IC, Carroll M, Goldfeder L, Lee SA, Holland SM, Eum S, Lee H, Barry CE III (2010) Polymorphisms associated with resistance and cross-resistance to aminoglycosides and capreomycin in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from South Korean patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 48:402–411
Yuan X, Zhang T, Kawakami K, Zhu J, Li H, Lei J, Tu S (2012) Molecular characterization of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in Jiangxi, China. J Clin Microbiol 50:2404–2413
Zaunbrecher MA, Sikes RD Jr, Metchock B, Shinnick TM, Posey JE (2009) Overexpression of the chromosomally encoded aminoglycoside acetyltransferase eis confers kanamycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20004–20009
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a fund (code#2011-E-45001-00) by Research of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jnawali, H.N., Yoo, H., Ryoo, S. et al. Molecular genetics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant to aminoglycosides and cyclic peptide capreomycin antibiotics in Korea. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 975–982 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1256-x