Abstract
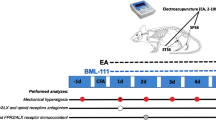
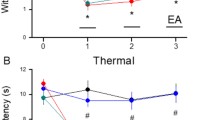
Although studies demonstrate that electroacupuncture (EA) alleviates the sensory dimension of pain, they have not addressed EA’s effect on the affective dimension. An inflammatory pain rat model, produced by a complete Freund adjuvant (CFA) injection into the hind paw, was combined with a conditioned place avoidance test to determine EA’s effects and its underpinning mechanism on the affective dimension of pain. CFA-injected rats showed place aversion, i.e. the affective dimension of pain, by spending less time in a pain-paired compartment after conditioning than before, while saline-injected rats did not. CFA rats given EA treatment at GB30 before a post-conditioning test showed no aversion to the pain-paired compartment, indicating that EA inhibited the affective response. Intra-rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) administration of a κ-, but not μ-opioid receptor antagonist, blocked EA action. These data demonstrate that EA activates opioid receptors in the rACC to inhibit the affective dimension of pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johansen JP, Fields HL, Manning BH (2001) The affective component of pain in rodents: direct evidence for a contribution of the anterior cingulate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:8077–8082
LaBuda CJ, Fuchs PN (2001) Low dose aspirin attenuates escape/avoidance behavior, but does not reduce mechanical hyperalgesia in a rodent model of inflammatory pain. Neurosci Lett 304:137–140
Boyce-Rustay JM, Zhong C, Kohnken R, Baker SJ, Simler GH, Wensink EJ, Decker MW, Honore P (2010) Comparison of mechanical allodynia and the affective component of inflammatory pain in rats. Neuropharmacology 58:537–543
Cheng X (1999) Chinese acupuncture and moxibustion. Foreign Languages Press, Beijing
Koo ST, Park YI, Lim KS, Chung K, Chung JM (2002) Acupuncture analgesia in a new rat model of ankle sprain pain. Pain 99:423–431
Zhang Y-Q, Ji G-C, Wu G-C, Zhao Z-Q (2002) Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists and electroacupuncture synergetically inhibit carrageenan-induced behavioral hyperalgesia and spinal fos expression in rats. Pain 99:525–535
Lao L, Zhang R-X, Zhang G, Wang X, Berman BM, Ren K (2004) A parametric study of electroacupuncture on persistent hyperalgesia and Fos protein expression in rats. Brain Res 1020:18–29
Hammes MG, Flatau B, Bäcker M, Ehinger S, Conrad B, Tölle TR (2002) Investigations on the effect of acupuncture on affective and sensory components of pain in patients with different stages of chronic pain. Schmerz 16:103–113
Hummel M, Lu P, Cummons TA, Whiteside GT (2008) The persistence of a long-term negative affective state following the induction of either acute or chronic pain. Pain 140:436–445
LaGraize SC, Labuda CJ, Rutledge MA, Jackson RL, Fuchs PN (2004) Differential effect of anterior cingulate cortex lesion on mechanical hypersensitivity and escape/avoidance behavior in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 188:139–148
Mayer DJ (2000) Biological mechanisms of acupuncture. Prog Brain Res 122:457–477
Fenu S, Spina L, Rivas E, Longoni R, Di Chiara G (2006) Morphine-conditioned single-trial place preference: role of nucleus accumbens shell dopamine receptors in acquisition, but not expression. Psychopharmacology 187:143–153
Zhang RX, Lao L, Wang L, Liu B, Wang X, Ren K, Berman BM (2004) Involvement of opioid receptors in electroacupuncture-produced anti-hyperalgesia in rats with peripheral inflammation. Brain Res 1020:12–17
Millan MJ (2002) Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol 66:355–474
Heinricher MM, Tavares I, Leith JL, Lumb BM (2009) Descending control of nociception: specificity, recruitment and plasticity. Brain Res Rev 60:214–225
Chen J-H, Liang J, Wang G-b, Han J-S, Cui C-l (2005) Repeated 2 Hz peripheral electrical stimulations suppress morphine-induced CPP and improve spatial memory ability in rats. Exp Neurol 194:550–556
Chae Y, Yeom M, Han JH, Park HJ, Hahm DH, Shim I, Lee HS, Lee H (2008) Effect of acupuncture on anxiety-like behavior during nicotine withdrawal and relevant mechanisms. Neurosci Lett 430:98–102
Park HJ, Chae Y, Jang J, Shim I, Lee H, Lim S (2005) The effect of acupuncture on anxiety and neuropeptide Y expression in the basolateral amygdala of maternally separated rats. Neurosci Lett 377:179–184
Lee B, Shim I, Lee HJ, Yang Y, Hahm DH (2009) Effects of acupuncture on chronic corticosterone-induced depression-like behavior and expression of neuropeptide Y in the rats. Neurosci Lett 453:151–156
Cao X (2002) Scientific bases of acupuncture analgesia. Acupunct Electrother Res 27:1–14
Han J-S (2003) Acupuncture neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci 26:17–22
Kanemitsu Y, Hosoi M, Zhu PJ, Weight FF, Peoples RW, McLaughlin JS, Zhang L (2003) Dynorphin A inhibits NMDA receptors through a pH-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:525–537
Lei L-G, Sun S, Gao Y-J, Zhao Z-Q, Zhang Y-Q (2004) NMDA receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex mediate pain-related aversion. Exp Neurol 189:413–421
McWilliams LA, Cox BJ, Enns MW (2003) Mood and anxiety disorders associated with chronic pain: an examination in a nationally representative sample. Pain 106:127–133
Acknowledgments
This publication was made possible by grant number R21AT005474-01 and P01AT002605 from the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) at the National Institutes of Health. We would like to thank Dr. Lyn Lowry for her editorial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Meng, X., Li, A. et al. Acupuncture Alleviates the Affective Dimension of Pain in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Hyperalgesia. Neurochem Res 36, 2104–2110 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0534-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0534-y