Abstract
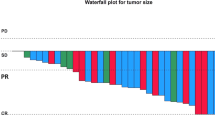
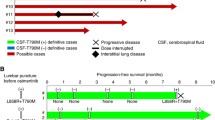
In the present study we assessed the activity of the next-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (-TKI) alectinib, in patients with ALK-postive, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and central nervous system (CNS) metastases. NSCLCs with ALK-positive disease, as assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and CNS metastases were treated with alectinib 600 mg BID. Included patients were followed prospectively in order to evaluate the efficacy of the drug, with particular emphasis on activity in the CNS. Eleven consecutive patients were enrolled. The majority of them were pretreated with crizotinib (n = 10, 90.9 %), and cranial radiotherapy (n = 8, 72.7 %). Six of the seven patients with measurable CNS disease experienced a CNS response, including three patients who were naïve for cranial radiation. Median duration of response was 8 months. For the whole population, median CNS-progression-free survival (-PFS), systemic-PFS, overall-PFS, overall survival, and 1-year survival were 8, 11, 8, 13 months, and 31.1 %, respectively. Two patients experiencing a CNS response were assessed for alectinib’s concentrations in serum and cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF), and showed a CSF-to-serum ratio ranging from 0.001 to 0.003 ng/mL. Alectinib is highly active against CNS metastases from ALK-positive NSCLCs, irrespective of prior treatment(s) with ALK-TKI(s) and/or cranial radiotherapy. The low CSF-to-serum ratio of alectinib suggests that measuring the concentrations of the drug in the CSF may not be a reliable surrogate of its distribution into the CNS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iacono D, Chiari R, Metro G et al (2015) Future options for ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 87:211–219
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW et al (2014) First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 371:2167–2177
Costa DB, Shaw AT, Ou SH (2015) Clinical experience with crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 33:1881–1888
Costa DB, Kobayashi S, Pandya SS et al (2011) CSF concentration of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor crizotinib. J Clin Oncol 29:e443–e445
Metro G, Lunardi G, Floridi P et al (2015) CSF concentration of crizotinib in two ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer patients with CNS metastases deriving clinical benefit from treatment. J Thorac Oncol 10:e26–e27
Kodama T, Hasegawa M, Takanashi K et al (2014) Antitumor activity of the selective ALK inhibitor alectinib in models of intracranial metastases. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74:1023–1028
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 4.0. http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_4.03_2010-06-14_QuickReference_5x7.pdf. Accessed 1 Jan 2016
Gadgeel S, Shaw T, Govindan R et al (2015) Pooled analysis of CNS response to alectinib in two studies of pre-treated ALK + NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 10(9Suppl 2):S238 (abstract)
Shaw AT, Gandhi L, Gadgeel S et al (2016) Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:234–242
Ou SH, Ahn JS, De Petris L et al (2016) Alectinib in crizotinib-refractory ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase II global study. J Clin Oncol 34:661–668
Gainor JF, Sherman CA, Willoughby K et al (2015) Alectinib salvages CNS relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib. J Thorac Oncol 10:232–236
Johung KL, Yeh N, Desai NB et al (2016) Extended survival and prognostic factors for patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol 34:123–129
Gadgeel SM, Gandhi L, Riely GJ et al (2014) Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol 15:1119–1128
Sakamoto H, Tsukaguchi T, Hiroshima S et al (2011) CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell 17:679–690
Acknowledgments
Supported by the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metro, G., Lunardi, G., Bennati, C. et al. Alectinib’s activity against CNS metastases from ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a single institution case series. J Neurooncol 129, 355–361 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2184-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2184-z