Abstract
This study investigated firstly the reliability and validity of an Indonesian version of the Questionnaire on Teacher Interaction (QTI). Second, perceptions of Indonesian secondary school teachers’ interpersonal behaviour as perceived by students and teachers were studied with the QTI. Third, differences between students’ and teachers’ perceptions regarding interpersonal teacher behaviour were compared. The QTI itself is based on the Model of Interpersonal Behaviour which maps teacher behaviour in terms of Influence (Dominance–Submission) and Proximity (Cooperation–Opposition). In this study, an Indonesian version of the QTI was constructed and distributed to 2,380 students of 69 teachers from 85 classes (grade 7–9) from 12 public lower secondary schools in Indonesia. The results showed high reliability and validity for the instrument. Students’ and teachers’ average ratings on Influence were similar, while teacher’s ratings of Proximity were higher than those of students.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
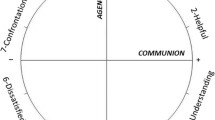
Dimension scores were set to range between −3 and +3. This numbers represent the amount of dominance vs submissiveness and cooperation vs opposition, respectively. The range of scores are 0–0.5 (moderately positive), 0.5–1 (positive) and >1 (very positive) (den Brok et al. 2006a, b; Telli et al. 2007a).
References
Ben-Chaim, D., & Zoller, U. (2001). Self-perceptions versus students’ perceptions of teacher interpersonal style in college science and mathematics courses. Research in Science Education, 31, 437–454.
Brekelmans, M., Holvast, A., & van Tartwijk, J. (1993). Changes in teacher communication style during the professional career. Journal of Classroom Interaction, 27, 13–22.
Brekelmans, M., & Wubbels, T. (1991). Student and teacher perceptions of interpersonal teacher behavior: A Dutch perspective. The Study of Learning Environments, 5, 19–30.
Brekelmans, M., Wubbels, T., & den Brok, P. (2002). Teacher experience and the teacher–student relationship in the classroom environment. In S. C. Goh & M. S. Khine (Eds.), Studies in educational learning environments: An international perspective (pp. 73–100). Singapore: World Scientific.
Central Intelligence Agency. (2007). The world fact book: Indonesia. https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/print/id.html. Accessed 3 April 2007.
den Brok, P. J. (2001). Teaching and student outcomes. A study on teachers’ thoughts and actions from an interpersonal and a learning activities perspective. Utrecht: W.C.C.
den Brok, P. J., Bergen, T., & Brekelmans, M. (2006a). Convergence and divergence between teachers’ and students’ perceptions of instructional behavior in Dutch secondary education. In D. L. Fisher & M. S. Khine (Eds.), Contemporary approaches to research on learning environments: World views (pp. 125–160). Singapore: World Scientific.
den Brok, P. J., Brekelmans, M., & Wubbels, T. (2004). Interpersonal teacher behavior and student outcomes. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 15, 407–442.
den Brok, P. J., Fisher, D., Brekelmans, M., Rickards, T., Wubbels, T., Levy, J., et al. (2003a, April). Students’ perceptions of secondary teachers’ interpersonal style in six countries: A study on the validity of the Questionnaire on Teacher Interaction. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Chicago.
den Brok, P. J., Fisher, D., Brekelmans, M., Rickards, T., Wubbels, T., Levy, J., et al. (2003b, April). The cross national validity of students’ perception of science teachers’ interpersonal behavior. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Association for Research on Science Teaching, Philadelphia, PA.
den Brok, P. J., Fisher, D., Brekelmans, M., Wubbels, T., & Rickards, T. (2006b). Secondary teachers’ interpersonal behavior in Singapore, Brunei and Australia: A cross-national comparison. Asia-Pacific Journal of Education, 26, 79–95.
den Brok, P. J., Fisher, D., & Koul, R. (2005a). The importance of teacher interpersonal behavior for secondary science students’ attitudes in Kashmir. Journal of Classroom Interaction, 40, 5–19.
den Brok, P. J., Fisher, D., & Scott, R. (2005b). The importance of teacher interpersonal behavior on students’ subject specific motivation. Journal of Classroom Interaction, 40(2), 20–33.
den Brok, P. J., Levy, J., Rodriguez, R., & Wubbels, T. (2002). Perception of Asian-American and Hispanic-American teachers and their students on interpersonal communication style. Teaching and Teacher Education, 18, 447–467.
Doyle, W. (1986). Classroom organization and management. In M. C. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching (3rd ed.). New York: Macmillan.
Evans, H., & Fisher, D. L. (2000). Cultural differences in students’ perceptions of science teachers’ interpersonal behavior. Australian Science Teachers Journal, 46(2), 9–18.
Fisher, D., Fraser, B., Wubbels, T., & Brekelmans, M. (1993, April). Associations between school environment and teacher interpersonal behavior in the classroom. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Atlanta, GA.
Fisher, D. L., & Rickards, T. (1998, April). A comparison of teacher–student interpersonal behavior in secondary science classes in USA, Singapore and Australia. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Science Teachers Association, Las Vegas, NV.
Fisher, D. L., & Rickards, T. (1999, January). Teacher–student interpersonal behavior as perceived by science teachers and their students. Paper presented at the second international conference on Science, Mathematics and Technology Education, Taipei.
Fisher, D. L., & Rickards, T. (2000). Teacher–student interpersonal behavior as perceived by science teachers and their students. In D. Fisher & J. Yang (Eds.), Improving classroom research through international cooperation (pp. 391–398). Taiwan: National Taiwan Normal University.
Fraser, B. J. (2002). Learning environments research: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. In S. C. Goh & M. S. Khine (Eds.), Studies in educational learning environments: An international perspective (pp. 1–25). Singapore: World Scientific.
Fraser, B. J., Aldridge, J. M., & Adolphe, F. S. G. (2010a). A cross-national study of secondary science classroom environments in Australia and Indonesia. Research in Science Education, 40, 551–571.
Fraser, B. J., Aldridge, J. M., & Soerjaningsih, W. (2010b). Instructor-student interpersonal interaction and student outcomes at the university level in Indonesia. The Open Education Journal, 3, 32–44.
Fraser, B. J., Pearse, R., & Azmi., (1982). A study of Indonesian student perceptions of classroom psychosocial environment. International Review of Education, 28, 337–355.
Hall, E. T. (1966). The hidden dimension. New York: Double day.
Henderson, D., Fisher, D. L., & Fraser, B. J. (2000). Interpersonal behavior, laboratory learning environments, and student outcomes in senior biology classes. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 37, 26–43.
Hofstede, G. (1991). Cultures and organizations: Software of the mind. London: McGraw-Hill.
Irianto, B., & Treagust, D. F. (2001, March). Teachers’ perception of the role of the laboratory in a national professional development centre. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, St. Louis, MO.
Khine, M. S. (2001). Association between teacher interpersonal behavior and aspects of classroom environment in Asian context. Unpublished doctoral thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Perth, Australia.
Khine, M. S., & Fisher, D. L. (2001, December). Classroom environment and teachers’ cultural background in secondary science classes in Asian context. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Australian Association for Research in Education, Perth.
Kim, H. B., Fısher, D. L., & Fraser, B. J. (2000). Environment and teacher interpersonal behavior in secondary science classes in Korea. Evaluation and Research in Education, 14(1), 3–22.
Leary, T. (1957). Interpersonal diagnosis of personality. New York: Ronald.
Lee, S. S. U., Fraser, B. J., & Fisher, D. L. (2003). Teacher-student interactions in Korean high school science classrooms. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 1, 67–85.
Mangindaan, C. S., Sembiring, R. K., & Livingstone, I. D. (1978). National assessment of the quality of Indonesian Education. Jakarta: Ministry of Education and Culture of Indonesia.
Mapiasse, S. (2007). Influence of the democratic climate of classrooms on student civic learning in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. International Education Journal, 8, 393–407.
Margianti, E. S., & Fraser, D. L. (2000, January). Learning environment, mathematical ability and students’ outcomes in university computing courses in Indonesia. Paper presented at the Second International Conference on Science, Mathematics and Technology Education, Taipei, Taiwan.
Margianti, E. S., Fraser, B. J., & Aldridge, J. M. (2001, April). Classroom environment and students’ outcomes among university computing students in Indonesia. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Seattle, WA.
Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (1999). Mplus users’ guide: The comprehensive modeling program for applied researchers. Los Angeles: Muthen and Muthen.
Paige, R. M. (1978). The impact of the classroom learning environment on academic achievement and individual modernity in East Java, Indonesia. Unpublished doctoral thesis, Stanford University, CA.
Quek, C. L., Wong, A. F. L., & Fraser, B. J. (2005). Student perceptions of chemistry laboratory learning environments, student-teacher interactions and attitudes in secondary school gifted education classes in Singapore. Research in Science Education, 35, 321–399.
Raj, L. L. (1998). A study of effects of a computer algebra system on the learning of, and attitudes toward, mathematics amongst engineering students in Papua New Guinea. Unpublished doctoral thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Perth.
Riah, H., & Fraser, B. J. (1998, April). Chemistry learning environment and its association with students’ achievement in chemistry. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, San Diego, CA.
Rickards, T., & Fisher, D. (2000, April). Three perspectives on perceptions of teacher-student interaction: A seed for change in science teaching. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, New Orleans, LA.
Rideng, I. M., & Schibeci, R. A. (1984). The development and validation of a test of biology-related attitudes. Research in Science and Technological Education, 2, 21–29.
Rochintaniawati, D., Wulan, A. R., & Sriyati, S. (2009). The needs of Cimahi and Bandung districts elementary teachers in conducting science teaching. Bandung, Indonesia. Department of Biology Education, Indonesia University of Education.
Schibeci, R. A., Rideng, I. M., & Fraser, B. J. (1987). Effects of classroom environment on science attitudes: A cross-cultural replication in Indonesia. International Journal of Science Education, 9, 169–186.
Scott, R. H., & Fisher, D. L. (2004). Development, validation and application of a Malay translation of an elementary version of the Questionnaire on Teacher Interaction (QTI). Research in Science Education, 34, 173–194.
She, H. C., & Fisher, D. L. (1999. March). The validation and use of the TCBQ in studying secondary science classroom interaction and its association with students’ attitudinal and cognitive outcomes in Taiwan. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, Boston.
Soeharto, S. (1998). The effects of a constructivist learning environment on grade six student achievement and attitude toward mathematics in Indonesian primary schools. Unpublished doctoral thesis, University of Houston, TX.
Telli, S. (2006). Students perceptions’ of their science teachers’ interpersonal behavior in two counties: Turkey and the Netherlands. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Middle East University, Ankara.
Telli, S., den Brok, P. J., & Cakiroglu, J. (2007a). Students’ perceptions of science teachers’ interpersonal behavior in secondary schools: Development of a Turkish version of the Questionnaire of Teacher Interaction. Learning Environments Research, 10, 115–129.
Telli, S., den Brok, P. J., & Cakiroglu, J. (2007b). Teacher-student interpersonal behavior in secondary science classes in Turkey. Journal of Classroom Interaction, 42, 31–40.
van Oord, L., & den Brok, P. J. (2004). The international teacher: Students’ and teachers’ perceptions of preferred teacher–student interpersonal behavior in two United World Colleges. Journal of Research in International Education, 3(2), 131–155.
Vansteenkiste, M., Simons, J., Lens, W., Sheldon, K. M., & Deci, E. L. (2004). Motivating learning, performance, and persistence: The synergistic role of intrinsic goals and autonomy-support. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87, 246–260.
Veenman, S. (1984). Perceived problems of beginning teachers. Review of Educational Research, 54, 143–178.
Wahyudi, & Treagust, D. F. (2004). The status of science classroom learning environments in Indonesian lower secondary education. Learning Environments Research, 7, 43–63.
Walberg, H. J., Singh, R., & Rasher, S. P. (1977). Predictive validity of student perception: A cross-cultural replication. American Educational Research Journal, 14, 45–49.
Wei, M., den Brok, P., & Zou, Y. (2009). Teacher interpersonal behavior and student achievement in English as a Foreign Language classrooms in China. Learning Environments Research, 12, 157–174.
Wong, F. L. A., & Fraser, B. J. (1996). Environment-attitude associations in the chemistry laboratory classroom. Research in Science and Technological Education, 14, 91–102.
Wubbels, T., & Brekelmans, M. (1998). The teacher factor in the social climate of the classroom. In B. J. Fraser & K. G. Tobin (Eds.), International handbook of science education (pp. 565–580). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Wubbels, T., & Brekelmans, M. (2005). Two decades of research on teacher-student relationships in class. International Journal of Educational Research, 43, 6–24.
Wubbels, T., Brekelmans, M., den Brok, P., & van Tartwijk, J. (2006). An interpersonal perspective on classroom management in secondary classrooms in the Netherlands. In. C. Evertson & C. S. Weinstein (Eds.), Handbook of classroom management: Research, practice and contemporary issues (pp. 1161–1191). New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Wubbels, T., Brekelmans, M., & Hermans, K. (1987). Teacher behavior: An important aspect of the learning environment? The Study of Learning Environments, 3, 10–25.
Wubbels, T., Brekelmans, M., & Hooymayers, H. P. (1992). Do teacher ideals distort the self reports of their interpersonal behavior? Teaching and Teacher Education, 8, 47–58.
Wubbels, T., Creton, H. A., & Hooymayers, H. P. (1985, April). Discipline problems of beginning teachers: Interactional teacher behavior mapped out. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association Research.
Wubbels, T., & Levy, J. (1991). A comparison of interpersonal behavior of Dutch and American teachers. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 15, 1–18.
Wubbels, T., & Levy, J. (Eds.). (1993). Do you know what you look like?. London: The Falmer Press.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editor and the two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments on the previous manuscript. This study was conducted as part of the PhD study of the first author. The second author was supported with a grant from Rosalind Franklin Fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maulana, R., Opdenakker, M.C.J.L., den Brok, P. et al. Teacher–student interpersonal relationships in Indonesian lower secondary education: Teacher and student perceptions. Learning Environ Res 15, 251–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-012-9113-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-012-9113-7