Abstract
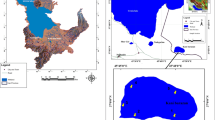
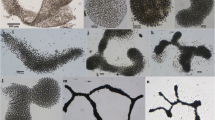
Cyanobacterial mats are common in Antarctic lakes, ponds and on moist soils. The species comprising these mats have adapted to tolerate extreme conditions (e.g. high salinities and UV radiation, freezing and extended periods of darkness). In this study, cyanobacterial mats were collected from shallow melt-water ponds in Pyramid Trough in Southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Eight strains were isolated and characterised by morphological and molecular (16S rRNA gene sequences) techniques and their fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) and lipid class profiles determined. These data were compared to parallel information obtained from cyanobacterial cultures isolated from New Zealand. In general, the morphological and molecular characterisation complemented each other, and the Antarctic strains identified belonged to the orders: Oscillatoriales (six), Nostocales (one) and Chroococcales (one). Two of the Antarctic strains (CYN67 and CYN68) showed low similarity (<96% 16S rRNA gene sequence) when compared to other cultured cyanobacteria. The fatty acid (FA) profiles from the Antarctic and New Zealand strains shared many similarities with palmitic (C16:0), stearic (C18:0) and oleic acid (C18:1n-9) most abundant. In contrast, the lipid class analysis differed among geographic locations with Antarctic strains containing higher amounts of hydrocarbons and eicosapentaenoic and hexadecatrienoic acids.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. A., B. A. Neilan, B. P. Burns, L. L. Jahnke & R. E. Summons, 2010. Lipid biomarkers in hamelin pool microbial mats and stromatolites. Organic Geochemistry 41: 1207–1218.
Benson, D. A., I. Karsch-Mizrachi, D. J. Lipman, J. Ostell & D. L. Wheeler, 2008. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Research 36: D25–D30.
Bligh, E. G. & W. G. Dyer, 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology 37: 911–917.
Bolch, C. J. S. & S. I. Blackburn, 1996. Isolation and purification of Australian isolates of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Journal of Applied Phycology 8: 5–13.
Brown, M. R., G. A. Dunstan, S. J. Norwood & K. A. Miller, 1996. Effects of harvest stage and light on the biochemical composition of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Journal of Phycology 32: 64–73.
Burja, A. M., B. Banaigs, E. Abou-Mansour, J. G. Burgess & P. C. Wright, 2001. Marine cyanobacteria – a prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron 57: 9347–9377.
Caudales, R., J. M. Wells & J. E. Butterfield, 2000. Cellular fatty acid composition of cyanobacteria assigned to subsection II, order Pleurocapsales. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 50: 1029–1034.
Cohen, Z., M. C. Margheri & L. Tomaselli, 1995. Chemotaxonomy of cyanobacteria. Phytochemistry 40: 1155–1158.
Comte, K., M. Sabacka, A. Carre-Mlouka, J. Elster & J. Komarek, 2007. Relationships between the Arctic and the Antarctic cyanobacteria; three Phormidium like strains evaluated by a polyphasic approach. Federation of European Microbiological Societies Microbiology Ecology 59: 366–376.
Connon, S. A. & S. J. Giovannoni, 2002. High-Throughput methods for culturing microorganisms in very-low-nutrient media yield diverse new marine isolates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68: 3878–3885.
Frazão, B., R. R. Martins & V. Vasconcelos, 2010. Are known cyanotoxins involved in the toxicity of picoplanktonic and filamentous North Atlantic marine cyanobacteria? Marine Drugs 6: 1908–1919.
Galhano, V., D. R. de Figueiredo, A. Alves, A. Correia, M. J. Pereira, J. Gomes-Laranjo & F. Peixoto, 2011. Morphological, biochemical and molecular characterization of Anabaena, Aphanizomenon and Nostoc strains (Cyanobacteria, Nostocales) isolated from Portuguese freshwater habitats. Hydrobiologia 663: 187–203.
Gibson, J. A. E., M. R. Miller, N. W. Davies, G. P. Neill, D. S. Nichols & J. K. Volkman, 2005. Unsaturated diether lipids in the psychrotrophic archaeon Halorubrum lacusprofundi. Systematic and Applied Microbiology 28: 19–26.
Gugger, M., C. Lyra, I. Suominen, I. Tsitko, J.-F. Humbert, M. S. Salkinoja-Salonen & K. Sivonen, 2002. Cellular fatty acids as chemotaxonomic markers of the genera Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Microcystis, Nostoc and Planktothrix (cyanobacteria). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 52: 1007–1015.
Hayes, J. K. & F. B. Shortland, 1951. The constitution of hexadecatrienoic acid from the glycerides of rape (Brassica napus L.) leaf. Biochemical Journal 49: 503–506.
Heath, M. W., S. A. Wood & K. G. Ryan, 2010. Polyphasic assessment of freshwater benthic mat-forming cyanobacteria isolated from New Zealand. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 73(1): 95–109.
Hu, Q., M. Sommerfeld, E. Jarvis, M. Ghirardi, M. Posewitz, M. Seibert & A. Darzins, 2008. Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant Journal 54: 621–639.
Jakobsen, M. U., E. J. O’Reilly, B. L. Heitmann, M. A. Pereira, K. Balter, G. E. Fraser, U. Goldbourt, G. Hallmans, P. Knekt, S. Liu, P. Pietinen, D. Spiegelman, J. Stevens, J. Virtamo, W. C. Willett & A. Ascherio, 2009. Major types of dietary fat and risk of coronary heart disease: a pooled analysis of 11 cohort studies. America Journal of Clinical Nutrition 98: 1425–1432.
Jungblut, A.-D., C. Lovejoy & W. F. Vincent, 2009. Global distribution of cyanobacterial ecotypes in the cold biosphere. The International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal 4: 191–202.
Jungblut, A.-D., S. A. Wood, I. Hawes, J. Webster-Brown & C. Harris, 2012. The Pyramid Trough Wetland: environment-biota relationships in a newly created protected area. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 82: 356–366.
Komárek, J., 2006. Cyanobacterial taxonomy: current problems and prospects for the integration of traditional and molecular approaches. Algae 21: 349–375.
Komárek, J., 2010. Modern taxonomic revision of planktic nostocacean cyanobacteria: a short review of genera. Hydrobiologia 639: 231–243.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 1989. Modern approach to the classification system of cyanophytes. 4 – Nostocales. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplement 56: 247–345.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 2000. Cyanoprokaryota. 1. Teil, Chroococcales. In Ettl, H., G. Gartner, H. Heynig & D. Molllenhauer (eds), Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa vol 19. Gustav Fisher, Jena: 548.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 2005. Cyanoprokaryota. 2. Teil, Oscillatoriales. In Budel, B., L. Krienitz, G. Gartner & M. Schagerl (eds), Süßwasserflora von mitteleuropa, Band 19/2 Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Elsevier GmbH. München, German.
Li, R. H. & M. M. Watanabe, 2001. Fatty acid profiles and their chemotaxonomy in planktonic species of Anabaena (Cyanobacteria) with straight trichomes. Phytochemistry 57: 727–773.
Li, R., A. Yokota, J. Sugiyama, M. Watanabe & M. M. Watanabe, 1998. Chemotaxonomy of planktonic cyanobacteria based on non polar and 3-hydroxy fatty acid composition. Phycological Research 46: 21–28.
Li, R., S. W. Wilhelm, W. W. Carmichael & M. M. Watanabe, 2008. Polyphasic characterization of water bloom forming Raphidiopsis species (cyanobacteria) from central China. Harmful Algae 7: 146–153.
Madigan, M. & J. Martinko, 2005. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 11th ed. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River: 992 pp.
McGregor, G., 2007. Freshwater cyanoprokaryota of North-Eastern Australia 1: Oscillatoriales. Australian Biological Resources Study, Canberra.
Murata, N. & H. Wada, 1995. Acyl-lipid desaturases and their importance in the tolerance and acclimatization to cold of cyanobacteria. Biochemical Journal 308: 1–8.
Murata, N., H. Wada & Z. Gombos, 1992. Modes of fatty-acid desaturation in cyanobacteria. Plant and Cell Physiology 33: 933–941.
Neilan, B. A., D. Jacobs, T. Del Dot, L. L. Blackall, P. R. Hawkins, P. T. Cox & A. E. Goodman, 1997. rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and nontoxic cyanobacteria of the genus Microcystis. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 47: 693–697.
Nichols, D. S., M. R. Miller, N. W. Davies, A. Goodchild, M. Raftery & R. Cavicchioli, 2004. Cold adaptation in the antarctic archaeon Methanococcoides burtonii involves membrane lipid unsaturation. Journal of Bacteriology 186: 8508–8515.
Pearl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2008. Blooms like it hot. Science 320: 57–58.
Pushparaj, B., A. Buccioni, R. Paperi, R. Piccardi, A. Ena, P. Carlozzi & C. Sili, 2008. Fatty acid composition of Antarctic cyanobacteria. Phycologia 47: 430–434.
Rasmussen, B., I. R. Fletcher, J. J. Brocks & R. R. Kilburn, 2008. Reassessing the first appearance of eukaryotes and cyanobacteria. Nature 455: 1101–1104.
Rastogi, R. P. & R. P. Sinha, 2009. Biotechnological and industrial significance of cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Biotechnology Advances 27: 521–539.
Saitou, N. & M. Nei, 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution 4: 406–425.
Saravanan, P., N. C. Davidson, E. B. Schmidt & P. C. Calder, 2010. Cardiovascular effects of marine omega-3 fatty acids. Lancet 375: 540–550.
Schloss, P. D. & J. Handelsman, 2005. Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Applied Environmental Microbiology 71: 1501–1506.
Schmidt, S. K., R. C. Lynch, A. J. King, D. Karki, M. S. Robeson, L. Nagy, M. W. Williams, M. S. Mitter & K. R. Freeman, 2011. Phylogeography of microbial phototrophs in the dry valleys of the high Himalayas and Antarctica. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 278: 702–708.
Shukla, E., S. S. Singh, P. Singh & A. K. Mishra, 2012. Chemotaxonomy of heterocystous cyanobacteria using FAME profiling as species markers. Protoplasma. 249: 651–661.
Singh, S. C., R. P. Sinha & D. P. Häder, 2002. Role of lipids and fatty acids in stress tolerance in cyanobacteria. Acta Protozoologica 41: 297–308.
Strunecký, O., J. Elster & J. Komárek, 2011. Taxonomic revision of the freshwater cyanobacterium Phormidium murrayi = Wilmottia murrayi. Fottea 11: 57–71.
Sushchik, N. N., G. S. Kalacheva, N. O. Zhila, M. I. Gladyshev & T. G. Volova, 2003. A temperature dependence of the intra- and extracellular fatty-acid composition of green algae and cyanobacterium. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 50: 374–380.
Tamura, K., J. Dudley, M. Nei & S. Kumar, 2007. MEGA4: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 24: 1596–1599.
Taton, A., S. Grubisic, D. Ertz, D. A. Hodgson, R. Piccardi, N. Biondi, M. R. Tredici, F. Marinelli & A. Wilmotte, 2006. Polyphasic study of Antartica cyanobacterial strains. Journal of Phycology 42: 1257–1270.
Temina, M., H. Rezankova, T. Rezanka & V. M. Dembitsky, 2007. Diversity of fatty acids of the Nostoc species and their statistical analysis. Microbioligical Research 162: 308–321.
Thomazeau, S., A. Houdan-Fourmont, A. Coute, C. Duval, A. Couloux, F. Rousseau & C. Bernard, 2010. The contribution of sub-Saharan African strains to the phylogeny of cyanobacteria: focusing on the Nostocaceae family (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Journal of Phycology 46: 564–579.
Vincent, W. F., 2000. Evolutionary origins of Antarctic microbiota: invasion, selection and endemism. Antarctic Science 12: 374–385.
Vopel, K. & I. Hawes, 2006. Photosynthetic performance of benthic microbial mats in Lake Hoare, Antarctica. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 1801–1812.
Whitton, B. A. & M. Potts (eds), 2000. The ecology of cyanobacteria [electronic resource] : their diversity in time and space. Kluwer Academic, Boston.
Wood, S. A., A. I. Selwood, A. Rueckert, P. T. Holland, J. R. Milne, K. F. Smith, B. Smits, L. F. Watts & C. S. Cary, 2007. First report of homoanatoxin-a and associated dog neurotoxicosis in New Zealand. Toxicon 50: 292–301.
Wood, S. A., M. Heath, J. Kuhajek & K. Ryan, 2010. Fine scale spatial variability of anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a production in benthic cyanobacteria; implication for monitoring and management. Journal of Applied Microbial Ecology 109: 2011–2018.
Wood, S. A., J. Kuhajek, M. de Winton & N. R. Phillips, 2012. Species composition and cyanotoxin production in periphyton mats from three lakes of varying trophic status. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 79(2): 312–326
Zakhia, F., A. D. Jungblut, A. Taton, W. F. Vincent & A. Wilmotte, 2009. Cyanobacteria in cold environments. In Margesin, R., F. Schinner, J. C. Marx & C. Gerday (eds), Psychrophiles: from biodiversity to biotechnology. Springer, New York: 121–135.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge logistic support of Antarctica New Zealand and the financial support from New Zealand Ministry of Science and Innovation through grants C01X-0306 to the National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research and the Cawthron Institute. We thank for technical assistance. MAP received funding from the Cawthron Institute Internal Investment Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Stefano Amalfitano
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martineau, E., Wood, S.A., Miller, M.R. et al. Characterisation of Antarctic cyanobacteria and comparison with New Zealand strains. Hydrobiologia 711, 139–154 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1473-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1473-1