Abstract
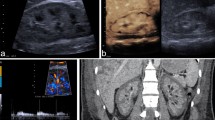
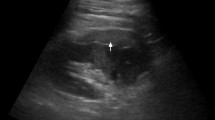
A 65-year-old male in the dilated phase of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and with persistent atrial fibrillation was admitted to our hospital because of an episode of ventricular fibrillation following an appropriate shock from an implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD). At admission, electrocardiography showed a normal sinus rhythm. He had complained of back pain 7 days after the ICD shock. Renal infarction was suspected, although computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging could not be performed because of chronic renal failure and the presence of his ICD. We, therefore, used contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with a contrast agent to evaluate his acute kidney injury. This showed the left kidney contained a wedge-shaped area that was not enhanced by the contrast agent, indicating an area of infarction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourgault M, Grimbert P, Verret C, et al. Acute renal infarction: a case series. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8:392–8.
Hazanov N, Somin M, Attali M, et al. Acute renal embolism. Forty-four cases of renal infarction in patients with atrial fibrillation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;83:292–9.
Kim SH, Park JH, Han JK, et al. Infarction of the kidney: role of contrast enhanced MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1992;16:924–8.
Antopolsky M, Simanovsky N, Stalnikowicz R, et al. Renal infarction in the ED: 10-year experience and review of the literature. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30:1055–60.
Bertolotto M, Martegani A, Aiani L, et al. Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for detecting renal infarcts proven by contrast enhanced CT. A feasibility study. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:376–83.
Setola SV, Catalano O, Sandomenico F, et al. Contrast-enhanced sonography of the kidney. Abdom Imaging. 2007;32:21–8.
Uran S, Landmark K, Normann PT, et al. A respiration-metabolism chamber system and a GC–MS method developed for studying exhalation of perfluorobutane in rats after intravenous injection of the ultrasound contrast agent Sonazoid. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005;15:746–51.
Kudo M, Hatanaka K, Maekawa K, et al. Newly developed novel ultrasound technique, defect reperfusion ultrasound imaging, using sonazoid in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2010;78:40–5.
Min JH, Lim HK, Lim S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of very-early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma inconspicuous on fusion imaging with B-mode US: value of fusion imaging with contrast-enhanced US. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2014;20:61–70.
Cokkinos D, Antypa E, Stefanidis K, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for imaging blunt abdominal trauma-indication, description of technique and imaging review. Ultrachall Med. 2012;33:60–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from the patient for whom identifying information is included in this article.
About this article
Cite this article
Miyoshi, T., Okayama, H., Hiasa, G. et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the evaluation of acute renal infarction. J Med Ultrasonics 43, 141–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0655-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0655-z