Abstract
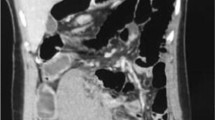
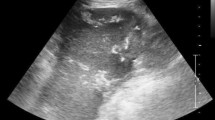
Abnormal location of the spleen, which is called wandering spleen, results from laxity or absence of the splenic pedicle. In the presence of an elongated splenic pedicle, torsion of the spleen or neighboring organs may occur, which results in acute or chronic abdominal pain. In this case report, we present imaging findings of a wandering spleen that manifested with volvulus of the pancreas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raissaki M, Prassopoulos P, Daskalogannaki M, et al. Acute abdomen due to torsion of wandering spleen: CT diagnosis. Eur Radiol. 1998;8:1409–12.
Gorsi U, Bhatia A, Gupta R, et al. Pancreatic volvulus with wandering spleen and gastric volvulus: an unusual triad for acute abdomen in a surgical emergency. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:195–8.
Sanchez R, Lobert P, Herman R, et al. Wandering spleen causing gastric outlet obstruction and pancreatitis. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40:89–91.
Smulewicz JJ, Clemett AR. Torsion of the wandering spleen. Am J Dig Dis. 1975;20:274–9.
Gilman RS, Thomas RL. Wandering spleen presenting as acute pancreatitis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;101:1100–2.
Lebron R, Self M, Mangram A, et al. Wandering spleen presenting as recurrent pancreatitis. JSLS. 2008;12:310–3.
Choudhary R, Ghazanfari A. Wandering spleen with pancreatic volvulus and colonic obstruction in an elderly patient. Int J Case Rep Imag. 2012;3:15–8.
Shirani S. Torsion of wandering spleen and tail of pancreas. Arch Iran Med. 2002;5:124–5.
Sheflin JR, Lee CM, Kretchmar KA. Torsion of wandering spleen and distal pancreas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;142:100–1.
Conflict of interest
Ali Devrim Karaosmanoglu, Mehmet Ruhi Onur, and Musturay Karcaaltıncaba declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical considerations
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Karaosmanoglu, A.D., Onur, M.R. & Karcaaltıncaba, M. Wandering spleen with volvulus of pancreas. J Med Ultrasonics 42, 413–416 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0622-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0622-8