Abstract
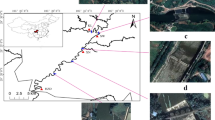
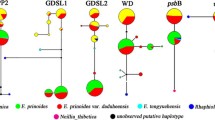
Inter-specific hybrid zones for Hylobates gibbons are known in Southeast Asia. Among these, one hybrid zone between Hylobates lar and H. pileatus is located in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand. To find molecular evidence for the natural hybridization of the gibbons in this region, we studied mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of 68 gibbons of the H. lar phenotype living adjacent to the hybrid zone. Nucleotide sequencing of a fragment of mtDNA spanning hyper variable segment I showed that nine gibbons had an mtDNA haplotype of H. pileatus, and that seven of these nine gibbons belonged to a single maternal lineage over three generations. It is thus confirmed that introgression between H. lar and H. pileatus exists and the initial hybridization took place ages ago.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andayani N, Morales JC, Forstner MRJ, Supriatna J, Melnick DJ (2001) Genetic variability in mtDNA of the silvery gibbon: implications for the conservation of a critically endangered species. Conserv Biol 15:770–775
Brandon-Jones D, Eudey AA, Geissmann T, Groves CP, Melnick DJ, Morales JC, Shekelle M, Stewart CB (2004) Asian primate classification. Int J Primatol 25:97–164
Brockelman WY (1978) Preliminary report on relations between the gibbons Hylobates lar and H. pileatus in Thailand. In: Chivers DJ, Joysey KA (eds) Recent advances in primatology, vol 3, Evolution. Academic Press, London, pp 315–318
Brockelman WY, Gittins SP (1984) Natural hybridization in the Hylobates lar species group: implications for speciation in gibbons. In: Preuschoft H, Chivers DJ, Brockelman WY, Creel N (eds) The lesser apes: evolutionary and behavioural biology. Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, pp 498–532
Brockelman WY, Schilling D (1984) Inheritance of stereotyped gibbon calls. Nature 312:634–636
Brockelman WY, Reichard U, Treesucon U, Raemaekers JJ (1998) Dispersal, pair formation and social structure in gibbons (Hylobates lar). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 42:329–339
Chan Y-C, Roos C, Inoue-Murayama M, Inoue E, Shih C-C, Pei KJ-C, Vigilant L (2010) Mitochondrial genome sequences effectively reveal the phylogeny of Hylobates gibbons. PLoS ONE 5:e14419
Geissmann T (1991) Sympatry between white-handed gibbons (Hylobates lar) and pileated gibbons (H. pileatus) in Southeastern Thailand. Primates 32:357–363
Kays R, Curtis A, Kirchman JJ (2010) Rapid adaptive evolution of northeastern coyotes via hybridization with wolves. Biol Lett 6:89–93
Kim SK, Carbone L, Becquet C, Mootnick AR, Li DJ, de Jong PJ, Wall JD (2011) Patterns of genetic variation within and between gibbon species. Mol Biol Evol 28:2211–2218
Marshall JT, Brockelman WY (1986) Pelage of hybrid gibbons (Hylobates lar × H. pileatus) observed in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand. Nat Hist Bull Siam Soc 34:145–157
Marshall J, Sugardjito J (1986) Gibbon systematics. In: Swindler DR, Erwin J (eds) Comparative primate biology, vol 1., Systematics, Evolution, and Anatomy. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 137–185
Marshall JT, Ross BA, Chantharojvong S (1972) The species of gibbons in Thailand. J Mammal 53:479–486
Matsudaira K, Ishida T (2010) Phylogenetic relationships and divergence dates of the whole mitochondrial genome sequences among three gibbon genera. Mol Phylogenet Evol 55:454–459
Mavárez J, Salazar CA, Bermingham E, Salcedo C, Jiggins CD, Linares M (2006) Speciation by hybridization in Heliconius butterflies. Nature 441:868–871
Nsubuga AM, Robbins MM, Roeder AD, Morin PA, Boesch C, Vigilant L (2004) Factors affecting the amount of genomic DNA extracted from ape faeces and the identification of an improved sample storage method. Mol Ecol 13:2089–2094
Reichard UH (2009) The social organization and mating system of Khao Yai white-handed gibbons: 1992–2006. In: Lappan S, Whittaker D (eds) The Gibbons: the new perspectives on small ape socioecology and population biology. Springer, New York, pp 347–384
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Suwanvecho U, Brockelman WY (2012) Interspecific territoriality in gibbons (Hylobates lar and H. pileatus) and its effects on the dynamics of interspecies contact zones. Primates 53:97–108
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thinh VN, Mootnick AR, Geissmann T, Li M, Ziegler T, Agil M, Moisson P, Nadler T, Walter L, Roos C (2010) Mitochondrial evidence for multiple radiations in the evolutionary history of small apes. BMC Evol Biol 10:74
Thompson DJ, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Whittaker DJ, Morales JC, Melnick DJ (2007) Resolution of the Hylobates phylogeny: congruence of mitochondrial D-loop sequences with molecular, behavioral, and morphological data sets. Mol Phylogenet Evol 45:620–628
Zinner D, Arnold ML, Roos C (2011) The strange blood: natural hybridization in primates. Evol Anthropol 20:96–103
Acknowledgments
We thank the Superintendent of Khao Yai National Park, Manoch Ganpanakngan, our field assistants (Chalaem Sagnate and Surasack Homros), and the Director of CITES Management Authority of Thailand, Watana Vetayaprasit. Kind help of Suraphong Chaweepak, Jacqueline Prime, Bunhoom Insumran, and Danai Tiwawech is also appreciated. We would like to express our gratitude to the National Research Council of Thailand, the Department of National Parks, Wildlife, and Plant Conservation, and Khao Yai National Park. This study was partly supported by the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from the Japan Science Society, the Academic Research Grant Program (International) from the University of Tokyo, the Global COE Program (Integrative Life Sciences Based on the Study of Biosignaling Mechanism), and KAKENHI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsudaira, K., Reichard, U.H., Malaivijitnond, S. et al. Molecular evidence for the introgression between Hylobates lar and H. pileatus in the wild. Primates 54, 33–37 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-012-0323-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-012-0323-5