Abstract
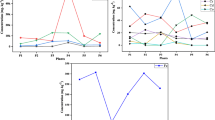
This is the first report on Pb in medicinal herbs from Jordan. Medicinal herbs may present a health risk due to the presence of toxic metals. Seventy-nine dry medicinal plant samples were collected from herbalist shops in Jordan. The plants were digested with acids and analyzed for total Pb concentration using atomic absorption spectrometry. Mean Pb concentration was 15.9 μg/g on a dry weight basis. Our results show that Pb concentrations in Jordan medicinal plants are higher than published data in other countries. The highest level of 33.4 μg Pb/g was determined in Inula viscosa, and the lowest level of 3.0 μg Pb/g was found in Nigella sativa. Calculated daily intakes of Pb of most analyzed herbs were high; most of them are higher than recommended values by the world health organization (WHO). Fortunately, the herbs that contain the highest Pb levels are the less commonly used medicinal herbs in Jordan. The mean Pb levels in the most commonly, commonly and less commonly used herbs in Jordan are 13.9, 13.1 and 16.9 μg Pb/g, respectively. The average dietary intake of Pb through a mixture of these medicinal herbs consumption, assuming 5.0 g herbs is consumed daily, is 79.5 μg Pb/day, which is higher than the maximum daily limit allowed by WHO. We conclude that most of the medicinal plants consumed in Jordan contain significant amount of Pb, and therefore, people of Jordan should not consume large amounts of these herbs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Sattar S, Seetharami Reddy B, Koteswara Rao V, Ramnarayana K, Naga Raju GJ, Bhuloka Reddy S, Phanisree T, Madhusudhana Rao PV (2012) Estimation of trace elements in some medicinal plants used in anti-cancer drugs by PIXE. X-Ray Spectrom 41:111–116
Abou-Arab AAK, Abou Donia MA (2000) Heavy metals in Egyptian Spices and medicinal plants and the effect of processing on their levels. J Agric Food Chem 48:2300–2304
Abou-Arab AAK, Kawther MS, El Tantawy ME, Badeaa IR, Khayria N (1999) Quantity estimation of some contaminants in commonly used medicinal plants in Egyptian market. Food Chem 67:357–363
Abugassa IO, Bashir AT, Doubali K, Etwir RH, Abu-Enawel M, Abugassa SO (2008) Characterization of trace elements in medicinal herbs by instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:559–563
Abu-Irmaileh BE, Afifi F (2000) Treatment with medicinal plants in Jordan. Dirasat 27:53–74 (in Arabic with english abstract)
Abu-Irmaileh BE, Afifi F (2003) Herbal medicine in Jordan with special emphasis on commonly used herbs. J Ethnopharmacol 89:193–197
Afifi F, Abu-Irmaileh BE (2000) Herbal medicine in Jordan with special emphasis on less commonly used medicinal herbs. J Ethnopharmacol 72:101–110
ATSDR (2007). Toxicological Profile for Lead. Atlanta, US Department Of Health and Humans Services 1–413
Basgel S, Erdemoglu SB (2006) Determination of mineral and trace elements in some medicinal herbs and their infusions consumed in Turkey. Sci Total Environ 359:82–89
Bergdahl IA (1988) Lead-binding proteins—a way to understand lead toxicity? Anal Mag 26:M81–M85
Chizzola R, Michitsch H, Franz C (2003) Monitoring of metallic micronutrients and heavy metals in herbs, spices and medicinal plants from Austria. Eur Food Res Technol 216:407–411
El-Rjoob AO, Massadeh AM, Omari MN (2008) Evaluation of Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd, Ni and Fe levels in Rosmarinus officinalis labaiatae (Rosemary) medicinal plant and soils in selected zones in Jordan. Environ Monit Assess 140:61–68
Gallaher RN, Gallaher K, Marshall AJ, Marshall AC (2006) Mineral analysis of ten types of commercially available tea. J Food Compos Anal 19:S53–S57
Garge AN, Kumar A, Nair AGC, Reddy AVR (2007) Analysis of some indian medicinal herbs by INAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:611–619
Gomes MR, Cerutti S, Sombra LL, Silva MF, Martinez LD (2007) Determination of heavy metals for the quality control in argentinian herbal medicines by ETAAS and ICP-OES. Food Chem Toxicol 45:1060–1064
Hamilton AC (2004) Medicinal plants, conservation and livelihoods. Biodivers Conserv 13:1477–1517
Herrador MA, Gonzalez AG (2001) Pattern recognition procedures for differentiation of Green, Black and Oolong teas according to their metal content from inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 53:1249–1257
Hiçsönmez Ü, Ereeş FS, Özdemir C, Özdemir A, Çam S (2009) Determination of major and minor elements in the Malva sylvestris L. from Turkey Using ICP-OES Techniques. Biol Trace Elem Res 128:248–257
HMRC (2003) Heavy metal handbook: a guide for healthcare practitioners. Vashon Press, Washington, USA, pp 1–10
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Jyothi NVV, Chandra mouli P, Reddy S, Reddy J (2003) Determination of zinc, copper, lead and cadmium in some medicinally important leaves by differential pulse anodic stripping analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 17:79–83
Kalny P, Fijalek Z, Daszczuk A, Ostapczuk P (2007) Determination of selected microelements in polish herbs and their infusions. Sci Total Environ 381:99–104
Lozak A, Soltyk K, Ostapczuk P, Fijalek Z (2002) Determination of selected trace elements in herbs and their infusions. Sci Total Environ 289:33–40
Mamania MCVL, Aleixom M, Abreub MF, Ratha S (2005) Simultaneous determination of cadmium and lead in medicinal plants by anodic stripping voltammetry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 37:709–713
Meena AK, Bansal P, Kumar S, Rao MM, Garg VK (2010) Estimation of heavy metals in commonly used medicinal plants: a market basket survey. Environ Monit Assess 170:657–660
Mitchell-Heggs C, Conway M, Cassar J (1990) Herbalmedicine as a cause of combined lead and arsenic poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol 9:195–196
Moore C, Adler R (2000) Herbal vitamins: lead toxicity and developmental delay. Pediatrics 106:600–602
Needleman HL, Bellinger D (1991) The health effects of low level exposure to lead. Annu Rev Public Health 12:111–140
Nomita Devia K, Nandakumar Sarma H (2009) Elemental content of some anti-diabetic medicinal plants using PIXE analysis. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 15:334–341
Pais I, Benton Jones JJ (eds) (1997) The handbook of trace elements. St. Lucie Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Pakade YB, Kumari A, Surjeet Singh S, Sharma R, Tewary DK (2011) Metals in herbal drugs from Himalayan Region. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:133–136
Pei S (2001) Ethnobotanical approaches of traditional medicine studies: some experiences from Asia. Pharmaceutical Bot 39:74–79
Queralt I, Ovejero M, Caravalho ML, Marques AF, Llabres JM (2005) Quantitative determination of essential and trace element content of medicinal plants and their infusions by XRF and ICP techniques. X-ray Specrom 34:213–217
Rai V, Kakkar P, Misra C, Ojha SK, Srivastava N, Mehrotra S (2007) Metals and organochlorine pesticide residues in some Herbal Ayurvedic formulations. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:269–272
Scancar J, Stibilj V, Milacic R (2004) Determination of aluminum in Slovenian foodstuffs and its leachability from aluminum-cookware. Food Chem 85:151–157
Sharma RP, Shupe JL (1977) Lead, cadmium and arsenic residues in animal tissues in relation to their surrounding habitat. Sci Total Environ 7:53–62
Smolinske SC (2005) Herbal product contamination and toxicity. J Pharm Pract 18(3):189–208
Sucharova J, Suchara I (2006) Determination of 36 elements in plant reference materials with different Si contents by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: comparison of microwave digestions assisted by three types of digestion mixtures. Anal Chim Acta 576:163–176
Wong YC, Sin DWM, Yip YC, Valiente L, Toervenyi A, Wang J, Labarraque G, Gupta P, Soni D, Surmadi HE, Yafa C, Cankur O, Uysal E, Turk G, Huertas R (2009) International comparison of the determination of cadmium and lead in herb: the Comite′ Consultatif pour la Quantite′ de Matie`re (CCQM) pilot study CCQM-P97. Accred Qual Assur 14:151–158
World Health Organization (1998). Quality control methods for medicinal plant materials, (Geneva:WHO)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alomary, A., Jamal, E.E., Al-Momani, I. et al. Pb in medicinal plants from Jordan. Environ Chem Lett 11, 55–63 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-012-0378-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-012-0378-y