Abstract.
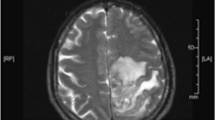
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) usually follows a viral infection or an immunization and is thought to be an immunomediated disease. We describe a patient with ADEM after multiple yellow jacket bee stings. The patient recovered after treatment with a high dose of methylprednisolone. Although the pathologic mechanism exact remains unclear, potential cross-reactivity between bee toxins and the central nervous system myelin could induce demyelination. ADEM should be considered a rare complication of bee stings.
Similar content being viewed by others

Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 April 2002 / Accepted in revised form: 5 December 2002
Correspondence to C. Boz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boz, C., Velioglu, S. & Ozmenoglu, M. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after bee sting. Neurol Sci 23, 313–315 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720300007
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720300007