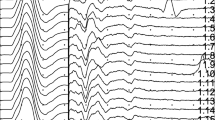
Abstract
A-wave is a late motor response that maintains the same characteristics of latency, amplitude and shape with every electrical stimuli at a proper given intensity. The presence of A-waves was reported both in chronic (CIDP) and acute (AIDP) forms of inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. It is attributed to the effect of either sprouting phenomena or ephaptic/ectopic discharge. In the first condition it could be a sign of functional recovery, while in the second it could represent an early indicator of demyelination. Aims of our research were to investigate retrospectively the presence of the A-waves, establishing whether its frequency is more common in CIDP or AIDP. Data from 77 patients, 57 male and 20 female, mean age 60.7 years (SD 15.4), were recovered from clinical records and their neurophysiological tests retrieved for reanalysis. Our results seem to indicate that A-waves can represent an early sign of acute pathology of peripheral nervous system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff C, Stalberg E, Falck B, Puksa L (1996) Significance of A-waves recorded in routine motor nerve conduction studies. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 101:528–533
Bischoff C (2002) Neurography: late responses. Muscle Nerve Suppl 11:S59–S65
Rowin J, Meriggioli MN (2000) Electrodiagnostic significance of supramaximally stimulated A-waves. Muscle Nerve 23:1117–1120
Causey G, Hoffman H (1955) Axon sprouting partially deneurotized nerves. Brain 78:661–668
Magistris MR, Roth G (1992) Motor axon reflex and indirect double discharge: ephaptic transmission? A reappraisal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:124–130
Sadjadpour K (1975) Postfacial palsy phenomena: faulty nerve regeneration or ephaptic transmission? Brain Res 95:403–406
Seltzer Z, Devor M (1979) Ephaptic transmission in chronically damaged peripheral nerves. Neurology 29:1061–1064
Colachis SC, Pease WS, Johnson EW (1992) Polyphasic motor unit action potentials in early radiculopathy: their presence and ephaptic transmission as an hypothesis. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:27–33
Havton LA, Hotson JR, Kellerth JO (2001) Partial peripheral motor nerve lesions induce changes in the conduction properties of remaining intact motoneurons. Muscle Nerve 24:662–666
Howe JF, Calvin WH, Loeser JD (1976) Impulses reflected from dorsal root ganglia and from focal nerve injuries. Brain Res 116:139–144
Rajabally YA, Jacob S (2006) Proximal nerve conduction studies in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2079–2084
Vucic S, Black K, Chong PS, Cros D (2007) Multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction block: distribution of demyelination and axonal degeneration. Clin Neurophysiol 118:124–130
Alexandrov AS, Christova LG, Ishpekova BA (2001) A-waves in patients with novel hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy Lom. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Bulg 26:55–58
Puksa L, Stalberg E, Falck B (2003) Occurrence of A-waves in F-wave studies of healthy nerves. Muscle Nerve 28:626–629
Roth G, Magistris MR (1999) Indirect discharges as an early nerve conduction abnormality in the Guillain–Barre syndrome. Eur Neurol 42:83–89
Fullerton PM, Gilliatt RW (1965) Axon reflexes in human motor nerve fibres. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 28:1–11
Albers JW, Kelly JJ Jr (1989) Acquired inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies: clinical and electrodiagnostic features. Muscle Nerve 12:435–451
Kornhuber ME, Bischoff C, Mentrup H, Conrad B (1999) Multiple A waves in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Muscle Nerve 22:394–399
Gordon PH, Wilbourn AJ (2001) Early electrodiagnostic findings in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Arch Neurol 58:913–917
Magda P, Latov N, Brannagan TH et al (2003) Comparison of electrodiagnostic abnormalities and criteria in a cohort of patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Arch Neurol 60:1755–1759
Van den Bergh PY, Pieret F (2004) Electrodiagnostic criteria for acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 29:565–574
Rajabally YA, Jacob S, Hbahbih M (2005) Optimizing the use of electrophysiology in the diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a study of 20 cases. J Peripher Nerv Syst 10:282–292
Saperstein DS, Katz JS, Amato AA, Barohn RJ (2001) Clinical spectrum of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Muscle Nerve 24:311–324
Sander HW, Latov N (2003) Research criteria for defining patients with CIDP. Neurology 60:S8–S15
Tankisi H, Pugdahl K, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A et al (2005) Pathophysiology inferred from electrodiagnostic nerve tests and classification of polyneuropathies. Suggested guidelines. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1571–1580
Hadden RD, Cornblath DR, Hughes RA et al (1998) Electrophysiological classification of Guillain–Barre syndrome: clinical associations and outcome. Plasma Exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain–Barre Syndrome Trial Group. Ann Neurol 44:780–788
Daube JR, Rubin DI (2009) Clinical neurophysiology, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Uncini A, Di Muzio A, Sabatelli M et al (1993) Sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic criteria for conduction block in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:161–169
Roth G (1993) Myo-axonal ephaptic responses and their F waves in case of chronic denervation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:252–260
Asbury AK, Cornblath DR (1990) Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain–Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol 27(Suppl):S21–S24
Deepak G, Muraleedharan N, Baheti NN, Sarma SP, Abraham K (2008) Electrodiagnostic and clinical aspects of Guillain–Barre syndrome: an analysis of 142 cases. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 10:42–51
Haq RU, Fries TJ, Pendlebury WW et al (2000) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a study of proposed electrodiagnostic and histologic criteria. Arch Neurol 57:1745–1750
Thaisetthawatkul P, Logigian EL, Herrmann DN (2002) Dispersion of the distal compound muscle action potential as a diagnostic criterion for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 59:1526–1532
Lewis RA (2007) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurol Clin 25:71–87
Cleland JC, Malik K, Thaisetthawatkul P, Herrmann DN, Logigian EL (2006) Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: contribution of a dispersed distal compound muscle action potential to electrodiagnosis. Muscle Nerve 33:771–777
Attal N, Bouhassira D (1999) Mechanisms of pain in peripheral neuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 173:12–24 (discussion 48–52)
Caselli A, Spallone V, Marfia GA et al (2006) Validation of the nerve axon reflex for the assessment of small nerve fibre dysfunction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:927–932
Gozke E, Celebi D, Dortcan N et al (2003) A-waves and electrophysiologically established diagnoses. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 43:33–35
Ito J (2001) Analysis of unusual late responses of peripheral nerves. Rinsho Byori 49:71–76
Magistris MR, Roth G (1992) Motor axon reflex and indirect double discharge: ephaptic transmission? A reappraisal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:124–130
Tomasulo RA (1982) Aberrant conduction in human peripheral nerve: ephaptic transmission? Neurology 32:712–719
Baba M, Ozaki I (1995) Electrodiagnostic features in inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 35:1365–1367
Hiraga A, Kuwabara S, Ogawara K et al (2005) Patterns and serial changes in electrodiagnostic abnormalities of axonal Guillain–Barre syndrome. Neurology 64:856–860
Rasminsky M (1980) Ephaptic transmission between single nerve fibres in the spinal nerve roots of dystrophic mice. J Physiol 305:151–169
Weber F (1997) Conduction block and abnormal temporal dispersion—diagnostic criteria. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 37:305–309
Viala K, Renie L, Maisonobe T et al (2004) Follow-up study and response to treatment in 23 patients with Lewis–Sumner syndrome. Brain 127:2010–2017
Oh SJ, Claussen GC, Kim DS (1997) Motor and sensory demyelinating mononeuropathy multiplex (multifocal motor and sensory demyelinating neuropathy): a separate entity or a variant of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy? J Peripher Nerv Syst 2:362–369
Gorson KC, Ropper AH, Weinberg DH (1999) Upper limb predominant, multifocal chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 22:758–765
Barriere G, Leblond H, Provencher J, Rossignol S (2008) Prominent role of the spinal central pattern generator in the recovery of locomotion after partial spinal cord injuries. J Neurosci 28:3976–3987
Al-Shekhlee A, Hachwi RN, Preston DC, Katirji B (2005) New criteria for early electrodiagnosis of acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 32:66–72
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the neurologists of Neuroscience Department, Unit of Neurology, at Pisa University Medical School, who referred their patients and permitted us to examine them electromyographically. We gratefully acknowledge the participation of all subjects, as well as Mr. A. Bruni and Ms. P. Angiolini for their excellent technical assistance. The paper was supported in part by the Italian operating and development MIUR PRIN grant year 2006, n. 2006062332_002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sartucci, F., Bocci, T., Borghetti, D. et al. Further insight on A-wave in acute and chronic demyelinating neuropathies. Neurol Sci 31, 609–616 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0354-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0354-x