Abstract
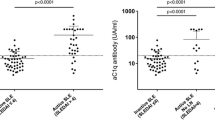
The aim of this study is to investigate the association of serum anti-C1q antibody levels with renal pathological characteristics in SLE patients with lupus nephritis. Fifty-two patients with biopsy-proven lupus nephritis were enrolled. Serum anti-C1q levels (units per milliliter) were measured before renal biopsy using ELISA kit. A cross-sectional study analyzed the association of anti-C1q antibody levels with SLE global activity, nephritic activity, and renal histopathology. Thirty-nine of 52 patients (75 %) were positive for anti-C1q antibody. Anti-C1q antibody levels were positively correlated with the values for the SLE Disease Activity Index (r = 0.628, p < 0.001), anti-nucleosome (r = 0.591, p < 0.001), and anti-dsDNA antibody (r = 0.507, p < 0.001), but negatively correlated to serum C3 (r = −0.626, p < 0.001) and C4 (r = −0.57, p < 0.001). The prevalence of anti-C1q in patients with proliferative LN (class III + class IV) was higher than those with mesangial LN (class II), but there is no statistical significance. Among different ISN/RPS classification, serum anti-C1q antibody level was highest in patients with class IV, followed by class III. The concentration of anti-C1q in patients with class IV was higher than those in class II [50.00 (23.00, 97.70) vs 20.25 (7.16, 54.78) U/ml, p<0.05]. The levels of anti-C1q antibody were positively correlated with renal active indices (r = 0.59, p < 0.001) while negatively correlated with chronic indices (r = −0.326, p < 0.05). Moreover, anti-C1q antibody was found to be positively associated with glomerular C1q deposition. These findings indicate that serum anti-C1q antibody is a valuable noninvasive biological marker for prediction of renal histopathology in lupus nephritis. Low or negative anti-C1q antibody titers might influence therapeutic decisions in SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isenberg DA, Ravirajan CT, Rahman A, Kalsi J (1997) The role of antibodies to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus—a review and introduction to an international workshop on DNA antibodies held in London, May 1996. Lupus 6(3):290–304
Hahn BH (1998) Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med 338(19):1359–1368
Siegert CE, Daha MR, Tseng CM, Coremans IE, van Es LA, Breedveld FC (1993) Predictive value of IgG autoantibodies against C1q for nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 52(12):851–856
Horvath L, Czirjak L, Fekete B, Jakab L, Pozsonyi T, Kalabay L, Romics L, Miklos K, Varga L, Prohaszka Z, Szakacs A, Nagy E, Daha MR, Fust G (2001) High levels of antibodies against Clq are associated with disease activity and nephritis but not with other organ manifestations in SLE patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19(6):667–672
Marto N, Bertolaccini ML, Calabuig E, Hughes GR, Khamashta MA (2005) Anti-C1q antibodies in nephritis: correlation between titres and renal disease activity and positive predictive value in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 64(3):444–448
Fang QY, Yu F, Tan Y, Xu LX, Wu LH, Liu G, Shao FM, Zhao MH (2009) Anti-C1q antibodies and IgG subclass distribution in sera from Chinese patients with lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(1):172–178
Zhang CQ, Ren L, Gao F, Mu FY, You YQ, Liu YH (2011) Anti-C1q antibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity and lupus nephritis in northeast of China. Clin Rheumatol 30(7):967–973
Gunnarsson I, Sundelin B, Heimburger M, Forslid J, van Vollenhoven R, Lundberg I, Jacobson SH (2002) Repeated renal biopsy in proliferative lupus nephritis—predictive role of serum C1q and albuminuria. J Rheumatol 29(4):693–699
Moroni G, Trendelenburg M, Del Papa N, Quaglini S, Raschi E, Panzeri P, Testoni C, Tincani A, Banfi G, Balestrieri G, Schifferli JA, Meroni PL, Ponticelli C (2001) Anti-C1q antibodies may help in diagnosing a renal flare in lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 37(3):490–498
Trendelenburg M, Lopez-Trascasa M, Potlukova E, Moll S, Regenass S, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Martinez-Ara J, Jancova E, Picazo ML, Honsova E, Tesar V, Sadallah S, Schifferli J (2006) High prevalence of anti-C1q antibodies in biopsy-proven active lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21(11):3115–3121
Meyer OC, Nicaise-Roland P, Cadoudal N, Grootenboer-Mignot S, Palazzo E, Hayem G, Dieude P, Chollet-Martin S (2009) Anti-C1q antibodies antedate patent active glomerulonephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 11(3):R87
Cai X, Yang X, Lian F, Lin X, Liang M, Li J, Chen X, Liang L, Qin S, Fu J (2010) Correlation between serum anti-C1q antibody levels and renal pathological characteristics and prognostic significance of anti-C1q antibody in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 37(4):759–765
Matrat A, Veysseyre-Balter C, Trolliet P, Villar E, Dijoud F, Bienvenu J, Fabien N (2011) Simultaneous detection of anti-C1q and anti-double stranded DNA autoantibodies in lupus nephritis: predictive value for renal flares. Lupus 20(1):28–34
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35(6):630–640
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijn JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennette JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65(2):521–530
Austin HA 3rd, Muenz LR, Joyce KM, Antonovych TT, Balow JE (1984) Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: identification of specific pathologic features affecting renal outcome. Kidney Int 25(4):689–695
Trendelenburg M (2005) Antibodies against C1q in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 27(3):276–285
Walport MJ (2001) Complement. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 344(14):1058–1066
Walport MJ (2001) Complement. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med 344(15):1140–1144
Sinico RA, Rimoldi L, Radice A, Bianchi L, Gallelli B, Moroni G (2009) Anti-C1q autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173:47–51
Katsumata Y, Miyake K, Kawaguchi Y, Okamoto Y, Kawamoto M, Gono T, Baba S, Hara M, Yamanaka H (2011) Anti-C1q antibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus global activity but not specifically with nephritis: a controlled study of 126 consecutive patients. Arthritis Rheum 63(8):2436–2444
Ronnelid J, Huang YH, Norrlander T, Rogberg S, Nilsson B, Gustafsson R, Klareskog L (1994) Short-term kinetics of the humoral anti-C1q response in SLE using the ELISPOT method: fast decline in production in response to steroids. Scand J Immunol 40(2):243–250
Trouw LA, Daha MR (2005) Role of anti-C1q autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 5(2):243–251
Trouw LA, Seelen MA, Duijs JM, Benediktsson H, Van Kooten C, Daha MR (2003) Glomerular deposition of C1q and anti-C1q antibodies in mice following injection of antimouse C1q antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol 132(1):32–39
Trouw LA, Groeneveld TW, Seelen MA, Duijs JM, Bajema IM, Prins FA, Kishore U, Salant DJ, Verbeek JS, van Kooten C, Daha MR (2004) Anti-C1q autoantibodies deposit in glomeruli but are only pathogenic in combination with glomerular C1q-containing immune complexes. J Clin Invest 114(5):679–688
Mannik M, Wener MH (1997) Deposition of antibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q in renal glomeruli of patients with proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum 40(8):1504–1511
Chen PC, Wang CR, Liu MF, Chen FF, Liang CC (2002) Correlation between the renal C1q deposition and serum anti-C1q antibody: a potential role of anti-C1q antibody in lupus nephritis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 20(4):223–227
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by a grant from Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (no. 090413129) and Educational Department of Anhui Province, China (KJ2009B072).
We appreciate Dr. Hai-Yan Weng, a senior pathologist in our hospital, for her excellent work in the evaluation of renal biopsy specimens.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wang, GS., Wang, GH. et al. Anti-C1q antibody is a valuable biological marker for prediction of renal pathological characteristics in lupus nephritis. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1323–1329 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2017-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2017-1