Abstract
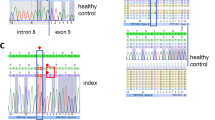
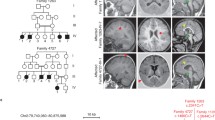
Rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton is controlled by RhoGTPases which are activated by RhoGEFs. We identified homozygosity for Arg204Trp mutation in the Rho guanidine exchange factor (RhoGEF) PLEKHG2 gene in five patients with profound mental retardation, dystonia, postnatal microcephaly, and distinct neuroimaging pattern. The activity of the mutant PLEKHG2 was significantly decreased, both in basal state and when Gβγ- or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-stimulated. SDF1a-stimulated actin polymerization was significantly impaired in patient cells, and this abnormality was duplicated in control cells when PLEKHG2 expression was downregulated. These results underscore the role of PLEKHG2 in actin polymerization and delineate the clinical and radiological findings in PLEKHG2 deficiency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2005) RhoGTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:247–269
Seabra MC (1998) Membrane association and targeting of prenylated Ras-like GTPases. Cell Signal 10:167–172
Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J (2005) GEF means go: turning on Rho GTPases with guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:167–180
Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ (2008) Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:690–701
Raftopoulou M, Hall A (2004) Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol 265:23–32
Ridley AJ (2001) Rho GTPases and cell migration. J Cell Sci 114:2713–2722
Gillis D, Krishnamohan A, Yaacov B, Shaag A, Jackman JE, Elpeleg O (2014) TRMT10A dysfunction is associated with abnormalities in glucose homeostasis, short stature and microcephaly. J Med Genet 51:581–586
Runne C, Chen S (2013) PLEKHG2 promotes heterotrimeric G protein betagamma-stimulated lymphocyte migration via Rac and Cdc42 activation and actin polymerization. Mol Cell Biol 33:4294–4307
Himmel KL, Bi F, Shen H, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Zheng Y, Largaespada DA (2002) Activation of clg, a novel dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factor gene, by proviral insertion at evi24, a common integration site in B cell and myeloid leukemias. J Biol Chem 277:13463–13472
Zheng Y (2001) Dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Trends Biochem Sci 26:724–732
Skowronek KR, Guo F, Zheng Y, Nassar N (2004) The C-terminal basic tail of RhoG assists the guanine nucleotide exchange factor trio in binding to phospholipids. J Biol Chem 279:37895–37907
Nakayama AY, Luo L (2000) Intracellular signaling pathways that regulate dendritic spine morphogenesis. Hippocampus 10:582–586
von Bohlen Und Halbach O (2010) Dendritic spine abnormalities in mental retardation. Cell Tissue Res 342:317–323
Ba W, van der Raadt J, Nadif KN (2013) Rho GTPase signaling at the synapse: implications for intellectual disability. Exp Cell Res 319:2368–2374
Ramakers GJ, Wolfer D, Rosenberger G, Kuchenbecker K, Kreienkamp HJ, Prange-Kiel J, Rune G, Richter K, Langnaese K, Masneuf S, Bösl MR, Fischer KD, Krugers HJ, Lipp HP, van Galen E, Kutsche K (2012) Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in the αPix/Arhgef6 mouse model of X-linked intellectual disability is paralleled by impaired structural and synaptic plasticity and cognitive deficits. Hum Mol Genet 21:268–286
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Droppelmann CA, Campos-Melo D, Volkening K, Strong MJ (2014) The emerging role of guanine nucleotide exchange factors in ALS and other neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 8:282
Acknowledgments
The clinical and molecular parts were performed within the frame of the Germany, Israel, and Palestine Trilateral research grant 443 ISR-113/228/0-1 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft on Inborn Leukoencephalopathies.
Authors’ contribution
SE, HW, SC, and OE conceived and designed the experiments. HW, BY, and YC performed the experiments. HW, BY, SC, and OE analyzed the data. SE, JG, SC, and OE wrote the paper, SE, TD, JG, and OA undertook patient management, collection of samples, and delineation of the phenotype.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Simon Edvardson and Talya Dor share equal contribution
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Figure 1
the structure of the PLEKHG2 DH-PH domains. Based on the crystal coordinates of trio DH-PH domain [13], the molecular structure of the PLEKHG2 DH-PH domains was constructed using the UCSF chimera package [16]. A-B, the location of R204 is shown in the space-filling (A) and ribbon (B) models of the PLEKHG2 DH-PH domains. C, the ribbon model of the trio DH-PH domains in complex with Rac. The location of trio L1398 equivalent to PLEKHG2 R204 is indicated. (GIF 228 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edvardson, S., Wang, H., Dor, T. et al. Microcephaly-dystonia due to mutated PLEKHG2 with impaired actin polymerization. Neurogenetics 17, 25–30 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-015-0464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-015-0464-y