Abstract
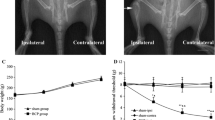
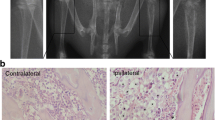
d-Amino acid oxidase (DAAO), a FAD-dependent peroxisomal flavoenzyme that catalyzes oxidation of d-amino acids to hydrogen peroxide, is distributed in the spinal cord almost exclusively expressed within astrocytes. The present study aims to explore potential contributions of spinal DAAO to the development of bone cancer pain and morphine tolerance to analgesia. Tibia inoculation of carcinoma cells produced mechanical allodynia (but not heat hyperalgesia), in synchronous with induction of DAAO expression and DAAO enzymatic activity, as well as activation of spinal astrocytes marked by GFAP. Subcutaneous and intrathecal injection of the specific DAAO inhibitor CBIO (5-chloro-benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol) blocked mechanical allodynia in a dose- and time-dependent manner in tumor-bearing rats, with maximum inhibition of 40–50 %. Multi-daily intrathecal injections of the DAAO gene silencer siRNA/DAAO also yielded anti-allodynic effects by approximately 40 % and the analgesia remained for at least 6 days. Subcutaneous injection of CBIO suppressed the production of spinal hydrogen peroxide and GFAP expression. 7-Day multiple bi-daily injections of CBIO produced anti-allodynia without inducing self-tolerance to analgesia or cross-tolerance to morphine, and concurrent injections of CBIO with morphine produced apparent additive anti-allodynia and completely prevented morphine tolerance in behaviors and spinal expression of μ-opioid receptors. Our results provide the first evidence that spinal DAAO contributes to the development of morphine tolerance to analgesia and bone cancer pain accounting for 40–50 % pain status, probably via production of hydrogen peroxide leading to activation of astrocytes. The unique characterizations of DAAO inhibitors make them a potential for the treatment of cancer pain when they are administered alone or in combination with morphine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angermüller S, Islinger M, Völkl A (2009) Peroxisomes and reactive oxygen species, a lasting challenge. Histochem Cell Biol 131:459–463
Bhargava HN, Gulati A (1990) Down-regulation of brain and spinal cord mu-opiate receptors in morphine tolerant-dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol 190:305–311
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chakraborty C (2007) Potentiality of small interfering RNAs (siRNA) as recent therapeutic targets for gene-silencing. Curr Drug Targets 8:469–482
Chaplan SR, Pogrel JW, Yaksh TL (1994) Role of voltage-dependent calcium channel subtypes in experimental tactile allodynia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:1117–1123
Chen XL, Li XY, Qian SB, Wang YC, Zhang PZ, Zhou XJ, Wang YX (2012) Down-regulation of spinal d-amino acid oxidase expression blocks formalin-induced tonic pain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 421:501–507
Coderre TJ, Melzack R (1992) The contribution of excitatory amino acids to central sensitization and persistent nociception after formalin-induced tissue injury. J Neurosci 12:3665–3670
Cook AJ, Woolf CJ, Wall PD, McMahon SB (1987) Dynamic receptive field plasticity in rat spinal cord dorsal horn following C-primary afferent input. Nature 325:151–153
D’Aniello A, D’Onofrio G, Pischetola M, D’Aniello G, Vetere A, Petrucelli L, Fisher GH (1993) Biological role of d-amino acid oxidase and d-aspartate oxidase. Effects of d-amino acids. J Biol Chem 268:26941–26949
Ferraris D, Duvall B, Ko YS, Thomas AG, Rojas C, Majer P, Hashimoto K, Tsukamoto T (2008) Synthesis and biological evaluation of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. J Med Chem 51:3357–3359
Goblirsch MJ, Zwolak PP, Clohisy DR (2006) Biology of bone cancer pain. Clin Cancer Res 12:6231s–6235s
Gong N, Gao ZY, Wang YC, Li XY, Huang JL, Hashimoto K, Wang YX (2011) A series of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors specifically prevent and reverse formalin-induced tonic pain in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:282–293
Gong N, Wang YC, Wang HL, Ma AN, Hashimoto K, Wang YX (2012) Interactions of the potent d-amino acid oxidase inhibitor CBIO with morphine in pain and tolerance to analgesia. Neuropharmacology 63:460–468
Goula D, Remy JS, Erbacher P, Wasowicz M, Levi G, Abdallah B, Demeneix BA (1998) Size, diffusibility and transfection performance of linear PEI/DNA complexes in the mouse central nervous system. Gene Ther 5:712–717
Gu X, Zheng Y, Ren B, Zhang R, Mei F, Zhang J, Ma Z (2010) Intraperitoneal injection of thalidomide attenuates bone cancer pain and decreases spinal tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in a mouse model. Mol Pain 6:64
Hald A, Nedergaard S, Hansen RR, Ding M, Heegaard AM (2009) Differential activation of spinal cord glial cells in murine models of neuropathic and cancer pain. Eur J Pain 13:138–145
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623
Honoré P, Schwei MJ, Rogers SD, Salak-Johnson JL, Finke MP, Ramnaraine ML, Clohisy DR, Mantyh PW (2000) Cellular and neurochemical remodeling of the spinal cord in bone cancer pain. Prog Brain Res 129:389–397
Horiike K, Tojo H, Arai R, Nozaki M, Maeda T (1994) d-Amino-acid oxidase is confined to the lower brain stem and cerebellum in rat brain: regional differentiation of astrocytes. Brain Res 652:297–303
Huang JL, Li M, Guo C, Wang YX (2010) Analgesic effects of CBIO, a potent inhibitor of d-amino acid oxidase, in the rat model of bone cancer pain. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol 24:427
Jiang Z-Y, Woollard ACS, Wolff SP (1990) Hydrogen peroxide production during experimental protein glycation. FEBS Lett 268:69–71
Kappor R, Kapoor V (1997) Distribution of d-amino acid oxidase (DAO) activity in the medulla and thoracic spinal cord of the rat: implications for a role for d-serine in autonomic function. Brain Res 771:351–355
Latremoliere A, Woolf CJ (2009) Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J Pain 10:895–926
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu JM, Gong N, Wang YC, Wang YX (2012) d-amino acid oxidase-mediated increase in spinal hydrogen peroxide is mainly responsible for formalin-induced tonic pain. Br J Pharmacol 165:1941–1955
Luger NM, Honore P, Sabino MAC, Schwei MJ, Rogers SD, Mach DB, Clohisy DR, Mantyh PW (2001) Osteoprotegerin diminishes advanced bone cancer pain. Cancer Res 61:4038–4047
Luger NM, Sabino MAC, Schwei MJ, Mach DB, Pomonis JD, Keyser CP, Rathbun M, Clohisy DR, Honore P, Yaksh TL, Mantyh PW (2002) Efficacy of systemic morphine suggests a fundamental difference in the mechanisms that generate bone cancer vs. inflammatory pain. Pain 99:397–406
Mao J, Price DD, Mayer DJ (1995) Mechanisms of hyperalgesia and morphine tolerance: a current view of their possible interactions. Pain 62:259–274
Mao-Ying QL, Zhao J, Dong ZQ, Wang J, Yu J, Yan MF, Zhang YQ, Wu GC, Wang YQ (2006) A rat model of bone cancer pain induced by intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:1292–1298
Martini L, Whistler JL (2007) The role of mu opioid receptor desensitization and endocytosis in morphine tolerance and dependence. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:556–564
Mayer DJ, Mao J, Holt J, Price DD (1999) Cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and their interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7731–7736
Medhurst SJ, Walker K, Bowes M, Kidd BL, Glatt M, Muller M, Hattenberger M, Vaxelaire J, O’Reilly T, Wotherspoon G, Winter J, Green J, Urban L (2002) A rat model of bone cancer pain. Pain 96:129–140
Miao XR, Gao XF, Wu JX, Lu ZJ, Huang ZX, Li XQ, He C, Yu WF (2010) Bilateral downregulation of Nav1.8 in dorsal root ganglia of rats with bone cancer pain induced by inoculation with Walker 256 breast tumor cells. BMC Cancer 10:1–10
Peters CM, Ghilardi JR, Keyser CP, Kubota K, Lindsay TH, Luger NM, Mach DB, Schwei MJ, Sevcik MA, Mantyh PW (2005) Tumor-induced injury of primary afferent sensory nerve fibers in bone cancer pain. Exp Neurol 193:85–100
Pollegioni L, Piubelli L, Sacchi S, Pilone M, Molla G (2007) Physiological functions of d-amino acid oxidases: from yeast to humans. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1373–1394
Schwei MJ, Honore P, Rogers SD, Salak-Johnson JL, Finke MP, Ramnaraine ML, Clohisy DR, Mantyh PW (1999) Neurochemical and cellular reorganization of the spinal cord in a murine model of bone cancer pain. J Neurosci1 9:10886–10897
Smith SM, Uslaner JM, Hutson PH (2010) The therapeutic potential of d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors. Open Med Chem J 4:3–9
Størkson RV, Kjørsvik A, Tjølsen A, Hole K (1996) Lumbar catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 65:167–172
Tan PH, Yang LC, Shih HC, Lan KC, Cheng JT (2005) Gene knockdown with intrathecal siRNA of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit reduces formalin-induced nociception in the rat. Gene Ther 12:59–66
Urch C (2004) The pathophysiology of cancer-induced bone pain: current understanding. Palliat Med 18:267–274
Wacnik PW, Eikmeier LJ, Ruggles TR, Ramnaraine ML, Walcheck BK, Beitz AJ, Wilcox GL (2001) Functional interactions between tumor and peripheral nerve: morphology, algogen identification, and behavioral characterization of a new murine model of cancer pain. J Neurosci 21:9355–9366
Wang YX, Pang CC (1993) Functional integrity of the central and sympathetic nervous systems is a prerequisite for pressor and tachycardic effects of diphenyleneiodonium, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:263–272
Wang YX, Gong N, Xin YF, Hao B, Zhou XJ, Pang CC (2012) Biological implications of oxidation and unidirectional chiral inversion of d-amino acids. Curr Drug Metab 13:321–331
Woolf CJ, Shortland P, Sivilotti LG (1994) Sensitization of high mechanothreshold superficial dorsal horn and flexor motor neurones following chemosensitive primary afferent activation. Pain 58:141–155
Xin YF, Zhou XJ, Cheng X, Wang YX (2005) Renal d-amino acid oxidase mediates chiral inversion of N(G)-nitro-d-arginine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:1090–1096
Xin YF, Li X, Hao B, Gong N, Sun WQ, Konno R, Wang YX (2010) Indispensable but insufficient role of renal d-amino acid oxidase in chiral inversion of NG-nitro-d-arginine. Chem Biodivers 7:1413–1423
Yanagisawa Y, Furue H, Kawamata T, Uta D, Yamamoto J, Furuse S, Katafuchi T, Imoto K, Iwamoto Y, Yoshimura M (2010) Bone cancer induces a unique central sensitization through synaptic changes in a wide area of the spinal cord. Mol Pain 6:38
Zhang X, Bao L, Shi TJ, Ju G, Elde R, Hökfelt T (1998) Down-regulation of mu-opioid receptors in rat and monkey dorsal root ganglion neurons and spinal cord after peripheral axotomy. Neuroscience 82:223–240
Zhang RX, Liu B, Wang L, Ren K, Qiao JT, Berman BM, Lao L (2005) Spinal glial activation in a new rat model of bone cancer pain produced by prostate cancer cell inoculation of the tibia. Pain 118:125–136
Zhao WJ, Konno R, Zhou XJ, Yin M, Wang YX (2008) Inhibition of d-amino-acid oxidase activity induces pain relief in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:581–591
Zhao WJ, Gao ZY, Wei H, Nie HZ, Zhao Q, Zhou XJ, Wang YX (2010) Spinal d-amino Acid oxidase contributes to neuropathic pain in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332:248–254
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by grants (No. 30973581 and No. 81072623) from National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shanghai Science and Technology Administration Innovation Project (No.11ZR1416400). The authors thank Dr. Kenji Hashimoto at Division of Clinical Neuroscience, Chiba University Center for Forensic Mental Health, Chiba, Japan, Dr. Quan-Hai Liu at Shanghai Institute of Pharmaceutical Industry, Shanghai, China, and Dr. Pei-Zuo Zhang at Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China for their kind gifts of CBIO and Walker 256 cell line, and synthesis of siRNA/DAAO, respectively.
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, JL., Chen, XL., Guo, C. et al. Contributions of spinal d-amino acid oxidase to bone cancer pain. Amino Acids 43, 1905–1918 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1390-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1390-z