Abstract
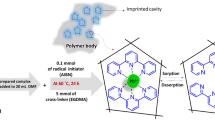
We report on the synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles (PNPs) containing a tetrakis(3-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrin, and their use for the separation of mercury(II) ion. The PNPs were prepared by bulk polymerization from methacrylic acid (the monomer), ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (the cross-linker), 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (the radical initiator) and the mercury(II) complex of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(3-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrin. The Hg(II) ion was then removed by treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid. The PNPs were characterized by colorimetry, FT-IR spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. The material is capable of binding Hg(II) from analyte samples. Bound Hg(II) ions can be eluted with dilute nitric acid and then quantified by cold vapor AAS. The extraction efficiency, the effects of pH, preconcentration and leaching times, sample volume, and of the nature, concentration and volume of eluent were investigated. The maximum adsorption capacity of the PNPs is 249 mg g−1, the relative standard deviation of the AAS assay is 2.2 %, and the limit of detection (3σ) is 8 ng.L−1. The nanoparticles exhibit excellent selectivity for Hg(II) ion over other metal ions and were successfully applied to the selective extraction and determination of Hg(II) ion in spiked water samples.

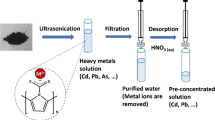
Schematic presentation of leaching process of mercury(II) ion from the prepared IIP





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly CA, Rudd JWM, Holoka MH (2003) Effect of pH on mercury uptake by an aquatic bacterium: implications for Hg cycling. Environ Sci Technol 37:2941
Andac M, Mirel S, Senel S, Say R, Ersoz A, Denizli A (2007) Ion-imprinted beads for molecular recognition based mercury removal from human serum. Int J Biol Macromol 40:159
Liu Y, Chang X, Wang S, Guo Y, Din B, Meng S (2004) Solid-phase extraction and preconcentration of cadmium(II) in aqueous solution with Cd(II)-imprinted resin (poly-Cd(II)-DAAB-VP) packed columns. Anal Chim Acta 519:173
Rao TP, Daniel S, Gladis JM (2004) Tailored materials for preconcentration or separation of metals by ion-imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction (IIP-SPE) Trac-Trend. Anal Chem 23:28
Rao TP, Kala R, Daniel S (2006) Metal ion-imprinted polymers-novel materials for selective recognition of inorganics. Anal Chim Acta 578:105
Cui A, Singh A, Kaplan DL (2002) Enzyme-based molecular imprinting with metals. Biomacromolecules 3:1353
Bozkurt SS, Ayata S, Kaynak I (2009) Fluorescence-based sensor for Pb(II) using tetra-(3-bromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrin in liquid and immobilized medium. Spectrochim Acta A 72:880
Shamsipur M, Soleymanpour A, Akhond M, Sharghi H, Hasaninejad AR (2003) Perchlorate selective membrane electrodes based on a phosphorus(V)–tetraphenylporphyrin complex. Sensors Actuators B 89:9
Balasoiu SC, Staden RS, Staden JF, Pruneanu S, Raduc G (2010) Carbon and diamond paste microelectrodes based on Mn(III) porphyrins for the determination of dopamine. Anal Chim Acta 668:201
Staden JF, Stadenm RIS (2010) Application of porphyrins in flow-injection analysis: a review. Talanta 80:1598
Singh DK, Mishra S (2010) Synthesis and characterization of Hg(II)-ion-imprinted polymer: kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalination 257:177
Qu W, Zhai Y, Meng S, Fan Y, Zhao Q (2008) Selective solid phase extraction and preconcentration of trace mercury(II) with poly-allylthiourea packed columns. Microchim Acta 163:277
Dakova I, Karadjova I, Georgieva V, Georgiev G (2009) Ion-imprinted polymethacrylic microbeads as new sorbent for preconcentration and speciation of mercury. Talanta 78:523
Wang Z, Wu G, He C (2009) Ion-imprinted thiol-functionalized silica gel sorbent for selective separation of mercury ions. Microchim Acta 165:15
Firouzzare M, Qiuquan W (2012) Synthesis and characterization of a high selective mercury(II)-imprinted polymer using novel aminothiol monomer. Talanta 101:261
Liu Y, Chang X, Yang D, Guo Y, Meng S (2005) Highly selective determination of inorganic mercury(II) after preconcentration with Hg(II)-imprinted diazoaminobenzene–vinylpyridine copolymers. Anal Chim Acta 538:85
Shamsipur M, Fasihi J, Ashtari K (2007) Grafting of ion-imprinted polymers on the surface of silica gel particles through covalently surface-bound initiators: a selective sorbent for uranyl ion. Anal Chem 79:7116
Shamsipur M, Fasihi J, Khanchi A, Hassani R, Alizadeh K, Shamsipur H (2007) A stoichiometric imprinted chelating resin for selective recognition of copper(II) ions in aqueous media. Anal Chim Acta 599:294
Shamsipur M, Besharati-Seidani A (2011) Synthesis of a novel nanostructured ion-imprinted polymer for very fast and highly selective recognition of copper(II) ions in aqueous media. React Funct Polym 71:131
Shamsipur M, Besharati-Seidani A, Fasihi J, Sharghi H (2010) Synthesis and characterization of novel ion-imprinted polymeric nanoparticles for very fast and highly selective recognition of copper(II) ions. Talanta 83:674
Shamsipur M, Rajabi HR (2013) Flame photometric determination of cesium ion after its preconcentration with nanoparticles imprinted with the cesium-dibenzo-24-crown-8 complex. Microchim Acta 180:243
Vatanpour V, Madaeni SS, Zinadini S, Rajabi HR (2011) Development of ion imprinted technique for designing nickel ion selective membrane. J Membr Sci 373:36
Zhang L, Chang X, Hu Z, Zhang L, Shi J, Gao R (2010) Selective solid phase extraction and preconcentration of mercury(II) from environmental and biological samples using nanometer silica functionalized by 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid. Microchim Acta 168:79–85
Zhai Y, Duan S, He Q, Yang X, Han Q (2010) Solid phase extraction and preconcentration of trace mercury(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic nanoparticles doped with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide. Microchim Acta 169:353–360
Jiang Y, Zhang H, He Q, Hu Z, Chang X (2012) Selective solid-phase extraction of trace mercury(II) using a silica gel modified with diethylenetriamine and thiourea. Microchim Acta 178:421–442
Labrou NE, Karagouni A, Clonis YD (1995) Biomimetic-dye affinity adsorbents for enzyme purification: application to the one-step purification of Candida boidinii formate dehydrogenase. Biotechnol Bioeng 48:278
Shamsipur M, Shokrollahi A, Sharghi H, Eskandari MM (2005) Solid phase extraction and determination of sub-ppb levels of hazardous Hg2+ ions. J Hazard Mater 117:129–133
Shirmardi-Dezaki A, Shamsipur M, Akhond M, Sharghi H (2013) Electroanal Chem 689:63–68
Zheng H, Geng T, Hu L (2008) Selective solid-phase extraction of Hg(II) using silica gel surface—imprinting technique. Chem Anal (Warsaw) 53:673
Fan Z (2006) Hg(II)-imprinted thiol-functionalized mesoporous sorbent micro-column preconcentration of trace mercury and determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Talanta 70:1164
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of this work by Iran Elites National Foundation (IENF) via the late Allameh Tabatabaei prize.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamsipur, M., Rajabi, H.R., Beyzavi, M.H. et al. Bulk polymer nanoparticles containing a tetrakis(3-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrin for fast and highly selective separation of mercury ions. Microchim Acta 180, 791–799 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0983-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-0983-x