Abstract
Introduction
To determine whether trabeculectomy affects postural-induced changes in intraocular pressure (IOP), and whether it is maintained.
Methods
Thirty-six eyes of 36 patients with open-angle glaucoma who were scheduled for their initial trabeculectomy with adjunctive mitomycin C were prospectively examined. The IOP was measured in the sitting and the lateral decubitus position with an ICare rebound tonometer before, and 1, 3, and 12 months after trabeculectomy.
Results
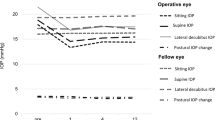
Twenty-nine eyes of 29 patients completed this study. The mean baseline IOP measured with the ICare tonometer was 17.4 ± 4.9 mmHg in the sitting position and 21.3 ± 5.6 mmHg in the lateral decubitus position (p < 0.001). This postural IOP difference, +3.9 mmHg, was reduced to +1.3 ± 1.7 mmHg at 1 month and to +0.8 ± 1.5 mmHg at 3 months after the trabeculectomy (p < 0.001 and p = 0.004 respectively). This decrease in the degree of posture-dependent IOP change was maintained at +1.7 ± 2.2 mmHg at 1 year postoperatively (p < 0.001). In three cases, the postural IOP changes returned to the baseline level, and all three had a failed bleb.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that trabeculectomy not only reduces the IOP but also reduces the degree of posture-induced changes in the IOP. Our findings also speculate that measuring the postural IOP changes after trabeculectomy might provide a clue on the functioning of a filtering bleb.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwase A, Araie M, Tomidokoro A, Yamamoto T, Shimizu H, Kitazawa Y, Tajimi Study Group (2006) Prevalence and causes of low vision and blindness in a Japanese adult population: the Tajimi Study. Ophthalmology 113:1354–1362
Prata TS, De Moraes CG, Kanadani FN, Ritch R, Paranhos A Jr (2010) Posture-induced intraocular pressure changes: considerations regarding body position in glaucoma patients. Surv Ophthalmol 55:445–453
Caprioli J, Coleman AL (2008) Intraocular pressure fluctuation. A risk factor for visual field progression at low intraocular pressures in the advanced glaucoma intervention study. Ophthalmology 115:1123–1129
Nouri-Mahdavi K, Hoffman D, Coleman AL, Liu G, Li G, Gaasterland D, Caprioli J, Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (2004) Predictive factors for glaucomatous visual field progression in the Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study. Ophthalmology 111:1627–1635
Hirooka K, Shiraga F (2003) Relationship between postural change of the intraocular pressure and visual field loss in primary open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma 12:379–382
Mizokami J, Yamada Y, Negi A, Nakamura M (2011) Postural changes in intraocular pressure are associated with asymmetrical retinal nerve fiber thinning in treated patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249:879–885
Kiuchi T, Motoyama Y, Oshika T (2006) Relationship of progression of visual field damage to postural changes in intraocular pressure in patients with normal-tension glaucoma. Ophthalmology 113:2150–2155
Abedin S, Simmons RJ, Grant WM (1982) Progressive low-tension glaucoma: treatment to stop glaucomatous cupping and field loss when these progress despite normal intraocular pressure. Ophthalmology 89:1–6
Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group (1998) Comparison of glaucomatous progression between untreated patients with normal-tension glaucoma and patients with therapeutically reduced intraocular pressures. Am J Ophthalmol 126:487–497
Mansouri K, Orguel S, Mermoud A, Haefliger I, Flammer J, Ravinet E, Shaarawy T (2008) Quality of diurnal intraocular pressure control in primary open-angle patients treated with latanoprost compared with surgically treated glaucoma patients: a prospective trial. Br J Ophthalmol 92:332–336
Miyake T, Sawada A, Yamamoto T, Miyake K, Sugiyama K, Kitazawa Y (2006) Incidence of disc hemorrhages in open-angle glaucoma before and after trabeculectomy. J Glaucoma 15:164–171
Anderson DR, Grant WM (1973) The influence of position on intraocular pressure. Invest Ophthalmol 12:204–212
Parsley J, Powell RG, Keightley SJ, Elkington AR (1987) Postural response of intraocular pressure in chronic open-angle glaucoma following trabeculectomy. Br J Ophthalmol 71:494–496
Hirooka K, Takenaka H, Baba T, Takagishi M, Mizote M, Shiraga F (2009) Effect of trabeculectomy on intraocular pressure fluctuation with postural change in eyes with open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma 18:689–691
Weizer JS, Goyal A, Ple-Plakon P, Trzcinka A, Strong BD, Bruno CA, Junn J, Tseng I, Niziol LM, Musch DC, Moroi SE (2010) Bleb morphology characteristics and effect on positional intraocular pressure variation. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 41:532–537
Kitazawa Y, Kawase K, Matsushita H, Minobe M (1991) Trabeculectomy with mitomycin C (a comparative study with fluorouracil). Arch Ophthalmol 109:1693–1698
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia-Sanchez J (2005) Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4578–4580
Jóhannesson G, Hallberg P, Eklund A, Lindén C (2008) Pascal, ICare and Goldmann applanation tonometry—a comparative study. Acta Ophthalmol 86:614–621
Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM, Pfeiffer N, Thieme H (2008) Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:875–879
Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS (2006) Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 84:206–209
Hwang JW, Jeon YT, Kim JH, Oh YS, Park HP (2006) The effect of the lateral decubitus position on the intraocular pressure in anesthetized patients undergoing lung surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 50:988–992
Loewen NA, Liu JH, Weinreb RN (2010) Increased 24-hour variation of human intraocular pressure with short axial length. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:933–937
Broadwater JJ, Schorling JJ, Herring IP, Elvinger F (2008) Effect of body position on intraocular pressure in dogs without glaucoma. Am J Vet Res 69:527–530
Armaly MF, Salamoun SG (1963) Schiotz and applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol 70:603–609
Hetland-Eriksen J (1966) On tonometry. 5. The pressure of glaucomatous eyes measured in the sitting and the lying positions by means of the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 44:515–521
Kiuchi T, Motoyama Y, Oshika T (2007) Influence of ocular hypotensive eyedrops on intraocular pressure fluctuation with postural change in eyes with normal-tension glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 143:693–695
Conflict of interest
The authors have no proprietary or financial interest in any products used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, A., Yamamoto, T. Effects of trabeculectomy on posture-induced intraocular pressure changes over time. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250, 1361–1366 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-1942-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-1942-7