Abstract
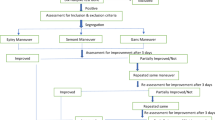
The treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) consists of a repositioning maneuver in order to remove otoliths from the posterior semicircular canal and subsequent postural restrictions to prevent debris from reentering the canal. However, the extent to which postural restrictions affect the final outcomes of BPPV is still uncertain. The purpose of this study is to determine the effects of postural restrictions in the treatment of BPPV, which is caused by otoliths in the posterior semicircular canal, and to evaluate its usefulness as a therapy. Seventy cases diagnosed as BPPV of the posterior semicircular canal were studied. All patients were treated utilizing the modified Epley maneuver. They were divided into two groups. The first group (group A, 35 patients) was instructed to sleep in a semi-sitting position and to avoid moving their heads forward or backward, whereas no instructions were given to the second group (group B, 35 patients). The information gathered from the patients was analyzed by age of onset, gender, duration of the disease and cure rates or recurrence rates. In group A, the average age was 54.5 years and the mean duration of symptoms was 116.5 days, whereas in group B, these measurements were 54.8 years and 86.7 days. The cure rates were 91.4 and 94.3%, respectively. Symptoms recurred in 12.5% of group A patients, while in group B, there was a 9.1% recurrence rate. Our study did not show any significant difference between the two groups. Postural restriction therapy, practiced after the modified Epley repositioning maneuver, did not have a significant effect on the final outcomes of BPPV. Based on our results, we do not recommend this therapy since there was no significant benefit for the patients who utilized postural restrictions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semont A, Freyss G, Vitte E (1998) Curing the BPPV with a liberatory maneuver. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 42:290–293
Epley JM (1992) The canalith repositioning procedure: For treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107:399–404
Marciano E, Marcelli V (2002) Postural restrictions in labyrintholithiasis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259:262–265
Massoud EA, Ireland DJ (1996) Post-treatment instructions in the nonsurgical management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Otolaryngol 25:121–125
Nuti D, Nati C, Passali D (2000) Treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: no need for postmaneuver restrictions. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:440–444
Lee JH, Bae MR, Yoo JB et al (2003) Results of otolith reposition therapy in various types of BPPV. Korean J Otolaryngol 46:289–295
Fung K, Hall SF (1996) Particle repositioning maneuver: effective treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Otolaryngol 25:243–248
Beynon GJ, Baguley DM, da Cruz MJ (2000) Recurrence of symptoms following treatment of posterior semicircular canal benign positional paroxysmal vertigo with a particle repositioning manoeuvre. J Otolaryngol 29:2–6
Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ, Zee DS, et al (1993) Single treatment approaches to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:450–454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, S.J., Bae, S.H., Kim, H.D. et al. The effect of postural restrictions in the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262, 408–411 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0836-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0836-7