Abstract
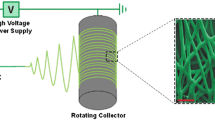
A salt-induced electrospinning method to produce porous polymer ultrafine fibers was reported in this work. Scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer, and BET surface area measurement were employed to evaluate the morphology, the element distribution, and the surface area of fibers, respectively. According to the investigation result, pores on the fiber were induced by water-soluble salt during electrospinning process in a humid spinning environment. There was no porous structure on the fiber surface when water-insoluble salt was used in a wet electrospinning environment or when water-soluble salt was used in a dry electrospinning environment. Compared with pure fibers, the average surface area of fibers containing salt increased significantly due to the porous structure. The possible mechanism of the porous structure induced by salt was proposed. Water-solubility salt and humid environment were considered as the key roles in the formation of porous structure. This method provided a new way to form porous structure during electrospinning.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards MD, Mitchell GR, Mohan SD, Olley RH (2010) Eur Polym J 46:1175
Reneker DH, Fong H (2006) Polymeric Nanofibers. ACS Symposium Series 918. Oxford University Press (USA)
Dai XS, Shivkumar S (2008) Mater Sci Eng C 28:336
Zhao XY, Wang CY, Zhang K, Zhou Z, Zhu MF (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:907
McKee MG, Layman JM, Cashion MP, Long TE (2006) Science 311:353
Li XR, Zhang H, Li H, Yuan XY (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:1113
Dayal P, Liu J, Kumar S, Kyu T (2007) Macromolecules 40:7689
Anthony LA (2008) Wiley 250
Jiang X, Lim SH, Mao HQ, Chew SY (2010) Exp Neurol 223:86
Lim SH, Mao HQ (2009) Adv Drug Deliver Rev 61:1084
Xie JW, Li XR, Xia YN (2008) Macromol Rapid Commun 29:1775
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE, Yong T, Ma ZW, Ramaseshan R (2006) Mater Today 9:40
Moroni L, De Wijn JR, Van Blitterswijk CA (2008) J Biomat Sci-Polym E 19:543
Thomas V, Dean DR, Vohra YK (2006) Curr Nanosci 2:155
Ji LW, Zhang XW (2009) Nanotechnology 20:155705
Bognitzki M, Czado W, Frese T, Schaper A, Hellwig M, Steinhart M et al (2001) Adv Mater 13:70
Zhang YZ, Feng Y, Huang ZM, Ramakrishna S, Lim CT (2006) Nanotechnology 17:901
You Y, Youk JH, Lee SW, Min BM, Lee SJ, Park WH (2006) Mater Lett 60:757
Li L, Hsieh YL (2006) Carbohyd Res 341:374
Pai CL, Boyce MC, Rutledge GC (2009) Macromolecules 42:2102
Gupta A, Saquing CD, Afshari M, Tonelli AE, Khan SA, Kotek R (2009) Macromolecules 42:709
Mit-uppatham C, Nithitanakul M, Supaphol P (2004) Macromol Chem Phys 205:2327
Bai J, Li YX, Li MY, Gao JL, Zhang XM, Wang SG et al (2008) Colloid Surface A 318:259
Cho YW, An SW, Song SC (2006) Macromol Chem Phys 207:412
Schmid A, Fujii S, Armes SP (2006) Langmuir 22:4923
Lin Z, Woodroof MD, Ji LW, Liang YZ, Krause W, Zhang XW (2010) J Appl Polym Sci 116:895
Park JH, Karim MR, Kim IK, Cheong IW, Kim JW, Bae DG et al (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:115
Zhang QC, Zhang YJ, Wei Q, Wang XJ, Liu J, Yang J et al (2011) J Appl Polym Sci 120:2648
Megelski S, Stephens JS, Chase DB, Rabolt JF (2002) Macromolecules 35:8456
Srinivasarao M, Collings D, Philips A, Patel S (2001) Science 292:79
Casper CL, Stephens JS, Tassi NG, Chase DB, Rabolt JF (2004) Macromolecules 37:573
Xu YY, Xu ZK (2005) Chemical Industry Press 117
Zhang QC, Liu J, Wang XJ, Li MX, Yang J (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:1385
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully appreciate the financial support by the National High Technology Foundation of China (Grant No. 2007AA03Z561). We are particularly indebted to Dr. Chaoliang Zhang for assistance of SEM testing in State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 459 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Li, M., Liu, J. et al. Porous ultrafine fibers via a salt-induced electrospinning method. Colloid Polym Sci 290, 793–799 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-011-2563-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-011-2563-0