Abstract
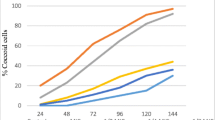
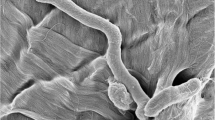
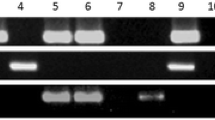
Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori) is an actively dividing spiral bacterium that changes to coccoid morphology under stressful environments. The infectivity of the coccoids is still controversial. The aim of this study was to determine the viability and expression of two important virulence genes (babA and cagE), in antibiotic-induced coccoid forms. Three strains of H. pylori, the standard 26695 and two clinical isolates (p1, p2) were converted to coccoid form by amoxicillin. Coccoids were identified according to Gram-staining and microscopic morphology. The viability of the cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. The expression of cagE and babA in coccoid forms were evaluated and compared to the spirals by quantitative PCR assay. The coccoid forms were developed after 72 h exposure of H. pylori to ½ MIC of amoxicillin, and the conversion form was completed (100 %) at 144 h in all of three isolates. Flow cytometry analyses showed that the majority of the induced coccoids (90–99.9 %) were viable. Expression of cagE and babA was seen in coccoids; however, in lower rate (cagE, ~3-fold and babA, ~10-fold) than these in spiral forms. Coccoid forms of two clinical isolates significantly expressed higher rate of cagE and babA than standard 26695 strain (P = 0.01). These results suggest that the induced coccoid form of H. pylori is not a passive entity but can actively infect the human by expression of the virulence genes for long time in stomach and probably play a role in chronic and severe disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi AT, Taghvaei T, Mobarez AM, Vaira G, Vaira D (2012) High correlation of babA2- positive strains of Helicobacter pylori with the presence of gastric cancer. Intern Emerg Med. doi 10.1007/s11739-011-0631-6
Amieva MR, EL–Omar E (2008) Host-bacterial interactions in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology 134:306–323
Andersen LP, Rasmussen L (2009) Helicobacter pylori—coccoid forms and biofilm formation. FEMS lmmunol Med Microbiol 56:112–115
Azevedo NF, Almeida C, Cerqueira L, Dias S, Keevil CW, Vieira MJ (2007) Coccoid form of Helicobacter pylori as a morphological manifestation of cell adaptation to the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3423–3427
Lima VP, Pereira MA et al (2010) The relationship between Helicobacter pylori genes cagE and virB11 and gastric cancer. Int J Infect Dis 14:e613–e617
Boonjakuakul JK, Canfield DR, Solnick JV (2005) Comparison of Helicobacter pylori virulence gene expression in vitro and in the rhesus macaque. Infect Immun 73(8):4895–4904
Bumann D, Habibi H, Kan B, Schmid M, Goosmann C, Brinkmann V, Meyer TF, Jungblut P (2004) Lack of stage-specific proteins in coccoid Helicobacter pylori cells. Infect Immun 72(11):6738–6742
Can F, karahan C, Dolapci I, Demirbilek M, Tekeli A, Arslan H (2008) Urease activity and urea gene sequencing of coccoid forms of H. pylori induced by different factors. Curr Microbiol 56:150–155
Citterio B, Casaroli A, Pierfelici L, Battistelli M, Falcieri E, Baffone W (2004) Morphological changes and outer membrane protein patterns in Helicobacter pylori during conversion from bacillary to coccoid form. Microbiol 27:353–360
Engstrand L (2001) Helicobacter in water and waterborne routes of transmission. J Appl Microbiol 30:80S–84S
Franco AT, Israel D, Washington M, Krishna U, Fox J, Rogers A et al (2005) Activation of β-catenin by carcinogenic Helicobacter pylori. PNAS 102:10646–10651
Fujimoto S, Ojo OO, Arnqvist A, Wu JY, Odenbreit S et al (2007) Helicobacter pylori BabA expression, gastric mucosal injury, and clinical outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:49–58
Goldstein N (2002) Chronic inactive gastritis and coccoid Helicobacter pylori in patients treated for gastroesophageal reflux disease or with H pylori eradication therapy. Am J Clin Pathol 118:719–726
Guillemin K, Salama NR, Tompkins LS, Falkow S (2002) Cag pathogenicity island-specific responses of gastric epithelial cells to Helicobacter pylori infection. PNAS 99(23):15136–15141
Hosseini E, Poursina F, Van de Wiele T, Ghasemian Safaei H, Adibi P (2012) Helicobacter pylori in Iran: a systematic review on the association of genotypes and gastroduodenal diseases. J Res Med Sci 17:280–292
Hwang MG, Oh JW, Katayama H, Ohgaki SH, Cho JK (2012) Application of multiparametric flow cytometry (FCM) to enumerate the diagnosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Environ Eng Res 17:35–39
Jekti DSD, Soemohardjo S, Muttaqin Z (2008) The absence of enzymatic activity of Helicobacter pylori coccoid form. Indonesian J Gastroentrol Hepathol Dig Endosc 9:35–41
Kusters JG, Gerrits MM, Strijp JA, Vandenbroucke-Girauls CM (1997) Coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori are the morphologic manifestation of cell death. Infect Immun 65:3672–3679
Kusters JG, Vliet AH, Kuipers E (2006) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:449–490
Mitsuno Y, Yoshida H, Maeda S, Ogura K, Hirata Y, Kawabe T, Shiratori Y, Omata M (2001) Helicobacter pylori induced transactivation of SRE and AP-1 through the ERK signalling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Gut 49:18–22
Mizoguchi H, Fujioka T, Kishi K, Nishizono A, Kodama R, Nasu M (1998) Diversity in protein synthesis and viability of Helicobacter pylori coccoid forms in response to various stimuli. Infect Immun 66:5555–5560
Monstein HJ, Jonasson J (2001) Differential virulence-gene mRNA expression in coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285:530–536
Moss SF, Malfertheiner P (2007) Helicobacter and gastric malignancies. Helicobacter 12:23–30
Nilsson HO, Blom J, Al-Soud WA, Ljungh A, Andersen LP, Wadstrom T (2002) Effect of cold starvation, acid stress, and nutrients on metabolic activity of Helicobacter pylori. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:11–19
Oliver JD (2005) The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J Microbiol 43:93–100
Safaei HG, Havaei SA, Tavakkoli H, Eshaghei M, Navabakbar F, Salehei R (2010) Relation of babA2 genotype of Helicobacter pylori infection with chronic active gastritis, duodenal ulcer and non-cardia active gastritis in Alzahra hospital Isfahan Iran. Jundishapur J Microbiol 3(3):93–98
Safaei H, Tavakkoli H, Mojtahedi A, Salehei R, Soleimani B, Pishva E (2008) Correlation of cagA positive Helicobacter pylori infection with clinical outcomes in Alzahra hospital, Isfahan Iran. JRMS 13:196–201
Saito N, Konishi K, Sato F, kato M, Takeda H, Sugiyama T et al (2003) Plural transformation- processes from spiral to coccoid Helicobacter pylori and its viability. J Infect 46:49–55
Sisto F, Brenciaglina MI, Scaltrito MM, Dubini F (2000) Helicobacter pylori : ure A, cagA and vacA expression during conversion to coccoid form. Int J Antimicrob Agents 15:277–282
She FF, Lin JY, Liu JY, Huang C, Su DH (2003) Virulence of water- induced coccoid Helicobacter pylori and its experimental infection in mice. World J Gastroenterol 9:516–520
She FF, Su DH, Lin JY, zhou LY (2001) Virulence and potential pathogenicity of coccoid Helicobacter pylori induced by antibiotics. World J Gastroenterol 7:254–258
Tiwari SK, Manoj G, Kumar GV, Sivaram G, Hassan SI, Prabhakar B, Devi U, Jalaluddin S, Kumar K, Ahmed S, Abid Z, Habeeb MA, Khan AA, Habibullah CM (2008) Prognostic significance of genotyping Helicobacter pylori infection in patients in younger age groups with gastric cancer. Postgrad Med J 84:193–197
Wang K, Wang XF (2004) Cloning and sequencing of cagA gene fragment of Helicobacter pylori with coccoid form. World J Gastroentrol 10:3511–3513
Yamaoka Y (2008) Roles of Helicobacter pylori BabA in gastroduodenal pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 14:4265–4272
Zeng H, Guo G, Mao XH, Tong WD, Zou QM (2008) Proteomic insights into Helicobacter pylori coccoid forms under oxidative stress. Curr Microbiol 57:281–286
Acknowledgments
This assay was supported by Grant No. 390009 from Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. We thank Mr. Kazemi and Mis. Jamshidian in Central Laboratory of Faculty of medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poursina, F., Faghri, J., Moghim, S. et al. Assessment of cagE and babA mRNA Expression During Morphological Conversion of Helicobacter pylori From Spiral to Coccoid. Curr Microbiol 66, 406–413 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0280-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0280-7