Abstract
Purpose
Metastasis of solid tumors to regional lymph nodes is facilitated by tumor lymphangiogenesis, which is primarily mediated by the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3). We conducted a phase 1 dose-escalation (part A) study of the VEGFR-3 human immunoglobulin G subclass 1 monoclonal antibody LY3022856 in advanced solid tumors, followed by a colorectal cancer (CRC) expansion (part B).
Methods
Part A evaluated the safety profile and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of LY3022856 in patients treated intravenously at doses of 5–30 mg/kg weekly (qwk). Part B further evaluated tolerability in CRC patients treated with 30 mg/kg. Secondary objectives were pharmacokinetics, anti-tumor activity, and pharmacodynamics (exploratory).
Results
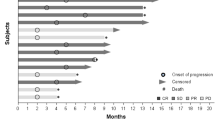
A total of 44 patients (23 in part A; 21 in part B) were treated; only one dose-limiting toxicity was observed at the lowest dose level. The MTD was not reached. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade included in ≥15 % of all patients were: nausea (41 %), fatigue (32 %), vomiting (30 %), decreased appetite (27 %), pyrexia (25 %), peripheral edema (23 %), and urinary tract infection (UTI, 20 %). The most common grade 3/4 TEAEs included UTI and small intestinal obstruction (7 % each). No radiographic responses were noted. Median progression-free survival in part B was 6.3 weeks (95 % confidence interval: 5.1, 14.4), and a best overall response of stable disease was observed in 4 CRC patients (19.0 %).
Conclusions
LY3022856 was well tolerated up to a dose of 30 mg/kg qwk, but with minimal anti-tumor activity in CRC.
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier
NCT01288989.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riquet M, Arame A, Foucault C, Le Pimpec BF (2010) Prognostic classifications of lymph node involvement in lung cancer and current International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer descriptive classification in zones. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 11:260–264
Bolster MJ, Pepels MJ, Wauters CA, Schapers RF, Meijer JW, Strobbe LJ, van Berlo CL, Klinkenbijl JH, Wobbes T, Voogd AC, Bult P, Tjan-Heijnen VC (2013) Is the sentinel lymph node pathology protocol in breast cancer patients associated with the risk of regional recurrence? Eur J Surg Oncol 39:437–441
Liu B, Ma J, Wang X, Su F, Li X, Yang S, Ma W, Zhang Y (2008) Lymphangiogenesis and its relationship with lymphatic metastasis and prognosis in malignant melanoma. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 291:1227–1235
Peppicelli S, Bianchini F, Calorini L (2014) Inflammatory cytokines induce vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression in melanoma-associated macrophages and stimulate melanoma lymph node metastasis. Oncol Lett 8:1133–1138
Ran S, Volk L, Hall K, Flister MJ (2010) Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer. Pathophysiology 17:229–251
Nisato RE, Tille JC, Pepper MS (2003) Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Thromb Haemost 90:591–597
Yu H, Zhang S, Zhang R, Zhang L (2009) The role of VEGF-C/D and Flt-4 in the lymphatic metastasis of early-stage invasive cervical carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:98
van Iterson V, Leidenius M, von Smitten K, Bono P, Heikkilä P (2007) VEGF-D in association with VEGFR-3 promotes nodal metastasis in human invasive lobular breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 128:759–766
Persaud K, Tille JC, Liu M, Zhu Z, Jimenez X, Pereira DS, Miao HQ, Brennan LA, Witte L, Pepper MS, Pytowski B (2004) Involvement of the VEGF receptor 3 in tubular morphogenesis demonstrated with a human anti-human VEGFR-3 monoclonal antibody that antagonizes receptor activation by VEGF-C. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 13):2745–2756
Jüttner S, Wissmann C, Jöns T, Vieth M, Hertel J, Gretschel S, Schlag PM, Kemmner W, Höcker M (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor-D and its receptor VEGFR-3: two novel independent prognostic markers in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:228–240
Tammela T, Alitalo K (2010) Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell 140:460–476
Kodama M, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M, Kuwai T, Tanaka S, Oue N, Yasui W, Chayama K (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor C stimulates progression of human gastric cancer via both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 14:7205–7214
Tammela T, Zarkada G, Wallgard E, Murtomäki A, Suchting S, Wirzenius M, Waltari M, Hellström M, Schomber T, Peltonen R, Freitas C, Duarte A, Isoniemi H, Laakkonen P, Christofori G, Ylä-Herttuala S, Shibuya M, Pytowski B, Eichmann A, Betsholtz C, Alitalo K (2008) Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature 454:656–660
Roberts N, Kloos B, Cassella M, Podgrabinska S, Persaud K, Wu Y, Pytowski B, Skobe M (2006) Inhibition of VEGFR-3 activation with the antagonistic antibody more potently suppresses lymph node and distant metastases than inactivation of VEGFR-2. Cancer Res 66:2650–2657
Pytowski B, Goldman J, Persaud K, Wu Y, Witte L, Hicklin DJ, Skobe M, Boardman KC, Swartz MA (2005) Complete and specific inhibition of adult lymphatic regeneration by a novel VEGFR-3 neutralizing antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:14–21
Chen H, Ding X, Gao Y, Jiang X, Liu X, Chen Y, Gao J, Zhou X, Cai Z, Sun Q (2013) Inhibition of angiogenesis by a novel neutralizing antibody targeting human VEGFR-3. MAbs 5:956–961
Alam A, Blanc I, Gueguen-Dorbes G, Duclos O, Bonnin J, Barron P, Laplace MC, Morin G, Gaujarengues F, Dol F, Hérault JP, Schaeffer P, Savi P, Bono F (2012) SAR131675, a potent and selective VEGFR-3-TK inhibitor with antilymphangiogenic, antitumoral, and antimetastatic activities. Mol Cancer Ther 11:1637–1649
Valtola R, Salven P, Heikkilä P, Taipale J, Joensuu H, Rehn M, Pihlajaniemi T, Weich H, deWaal R, Alitalo K (1999) VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 154:1381–1390
Smith NR, Baker D, James NH, Ratcliffe K, Jenkins M, Ashton SE, Sproat G, Swann R, Gray N, Ryan A, Jürgensmeier JM, Womack C (2010) Vascular endothelial growth receptors VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 are localized primarily to the vasculature in human primary solid cancers. Clin Cancer Res 16:3548–3561
Laakkonen P, Waltari M, Holopainen T, Takahashi T, Pytowski B, Steiner P, Hicklin D, Persaud K, Tonra JR, Witte L, Alitalo K (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 is involved in tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res 67:593–599
Achen MG, Mann GB, Stacker SA (2006) Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. Br J Cancer 94:1355–1360
Burton JB, Priceman SJ, Sung JL, Brakenhielm E, An DS, Pytowski B, Alitalo K, Wu L (2008) Suppression of prostate cancer nodal and systemic metastasis by blockade of the lymphangiogenic axis. Cancer Res 68:7828–7837
Hoshida T, Isaka N, Hagendoorn J, di Tomaso E, Chen YL, Pytowski B, Fukumura D, Padera TP, Jain RK (2006) Imaging steps of lymphatic metastasis reveals that vascular endothelial growth factor-C increases metastasis by increasing delivery of cancer cells to lymph nodes: therapeutic implications. Cancer Res 66:8065–8075
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Ma W, Xu M, Liu Y, Liu H, Huang J, Zhu Y, Ji LJ, Qi X (2015) Safety profile of combined therapy inhibiting EFGR and VEGF pathways in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of 15 phase II/III randomized trials. Int J Cancer 137:409–419
Fuchs CS, Tomasek J, Yong CJ, Dumitru F, Passalacqua R, Goswami C, Safran H, Vieira dos Santos L, Aprile G, Ferry DR, Melichar B, Tehfe M, Topuzov E, Zalcberg JR, Chau I, Campbell W, Sivanandan C, Pikiel J, Koshiji M, Hsu Y, Liepa AM, Gao L, Schwartz JD, Tabernero JD, for the REGARD Trial Investigators (2014) Ramucirumab monotherapy for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (REGARD): an international, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 383:31–39
Escudier B, Szczylik C, Hutson TE, Demkow T, Staehler M, Rolland F, Negrier S, Laferriere N, Scheuring UJ, Cella D, Shah S, Bukowski RM (2009) Randomized phase II trial of first-line treatment with sorafenib versus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:1280–1289
Joukov V, Sorsa T, Kumar V, Jeltsch M, Claesson-Welsh L, Cao Y, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N, Alitalo K (1997) Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity of VEGF-C. EMBO J 16:3898–3911
Stacker SA, Stenvers K, Caesar C, Vitali A, Domagala T, Nice E, Roufail S, Simpson RJ, Moritz R, Karpanen T, Alitalo K, Achen MG (1999) Biosynthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor-D involves proteolytic processing which generates non-covalent homodimers. J Biol Chem 274:32127–32136
Choueiri TK, Escudier B, Powles T, Mainwaring PN, Rini BI, Donskov F, Hammers H, Hutson TE, Lee J-L, Peltola K, Roth BJ, Bjarnason GA, Géczi L, Keam B, Maroto P, Heng DYC, Schmidinger M, Kantoff PW, Borgman-Hagey A, Hessel C, Scheffold C, Schwab GM, Tannir NM, Motzer RJ, for the METEOR Investigators (2015) Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373:1814–1823
Hutson TE, Lesovoy V, Al-Shukri S, Stus VP, Lipatov ON, Bair AH, Rosbrook B, Chen C, Kim S, Vogelzang NJ (2013) Axitinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:1287–1294
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:115–124
Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, Habra MA, Newbold K, Shah MH, Hoff AO, Gianoukakis AG, Kiyota N, Taylor MH, Kim S-B, Krzyzanowska MK, Dutcus CE, de las Heras B, Zhu J, Sherman SI (2015) Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 372:621–630
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA, Kavina A, Zarbá JJ, Chen M, McCann L, Pandite L, Roychowdhury DF, Hawkins RE (2010) Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 28:1061–1068
Li J, Qin S, Xu R, Yau TC, Ma B, Pan H, Xu J, Bai Y, Chi Y, Wang L, Yeh K-H, Bi F, Cheng Y, Le AT, Lin J-K, Liu T, Ma D, Kappeler C, Kalmus J, Kim TW, on behalf of the CONCUR Investigators (2015) Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 16:619–629
Motzer RJ, Nosov D, Eisen T, Bondarenko I, Lesovoy V, Lipatov O, Tomczak P, Lyulko O, Alyasova A, Harza M, Kogan M, Alekseev BY, Sternberg CN, Szczylik C, Cella D, Ivanescu C, Krivoshik A, Strahs A, Esteves B, Berkenblit A, Hutson TE (2013) Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 31:3791–3799
Reck M, Kaiser R, Mellemgaard A, Douillard J-Y, Orlov S, Krzakowski M, von Pawel J, Gottfried M, Bondarenko I, Liao M, Gann C-N, Barrueco J, Gaschler-Markefski B, Novello S, for the LUME-Lung 1 Study Group (2014) Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): a phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 15:143–155
Schmidinger M (2013) Understanding and managing toxicities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors. EJC Suppl 11:172–191
Spratlin JL, Cohen RB, Eadens M, Gore L, Camidge DR, Diab S, Leong S, O’Bryant C, Chow LQ, Serkova NJ, Meropol NJ, Lewis NL, Chiorean EG, Fox F, Youssoufian H, Rowinsky EK, Eckhardt SG (2010) Phase I pharmacologic and biologic study of ramucirumab (IMC-1121B), a fully human immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. J Clin Oncol 28:780–787
Vermeulen PB, van Golen KL, Dirix LY (2010) Angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, growth pattern, and tumor emboli in inflammatory breast cancer: a review of the current knowledge. Cancer 116(11 Suppl):2748–2754
Schoppmann SF, Jesch B, Zacherl J, Riegler MF, Friedrich J, Birner P (2013) Lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular invasion diminishes prognosis in esophageal cancer. Surgery 153:526–534
Sugiura T, Inoue Y, Matsuki R, Ishii K, Takahashi M, Abe M, Shirasuna K (2009) VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression is correlated with lymphatic vessel density and lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma: implications for use as a prognostic marker. Int J Oncol 34:673–680
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients, their families, the study sites, and the study personnel who participated in this clinical trial. Eli Lilly and Company contracted with inVentiv Health Clinical for writing and editorial support, provided by Emily Cullinan, Ph.D., and Noelle Gasco, respectively.
Funding
This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company (NCT01288989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Saif received research grants from Eli Lilly and Company; served on speaker bureaus for Celgene, Genentech, Ipsen, and Sirtex; and received research funding from Celgene, Genentech, Taiho, Eli Lilly and Company, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, and Gilead. Dr Chiorean declares her institution received a research grant from Eli Lilly and Company. Dr O’Neil received honorarium from Eli Lilly and Company. Dr Knost has no conflicts to declare. Dr Kambhampati, Dr Yu, Dr Pytowski, Dr Qin, and Dr Kauh are employed by Eli Lilly and Company and are minor stockholders in Eli Lilly and Company.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saif, M.W., Knost, J.A., Chiorean, E.G. et al. Phase 1 study of the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 monoclonal antibody LY3022856/IMC-3C5 in patients with advanced and refractory solid tumors and advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78, 815–824 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3134-3