Abstract
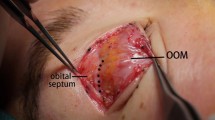
Upper-eyelid blepharoplasty is a very common procedure in aesthetic plastic surgery. Among all the literature in favor of orbicularis muscle resection, there are no commentaries associated with orbicularis muscle suture and its convenience. This article discusses a new approach: independent resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle similar in size to the resected skin and the subsequent suture of the orbicularis muscle after its resection. This results in a fine reconstruction of the upper-eyelid crease, achieves a good definition of this anatomical structure, and allows correction of asymmetries with the contralateral upper eyelid. The results obtained (98 % of patients satisfied) and no complications with this procedure make it a safe alternative for upper blepharoplasty.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Lei B, Timmerman IS, Cromheecke M, Hofer SO (2007) Bipolar coagulation-assisted orbital (BICO) septoblepharoplasty: a retrospective analysis of a new fat-saving upper-eyelid blepharoplasty technique. Ann Plast Surg 59:263–267
Jacono AA, Moskowitz B (2011) Transconjunctival versus transcutaneous approach in upper and lower blepharoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 17:21–28
Serra F (2004) Upper cosmetic blepharoplasty and the eye brow. J Fr Ophtalmol 27:644–650
Gradinger GP (1988) Cosmetic upper blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 15:289–297
Rohrich RJ, Coberly DM, Fagien S, Stuzin JM (2004) Current concepts in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:32e–42e
Flowers RS (1991) Periorbital aesthetic surgery for men. Eyelids and related structures. Clin Plast Surg 18:689–729
D’Assumpcao EA (1999) Blepharoplasty: a personal tactical approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 23:28–31
Chen WP (1996) Concept of triangular, trapezoidal, and rectangular debulking of eyelid tissues: application in Asian blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 97:212–218
Fagien S (2002) Advanced rejuvenative upper blepharoplasty: enhancing aesthetics of the upper periorbita. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:278–291
Fagien S (2010) The role of the orbicularis oculi muscle and the eyelid crease in optimizing results in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty: a new look at the surgical treatment of mild upper eyelid fissure and fold asymmetries. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:653–666
Older JJ (1995) Ptosis repair and blepharoplasty in the adult. Ophthalmic Surg 26:304–308
Brown MS, Putterman AM (2000) The effect of upper blepharoplasty on eyelid position when performed concomitantly with Muller muscle-conjunctival resection. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 16:94–100
Baker TJ (1981) Upper blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 8:635–641
Zide BM (1981) Anatomy of the eyelids. Clin Plast Surg 8:623–634
Tebbetts JB (1992) Blepharoplasty. A refined technique emphasizing accuracy and control. Clin Plast Surg 19:329–349
Damasceno RW, Cariello AJ, Cardoso EB, Viana GA, Osaki MH (2011) Upper blepharoplasty with or without resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle: a randomized double-blind left-right study. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 27:195–197
Hoorntje LE, Lei B, Stollenwerck GA, Kon M (2010) Resecting orbicularis oculi muscle in upper eyelid blepharoplasty: a review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:787–792
Siegel RJ (1993) Essential anatomy for contemporary upper lid blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 20:209–212
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 9,014 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bas, C.T., Pérez-Guisado, J. A New Approach: Resection and Suture of Orbicularis Oculi Muscle to Define the Upper Eyelid Fold and Correct Asymmetries. Aesth Plast Surg 37, 46–50 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9953-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9953-7