Abstract
Purpose
The aims of this anatomical study were to evaluate the feasibility of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a posterolateral approach in distal tibial fractures and to study the relationship between neurovascular structures and the plate.
Methods
Two separate incisions, one proximal and one distal, were made on the posterolateral aspect of ten cadaveric legs in the prone position. A 14-hole contralateral anterolateral distal tibial locking plate was inserted into the submuscular tunnel using a posterolateral approach, and one screw was fixed on each side of the proximal and distal tibia. The MIPO tunnel was then explored to identify the relationship between neurovascular bundles and plate.
Results
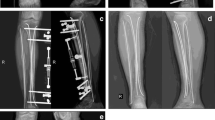
For the proximal incision, retraction of the flexor hallucis longus and the tibialis posterior muscles medially was very important because it could protect the posterior tibial artery and the tibial nerve during plating. The sural nerve and lesser saphenous vein were easily identified and retracted in the superficial layer of the distal incision. In addition, we achieved satisfactory outcomes after using this MIPO technique in one patient.
Conclusion
Based on the results of our study, it seems that using the MIPO technique through a posterolateral approach should be a reasonable and safe treatment option for distal tibial fractures, especially when the anterior soft tissue is compromised. However, studies with a higher level of evidence should be done in more patients to confirm the clinical safety of using this technique.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patterson MJ, Cole JD (1999) Two-staged delayed open reduction and internal fixation of severe pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(2):85–91
Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T et al (1999) A stage protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13(2):73–84
Harmon PH (1945) A simplified surgical approach to the posterior tibia for bone-grafting and fibular transference. J Bone Joint Surg Am 27(3):496–498
Abdelgawad AA, Kadous A, Kanlic E (2011) Posterolateral approach for treatment of posterior malleolus fracture of the ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg 50(5):607–611
Amorosa LF, Brown GD, Greisberg J (2010) A surgical approach to posterior pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(3):188–193
Gobezie RG, Ponce BA, Vrahas MS (2003) Pilon fractures: use of the posterolateral approach for ORIF. Oper Tech Orthop 13(2):113–119
Ketz J, Sanders R (2012) Staged posterior tibial plating for the treatment of Orthopaedic Trauma Association 43C2 and 43C3 tibial pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 26(6):341–347
Konrath GA, Hopkins G 2nd (1999) Posterolateral approach for tibial pilon fractures: a report of two cases. J Orthop Trauma 13(8):586–589
Sheerin DV, Turen CH, Nascone JW (2006) Reconstruction of distal tibia fractures using a posterolateral approach and a blade plate. J Orthop Trauma 20(4):247–252
Tornetta P 3rd, Ricci W, Nork S et al (2011) The posterolateral approach to the tibia for displaced posterior malleolus injuries. J Orthop Trauma 25(2):123–126
Borg T, Larsson S, Lindsjo U (2004) Percutaneous plating of distal tibia fractures: preliminary results in 21 patients. Injury 35(6):608–614
Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E et al (2002) Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma 16(10):691–695
Collinge C, Protzman R (2010) Outcomes of minimally invasive osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(1):24–29
Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R (2007) Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury 38(3):365–370
Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D et al (1997) Minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury 28(Suppl 1):A42–A48
Mushtaq A, Shahid R, Asif M et al (2009) Distal tibial fracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 35(2):159–164
Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJM (2004) Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury 35(6):615–620
Sohn OJ, Kang DH (2011) Staged protocol in the treatment of open distal tibia fracture: using lateral MIPO. Clin Orthop Surg 3(1):69–76
Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A et al (2004) Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop 28(3):159–162
Cheng W, Li Y, Manyi W (2011) Comparison study of two surgical options for distal tibia fracture-minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs. open reduction and internal fixation. Int Orthop 35(5):737–742
Lawrence SJ, Botte MJ (1994) The sural nerve in the foot and ankle: an anatomical study with clinical and surgical implications. Foot Ankle Int 15(9):490–494
Webb J, Moorjani N, Radford M (2000) Anatomy of the sural nerve and its relation to the Achilles tendon. Foot Ankle Int 21(6):475–477
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Suthorn Bavornratanavech, MD, of Bangkok Hospital Bangkok, Kanyika Chamniprasas, MD, of the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Physical Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University and Theerachai Apivatthakakul, MD, of the Department of Orthopaedics, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, for their support
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kritsaneephaiboon, A., Vaseenon, T. & Tangtrakulwanich, B. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fracture using a posterolateral approach: a cadaveric study and preliminary report. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 105–111 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1712-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1712-5