Abstract
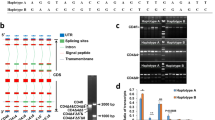
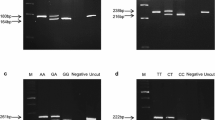
The Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) plays a crucial role in host defense against flagellated bacteria by recognizing flagellin. Accumulating evidence suggests that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TLR5 have an effect on flagellin recognition and are associated with susceptibility/resistance to disease. In this study, we analyzed association of SNPs, including c.834T>G, c.1065T>C, c.1205C>T, c.1246A>T, c.1269G>A, and c.1398C>T, as well as mRNA level of TLR5 with the abundance of transcripts of cytokines in pigs. SNPs c.1246A>T and c.1269G>A were significantly associated with the transcript abundance of interleukin (IL)-2, and SNPs c.834T>G and c.1398C>T with IL-10 (P < 0.05); the haplotypes showed a tendency to affect the transcript abundance of IL-10 (P = 0.0660) and significantly associated with the transcription of TLR5 (P < 0.01); the abundance of transcripts of TLR5 and IL-10 were strongly correlated (P < 0.01). The results indicated that the SNPs, associated with the transcript abundance of cytokines, were related to immune responsiveness mediated by cytokine, which, in turn, would have a role in pig breeding for disease resistance. Furthermore, the positive correlation between the abundance of TLR5 and IL10 suggest a link between TLR5 activation and IL-10 expression in porcine.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blander JM, Medzhitov R (2004) Regulation of phagosome maturation by signals from Toll-like receptors. Science 304:1014–1018
Chang ZL (2010) Important aspects of Toll-like receptors, ligands and their signaling pathways. Inflamm Res 59:791–808
Chung WS, Nam DH, Jo DJ, Lee JH (2011) Association of Toll-like receptor 5 gene polymorphism with susceptibility to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine in Korean population. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 49:8–12
Dasgupta S, Pal P, Mukhopadhyay ND, Fu Y, Ratovitski EA, Moon CS, Hoque MO, Fisher PB, Trink B (2012) A single nucleotide polymorphism in the human PIGK gene associates with low PIGK expression in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Oncol. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1567
Didierlaurent A, Ferrero I, Otten LA, Dubois B, Reinhardt M, Carlsen H, Blomhoff R, Akira S, Kraehenbuhl JP, Sirard JC (2004) Flagellin promotes myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent development of Th2-type response. J Immunol 172:6922–6930
Feuillet V, Medjane S, Mondor I, Demaria O, Pagni PP, Galán JE, Flavell RA, Alexopoulou L (2006) Involvement of Toll-like receptor 5 in the recognition of flagellated bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12487–12492
Gao Y, Flori L, Lecardonnel J, Esquerré D, Hu ZL, Teillaud A, Lemonnier G, Lefèvre F, Oswald IP, Rogel-Gaillard C (2011) Transcriptome analysis of porcine PBMCs after in vitro stimulation by LPS or PMA/ionomycin using an expression array targeting the pig immune response. BMC Genom 11:292
Goudy KS, Johnson MC, Garland A, Li C, Samulski RJ, Wang B, Tisch R (2011) Reduced IL-2 expression in NOD mice leads to a temporal increase in CD62Llo FoxP3+ CD4+ T cells with limited suppressor activity. Eur J Immunol 41:1480–1490
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410:1099–1103
Hawn TR, Verbon A, Lettinga KD, Zhao LP, Li SS, Laws RJ, Skerrett SJ, Beutler B, Schroeder L, Nachman A, Ozinsky A, Smith KD, Aderem A (2003) A common dominant TLR5 stop codon polymorphism abolishes flagellin signaling and is associated with susceptibility to Legionnaires' disease. J Exp Med 198:1563–1572
Hawn TR, Scholes D, Li SS, Wang H, Yang Y, Roberts PL, Stapleton AE, Janer M, Aderem A, Stamm WE, Zhao LP, Hooton TM (2009) Toll-like receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to urinary tract infections in adult women. PLoS One 4:e5990
Holm S, Mackiewicz Z, Holm AK, Konttinen YT, Kouri VP, Indahl A, Salo J (2009) Pro-inflammatory, pleiotropic, and anti-inflammatory TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-10 in experimental porcine intervertebral disk degeneration. Vet Pathol 46:1292–1300
House AK, Gregory SP, Catchpole B (2008) Pattern-recognition receptor mRNA expression and function in canine monocyte/macrophages and relevance to canine anal furunuclosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 124:230–240
Kathrani A, Holder A, Catchpole B et al (2012) TLR5 risk-associated haplotype for canine inflammatory bowel disease confers hyper-responsiveness to flagellin. PLoS One 7:e30117
Kathrani A, House A, Catchpole B et al (2010) Polymorphisms in the TLR4 and TLR5 gene are significantly associated with inflammatory bowel disease in German shepherd dogs. PLoS One 5:e15740
Kathrani A, House A, Catchpole B, Murphy A, Werling D, Allenspach K (2011) Breed-independent Toll-like receptor 5 polymorphisms show association with canine inflammatory bowel disease. Tissue Antigens 78:94–101
Keirstead ND, Hayes MA, Vandervoort GE, Brooks AS, Squires EJ, Lillie BN (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in collagenous lectins and other innate immune genes in pigs with common infectious diseases. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 142:1–13
Kim S, Cho H, Lee D et al (2012) Association between SNPs and gene expression in multiple regions of the human brain. Transl Psychiatry 2:e113
Lodes MJ, Cong Y, Elson CO, Mohamath R, Landers CJ, Targan SR, Fort M, Hershberg RM (2004) Bacterial flagellin is a dominant antigen in Crohn disease. J Clin Invest 113:1296–1306
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS, Michalek SM (2005) Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat Immunol 6:777–784
Merlo A, Calcaterra C, Mènard S, Balsari A (2007) Cross-talk between Toll-like receptors 5 and 9 on activation of human immune responses. J Leukoc Biol 82:509–518
Nerren JR, Swaggerty CL, MacKinnon KM, Genovese KJ, He H, Pevzner I, Kogut MH (2009) Differential mRNA expression of the avian-specific Toll-like receptor 15 between heterophils from Salmonella-susceptible and -resistant chickens. Immunogenetics 61:71–77
Ortega-Cava CF, Ishihara S, Rumi MA, Kawashima K, Ishimura N, Kazumori H, Udagawa J, Kadowaki Y, Kinoshita Y (2003) Strategic compartmentalization of Toll-like receptor 4 in the mouse gut. J Immunol 170:3977–3985
Ramírez Cruz NE, Maldonado Bernal C, Cuevas Urióstegui ML, Castañoń J, López Macías C, Isibasi A (2004) Toll-like receptors: dysregulation in vivo in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Rev Alerg Mex 51:210–217
Re F, Strominger JL (2004) IL-10 released by concomitant TLR2 stimulation blocks the induction of a subset of Th1 cytokines that are specifically induced by TLR4 or TLR3 in human dendritic cells. J Immunol 173:7548–7555
Reuss E, Fimmers R, Kruger A, Becker C, Rittner C, Höhler T (2002) Differential regulation of interleukin-10 production by genetic and environmental factors—a twin study. Genes Immun 3:407–413
Shinkai H, Suzuki R, Akiba M, Okumura N, Uenishi H (2011) Porcine Toll-like receptors: recognition of Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis and influence of polymorphisms. Mol Immunol 48:1114–1120
Shinkai H, Tanaka M, Morozumi T, Eguchi-Ogawa T, Okumura N, Muneta Y, Awata T, Uenishi H (2006) Biased distribution of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in porcine Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1), TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, and TLR6 genes. Immunogenetics 58:324–330
Sitaraman SV, Klapproth JM, Moore DA 3rd, Landers C, Targan S, Williams IR, Gewirtz AT (2005) Elevated flagellin-specific immunoglobulins in Crohn's disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G403–G406
Smith KD, Andersen-Nissen E, Hayashi F, Strobe K, Bergman MA, Barrett SL, Cookson BT, Aderem A (2003) Toll-like receptor 5 recognizes a conserved site on flagellin required for protofilament formation and bacterial motility. Nat Immunol 4:1247–1253
Strle K, Shin JJ, Glickstein LJ, Steere AC (2012) Association of a Toll-like receptor 1 polymorphism with heightened Th1 inflammatory responses and antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 64:1497–1507
Suradhat S, Thanawongnuwech R, Poovorawan Y (2003) Upregulation of IL-10 gene expression in porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Gen Virol 84:453–459
Suradhat S, Thanawongnuwech R (2003) Upregulation of interleukin-10 gene expression in the leukocytes of pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Gen Virol 84:2755–2760
Tworek D, Kuna P (2005) The role of interleukin 10 in allergic inflammation. Pol Merkur Lekarski 18:125–128
Vicente-Suarez I, Takahashi Y, Cheng F, Horna P, Wang HW, Wang HG, Sotomayor EM (2007) Identification of a novel negative role of flagellin in regulating IL-10 production. Eur J Immunol 37:3164–3175
Vijay-Kumar M, Sanders CJ, Taylor RT, Kumar A, Aitken JD, Sitaraman SV, Neish AS, Uematsu S, Akira S, Williams IR, Gewirtz AT (2007) Deletion of TLR5 results in spontaneous colitis in mice. J Clin Invest 117:3909–3921
Weaver LK, Pioli PA, Wardwell K, Vogel SN, Guyre PM (2007) Up-regulation of human monocyte CD163 upon activation of cell-surface Toll-like receptors. J Leukoc Biol 81:663–671
Xiao S, Jia J, Mo D et al (2010) Understanding PRRSV infection in porcine lung based on genome-wide transcriptome response identified by deep sequencing. PLoS One 5:e11377
Yang XQ, Murani E, Ponsuksili S, Wimmers K (2012) Association of TLR4 polymorphism with cytokine expression level and pulmonary lesion score in pigs. Mol Biol Rep 39:7003–7009
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31072007) and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (FUGATOplus-GeneDialog, FKZ 0315130 A) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Murani, E., Ponsuksili, S. et al. Association of TLR5 sequence variants and mRNA level with cytokine transcription in pigs. Immunogenetics 65, 125–132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-012-0662-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-012-0662-9