Abstract
Here, we review the current knowledge about the energetics of arginine insertion into the bilayer hydrocarbon core, and we discuss discrepancies between experimental and computational studies of the insertion process. While simulations suggest that it should be very costly to place arginine into the hydrocarbon core, experiments show that arginine is found there. Both types of studies suggest that arginine insertion into the bilayer involves substantial bilayer deformation, with multiple hydrogen bonds between the arginine guanidinium group and lipid polar groups. It is possible that the discrepancies concerning the insertion cost of arginine arise because simulations overestimate the cost associated with bilayer deformation and underestimate the ability of the bilayer to adapt to charged and polar groups. This is an active area of research, and there is no doubt that a consensus view of arginine in membranes will soon emerge.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorairaj S, Allen TW (2007) On the thermodynamic stability of a charged arginine side chain in a transmembrane helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:4943–4948
Engelman DM, Steitz TA, Goldman A (1986) Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem 15:321–353
Freeman TC Jr, Wimley WC (2010) A highly accurate statistical approach for the prediction of transmembrane beta-barrels. Bioinformatics 26:1965–1974
Freites JA et al (2005) Interface connections of a transmembrane voltage sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15059–15064
Freites JA, Tobias DJ, White SH (2006) A voltage sensor water pore. Biophys J 91:L90–L92
Han X, Mihailescu M, Hristova K (2006) Neutron diffraction studies of fluid bilayers with transmembrane proteins: structural consequences of the achondroplasia mutation. Biophys J 91:3736–3747
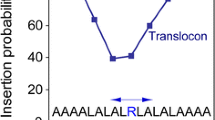
Hessa T et al (2005a) Recognition of transmembrane helices by the endoplasmic reticulum translocon. Nature 433:377–381
Hessa T, White SH, von Heijne G (2005b) Membrane insertion of a potassium-channel voltage sensor. Science 307:1427
Hessa T et al (2007) Molecular code for transmembrane-helix recognition by the Sec61 translocon. Nature 450:1026–1030
Jayasinghe S, Hristova K, White SH (2001) Energetics, stability, and prediction of transmembrane helices. J Mol Biol 312:927–934
Jiang Y et al (2003a) X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 423:33–41
Jiang Y et al (2003b) The principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 423:42–48
Jiang Z et al (2008) Effects of net charge and the number of positively charged residues on the biological activity of amphipathic alpha-helical cationic antimicrobial peptides. Biopolymers 90:369–383
Krepkiy D et al (2009) Structure and hydration of membranes embedded with voltage-sensing domains. Nature 462:473–479
Krishnakumar SS, London E (2007) Effect of sequence hydrophobicity and bilayer width upon the minimum length required for the formation of transmembrane helices in membranes. J Mol Biol 374:671–687
Li L et al (2008) Is arginine charged in a membrane? Biophys J 94:L11–L13
MacCallum JL, Bennett WF, Tieleman DP (2007) Partitioning of amino acid side chains into lipid bilayers: results from computer simulations and comparison to experiment. J Gen Physiol 129:371–377
MacCallum JL, Bennett WF, Tieleman DP (2008) Distribution of amino acids in a lipid bilayer from computer simulations. Biophys J 94:3393–3404
Miller G (2003) The puzzling portrait of a pore. Science 300:2020–2022
Parsegian A (1969) Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: solutions to four relevant electrostatic problems. Nature 221:844–846
Rathinakumar R, Wimley WC (2008) Biomolecular engineering by combinatorial design and high-throughput screening: small, soluble peptides that permeabilize membranes. J Am Chem Soc 130:9849–9858
Rathinakumar R, Walkenhorst WF, Wimley WC (2009) Broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides by rational combinatorial design and high-throughput screening: the importance of interfacial activity. J Am Chem Soc 131:7609–7617
Snider C et al (2009) MPEx: a tool for exploring membrane proteins. Protein Sci 18:2624–2628
Ulmschneider MB, Sansom MS, Di NA (2005) Properties of integral membrane protein structures: derivation of an implicit membrane potential. Proteins 59:252–265
White SH, Wimley WC (1999) Membrane protein folding and stability: physical principles. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 28:319–365
White SH, Wimley WC, Selsted ME (1995) Structure, function, and membrane integration of defensins. Curr Opin Struc Biol 5:521–527
White SH et al (2001) How membranes shape protein structure. J Biol Chem 276:32395–32398
Wimley WC (2002) Toward genomic identification of beta-barrel membrane proteins: composition and architecture of known structures. Protein Sci 11:301–312
Wimley WC (2003) The versatile beta-barrel membrane protein. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13:404–411
Wimley WC, White SH (1996) Experimentally determined hydrophobicity scale for proteins at membrane interfaces. Nat Struct Biol 3:842–848
Wimley WC, Creamer TP, White SH (1996) Solvation energies of amino acid sidechains and backbone in a family of host-guest pentapeptides. Biochemistry 35:5109–5124
Wolfenden R et al (1981) Affinities of amino acid side chains for solvent water. Biochemistry 20:849–855
Yount NY, Yeaman MR (2004) Multidimensional signatures in antimicrobial peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7363–7368
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our mentor, Stephen H. White, for countless moments of inspiration, and for helping us learn to be successful scientists and effective teachers. We would also like to thank the members of our own labs, past and present, for their constant hard work and for giving us the opportunity to share Steve’s lessons with the next generation. This work was supported by NIH grants GM60000 and GM068619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hristova, K., Wimley, W.C. A Look at Arginine in Membranes. J Membrane Biol 239, 49–56 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9323-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9323-9