Abstract
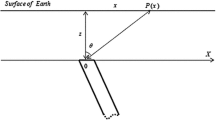
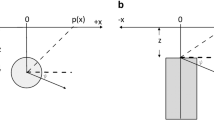
A quantitative interpretation method of self-potential field anomalies has been proposed. The method is designed and implemented for the estimation of center depth, electric dipole moment or magnitude of polarization, polarization angle, and geometric shape factor of a buried body from SP field data, related to simple geometric structures such as cylinders, spheres and sheet-like bodies. The proposed method is based on Fair function minimization and also on stochastic optimization modeling. This new technique was first tested on theoretical synthetic data randomly generated by a chosen statistical distribution from a known model with different random noise components. Such mathematical simulation shows a very close agreement between assumed and estimated model parameters. Being theoretically proven, it has been applied and tested on self-potential field data taken from the United States, Germany, India and Turkey. The agreement between results obtained by the suggested method and those obtained by other previous methods is good and comparable. Moreover, the depth obtained by this method is found to be in high accordance with that obtained from drilling information.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman, E.M., Ammar, A.A., Hassanein, H.I. and Hafez, M.A. (1998) Derivative analysis of SP anomalies, Geophys, 63: 890-897.
Abdelrahman. E.M., El-Arabi. H.M., Hassaneen. A.R. and Hafez. M.A. (2003) New methods for shape and depth determinations from SP data, Geophys, 68: 1202-1210.
Abdelrahman, E.S.M., El-Araby, T.M., Ammar, A.A. and Hassanein, H.I. (1997) A least-squares approach to shape determination from residual self-potential anomalies, Pure and Appl Geophys, 150: 121-128.
Abdelrahman, E.S.M. and Sharafeldin, S.M. (1997) A least-squares approach to depth determination from self-potential anomalies caused by horizontal cylinders and spheres, Geophys, 62:44-48.
Abdelrahman, E.S.M., Hassaneen, E.G. and Hafez, M, A. (1999) A least-squares approach for interpretation of self-potential anomaly over a two-dimensional inclined sheet, Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 24(1A): 35-42.
Abdelrahman, E.M., Saber, H.S., Essa, K.S., and Fouda, M.A. (2004) A least-squares approach to depth determination from numerical horizontal self-potential gradients, Pure and Appl Geophys, 161: 399-411.
Arora, N., and Biegler, L.T., 2001. Redescending estimators for data reconciliation and parameter estimation, Computer and Chemical Engineering 25, 1585-1599.
Asfahani, J. and Tlas, M. (2005) A constrained nonlinear inversion approach to quantitative interpretation of self-potential anomalies caused by cylinders, spheres and sheet-like structures, Pure and Appl Geophys, 162: 609-624.
Asfahani, J. and Tlas, M. (2007) A robust nonlinear inversion for the interpretation of magnetic anomalies caused by faults, thin dikes and spheres like structure using stochastic algorithms, Pure and Appl Geophys, 164:2023-2042.
Asfahani, J. and Tlas, M. (2011) Fair function minimization for direct interpretation of residual gravity anomaly profiles due to spheres and cylinders, Pure and Appl Geophys, Published on line: 05/25/2011.
Atchuta, Rao., Ram Babu. and Sivakumar Sinha, G.D.J. (1982) A Fourier transform method for the interpretation of self-potential anomalies due to two to two-dimensional inclined sheets of finite depth extent, Pure and Appl Geophys, 120: 365-374.
Bhattacharya, B.B. and Roy, N. (1981) A note on use of a Nomogram for self-potential anomalies, Geophys Prosp, 29: 102-107.
Chen, X., Pike, R.W., Hertwig, T.A., and Hopper, J.R., 1998. Optimal implementation of on-line optimization, Computer and Chemical Engineering 22 , 435-442.
Dobrin, M.B. (1960) Introduction to geophysical prospecting, McGraw-Hill book company, Inc.
Ingber, L. (1989) Very fast simulated re-annealing, Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 12(8): 967-973.
Ingber, L. (1996) Adaptive simulated annealing (ASA): lessons learned, J. Control and Cybernetics, 25: 33-54.
Ingber, L. and Rosen, B. (1992) Genetic algorithms and very fast simulated re-annealing: A comparison, Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 16 (11): 87-100.
Meiser, P. (1962) A method of quantitative interpretation of self- potential measurements, Geophys Prosp, 10 : 203-218.
Ozyurt, D.B., and Pike, R.W., 2004. Theory and practice of simultaneous data reconciliation and gross error detection for chemical processes, Computer and Chemical Engineering 28 , 381-402.
Paul, M.K. (1965) Direct interpretation of self–potential anomalies caused by inclined sheets of infinite extension, Geophys, 30: 418-423.
Roy, A. and Chowdhury, D.K. (1959) Interpretation of self-potential data for tabular bodies, J. Sci. Engng Res, 3 : 35-54.
Sen, M. and Stoffa, P.L. (1996) Bayesian inference, Gibbs’ sampler and uncertainty estimation in geophysical inversion, Geophys. Prospecting 44, 313-350.
Shalivahan, Bimalendu, B, Bhattacharya. and Mrinal,K.Sen. (1998) Interpretation of self-potential anomalies by nonlinear inversion, Journal of Geophysics, 19 (4):219-224.
Sundararajan, N., Arun Kumar,I., Mohan, N.L. and Seshagiri Rao, S.V. (1990) Use of Hilbert transform to interpret self-potential anomalies due to two dimensional inclined sheets, Pure and Appl Geophys, 133:117-126.
Sundararajan, N., Srinivas. Y. (1996) A modified Hilbert transform and its application to self-potential interpretation, J. Appl. Geophys, 36: 137-143.
Sundararajan, N., Srinivasa Rao, P. and Sunitha, V. (1998) An analytical method to interpret self-potential anomalies caused by 2-D inclined sheets, Geophys, 63(5):1551-1555.
Tlas, M. and Asfahani, J. (2007) A best-estimate approach for determining self-potential parameters related to simple geometric shaped structures, Pure and Appl Geophys, 164:2313-2328.
Yungul, S. (1950) Interpretation of spontaneous polarization anomalies caused by spherical ore bodies, Geophys, 15 : 237-246.
Yungul, S. (1954) Spontaneous potential survey of a copper deposit at Sariyer, Turkey, Geophys, 19 : 455-458.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. I. Othman, Director General of the Atomic Energy Commission of Syria, for his continuous encouragement and guidance in achieving this research. The reviewers are deeply thanked for their constructive remarks and suggestions which considerably improved the final version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tlas, M., Asfahani, J. An Approach for Interpretation of Self-Potential Anomalies due to Simple Geometrical Structures Using Fair Function Minimization. Pure Appl. Geophys. 170, 895–905 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0594-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0594-1