Abstract.
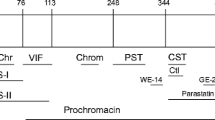
Chromogranin A (CgA) belongs to the granin family of uniquely acidic secretory proteins co-stored and co-secreted with other hormones and peptides in elements of the diffuse neuroendocrine system. The granins arise from different genes and are characterized by numerous sites for post-translational cleavage into shorter peptides with postulated regulatory properties. This review is directed towards endocrine aspects of CgA and its biologically active peptides. There is ample evidence from in vitro studies of distinct effects and targets for three CgA-derived peptides, vasostatin-I, pancreastatin and catestatin. Endocrine regulations are indicated from in vivo studies, consistent with the postulated prohormone function of CgA for peptides with regulatory properties. Most of the effects fit into patterns of direct or indirect, inhibitory modulations of major functions, implicating CgA peptides in regulation of calcium and glucose metabolism, cardiovascular functions, gastrointestinal motility and nociception, tissue repair, inflammatory responses and as host defense peptides in the first phase of microbial invasions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 1 June 2007; received after revision 11 July 2007; accepted 12 July 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helle, K.B., Corti, A., Metz-Boutigue, MH. et al. The endocrine role for chromogranin A: A prohormone for peptides with regulatory properties. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 2863–2886 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7254-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7254-0