Summary
Several investigators have studied the drug-drug interaction that may exist when alcohol and H2-receptor antagonists (i.e. cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine) are administered concomitantly. Results from these studies have been mixed. However, no systematic investigation of the change in blood alcohol concentrations in the social drinker versus the chronic drinker challenged by concurrent intake of alcohol and H2-receptor antagonist has been conducted.
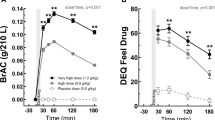
Eleven volunteers participated in this 14-day study. On day 0, study participants were administered an oral alcohol dose of 0.15 g/kg. On days 1 to 9, no medication was given. All volunteers then received cimetidine 400mg twice daily on days 10 to 13. On day 14, study participants received an oral alcohol dose of 0.15 g/kg after their morning dose of cimetidine. Blood sampling was performed on days 0 and 14 after alcohol administration.
The comparative alcohol availabilities, pre- and post-cimetidine, were determined by comparing the time to peak plasma concentration (tmax), peak plasma concentration (Cmax), and the total area under the concentration-time curve (AUC). In the chronic drinkers, tmax was significantly shorter than in the social drinkers following cimetidine administration (p=0.008).
Chronic drinkers who drink after cimetidine administration will have higher concentrations of alcohol faster than social drinkers. Medicolegal consequences resulting from this drug-drug interaction may occur; clinicians should therefore counsel patients about the possibility of enhanced impairment resulting from concurrent administration of these 2 drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caballeria J, Barona E, Rodamilans M, et al. Effects of cimetidine on gastric alcohol dehydrogenase activity and blood ethanol levels. Gastroenterology 96: 388–392, 1989
Caballeria J. Interactions between alcohol and gastric metabolizing enzymes: practical implications. Clinical Therapeutics 13: 511–520, 1991
DiPadova C, Roine R, Frezza M, et al. Effects of ranitidine on blood alcohol levels after ethanol ingestion. Journal of the American Medical Association 267: 83–86, 1992
Dobrilla G, de Pretis G, Piazzi L, et al. Is ethanol metabolism affected by oral administration of cimetidine and ranitidine at therapeutic doses? Hepatogastroenterology 31: 35–37, 1984
Feely J, Wood AJJ. Effects of cimetidine on the elimination and actions of ethanol. Journal of the American Medical Association 247: 2819–2821, 1982
Kleine M, Ertl D. Comparative trial in volunteers to investigate possible ethanol-ranitidine interaction. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 27: 841–845, 1993
Powell JR, Donn KH. The pharmacokinetic basis for H-2 antagonist drug interactions: concepts and implications. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 5 (Suppl.): 95–113, 1983
Raufman J, Notar-Francesco V, Raffaniello RD, Straus EW. Histamine-2 receptor antagonists do not alter serum ethanol levels in fed, nonalcoholic men. Annals of Internal Medicine 118: 488–494, 1993
Shumaker RC. PKCALC: A BASIC interactive computer program for statistical and pharmacokinetic analysis of data. Drug Metabolism Reviews 17: 331–348, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cook, M.D., Cold, J.A. & Strom, J.G. Effect of Cimetidine on the Pharmacokinetics of Alcohol in Social and Chronic Drinkers. Drug Invest 7, 84–92 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257403
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257403