Abstract
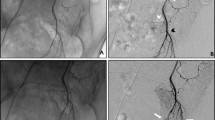
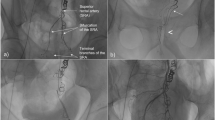
Four patients, aged 54–84 years, presenting with life-threatening rectal bleeding from the superior hemorrhoidal artery, underwent percutaneous fibered platinum coil embolization via coaxial catheters. Preprocedure sigmoidoscopy had failed to identify the source of hemorrhage, because the rectum was filled with fresh blood. Embolization was technically and clinically successful in all four patients. Subsequent sigmoidoscopy confirmed the diagnoses in three patients as a solitary rectal ulcer, iatrogenic traumatic ulceration following manual evacuation, and a rectal Dieulafoy’s lesion. The other case was angiographically seen to be due to a rectal angiodysplasia. Embolization is an effective procedure in life-threatening superior hemorrhoidal arterial bleeding when endoscopic treatment fails, and should be preferred to rectosigmoid resection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitaker SC, Gregson RH (1993) The role of angiography in the investigation of acute or chronic gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Clin Radiol 47:382–388
Rosen RJ, Sanchez G (1994) Angiographic diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal hemorrhage: Current concepts. Radiol Clin North Am 31:951–967
Zuckerman DA, Bocchini TP, Birnbaum EH (1993) Massive hemorrhage in the lower gastrointestinal tract in adults: Diagnostic imaging and intervention. AJR 161:703–711
Shapiro MJ (1994) The role of the radiologist in the management of gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 23:123–181
Hoch J, Janik V (1993) Arterial embolization in the case of massive haemorrhage from the rectum. Rozhledy V Chirurgii 72:255–257
Duff JH, Wright FF (1981) Acute and chronic benign ulcers of the rectum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 78:83–85
Basso L, Ahmed I (1996) Sengstaken tube for rectal angiodysplasia. Br J Surg 83:1795
Goldberger JE, Bookstein JJ (1977) Transcatheter embolization for treatment of diverticular hemorrhage. Radiology 122:613–617
Matolo NM, Link DP (1979) Selective embolization for control of gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Am J Surg 138:840–844
O’Halpin D, Legge D, MacErlean DP (1984) Therapeutic arterial embolisation: Report of five years’ experience. Clin Radiol 35:85–93
Kaufman SL, Martin LG, Zuckerman AM, Koch SR, Silverstein MI, Barton JW (1992) Peripheral transcatheter embolization with platinum microcoils. Radiology 184:369–372
Mitty HA, Efremedis S, Keller RJ (1979) Colonic stricture after transcatheter embolization for diverticular bleeding. AJR 133:591–521
Miller LS, Barbarevech C, Friedman LS (1994) Less frequent causes of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 23:21–52
Contractor TQ, Contractor QQ (1995) Traumatic solitary rectal ulcer in Saudi Arabia. A distinct entity? J Clin Gastroenterol 21:298–300
Bhargava SA, Putnam PE, Kocoshis SA, Hanchett JM (1996) Rectal bleeding in Prader-Willi syndrome. Pediatrics 97:265–267
Binderow SR, Mayer R, Freed JS (1995) Massive rectal hemorrhage from solitary rectal ulcer: Toward a definitive treatment. Mount Sinai J Med 62:308–311
Reinus JF, Brandt LJ (1994) Vascular ectasias and diverticulosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 23:1–20
Thompson JN, Salem RR, Hemingway AP, Rees HC, Hodgson HJ, Wood CB, Allison DJ, Spencer J (1987) Specialist investigation of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Gut 28:47–51
Roy MK, Rhodes M, Ruttley MS, Wheeler MH (1996) Sengstaken tube for bleeding rectal angiodysplasias. Br J Surg 83:1477
Reilly HF, Al-Kawas FH (1991) Dieulafoy’s lesion: Diagnosis and management. Dig Dis Sci 36:1702–1707
Pollack R, Lipsky H, Goldberg RI (1993) Duodenal Dieulafoy’s lesion. Gastrointest Endosc 39:820–822
Boron B, Mobarhan S (1987) Endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy’s hemorrhage. J Clin Gastroenterol 9:518–520
Franko E, Chardavoyne R, Wise L (1991) Massive rectal bleeding from a Dieulafoy’s lesion: A review of this unusual disease. Am J Gastroenterol 86:1546–1547
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobson, C.C., Nicholson, A.A. Treatment of rectal hemorrhage by coil embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22, 143–146 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03035356
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03035356