Abstract
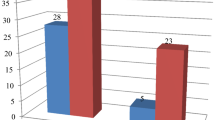
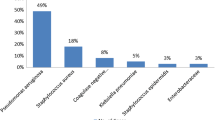
A total of 146 cases of chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM), comprising of 77 males and 69 females in different age groups were studied. A total of 132(77.6%) strains of different bacterial species were isolated as single infecting organism(monobacterial). Two or more bacterial species were obtained from 26 cultures revealing polybacterial growth of 15.3%. Out of total 192 isolates, Pseudomonas sp. ranked highest with 438% incidence followed by staphylococcus pyogenes(18.2%), proteus sp.(12%), Klebsiella sp.(7.3%) and Diphtheroides (6.7%). 86.4% of total bacteria put for antibiotic sensitivity tests showed susceptibility towards gentamycin followed by chloramphenicol(31.3%) and Ampicillin(14.8%).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baruah, P. C., Agarwal, S. C., Arora, M. M. L. and Mehra, Y. N. (1972): Clinical and Microbiological Studies in Suppurative Otitis Media. In Chandigarh.Indian journal of otolaryngology,24 : 157–160.
Bluestone, C. D. and Klein, J. O. (1988): Otitis Media in infants and Children. W. B. Saunders Company,Philadelphia, p.50.
Chhangani, D. L. and Goyal, O. P. (1976): Bacteriological study in Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaIndian Journal of Otolaryngology,28 : 41–45.
Cruickshank, R. (1975): Medical Microbiology ; 12th Ed. Vol. 11, Churchill, Livingstone.
Ersner, M. S. and Alexander, M. II. (1957): Otolaryngology, Prior,Maryland.
Fowler, E. P. Jr. (1948): Medicine of the year, Nelson,New york.
Klein, J. O. (1988): Antipseudomonal antibiotics. An overview.Annals of otology, Rhinology and Laryngology (supplement 131 : Mcrch–April, 1988) Vol. 97 (2) :Part 2 : 32–34.
Lakshmipathi, G. and Bhaskaran, C. S. (1965): Bacteriology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.Journal of Indian Medical Association,45 : 436–440.
Malik, A. K., Nangia, I. P., Sabharwal, V., Saini, S. and Chugh, T. D. (1982): Microbial Flora in Causes of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.Indian Medical Gazette,116 (10) : 305–307.
Mawson, S. R. (1963): Disease of Ear, 1st Ed., Arnold,London, pp. 293–294.
Pollack, M. (1988): “Special role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media” Workshop on CSOM. Etiology and Management. Eds. Bluestone, C. D., and Kenna, M., Published inAnnals of Otology Rhinology and Laryngology supplement 131., March–April 1988, Vol. 97 (2) ;Part 2 : 10–13.
Rao, M. V. R. and Jayakar, P. A. (1980): Bacteriological study of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.Journal of Indian Medical Association.75 : 30–34
Singh, M. P. Prabhakar, H. and Arora, S. (1985): Anaerobes and fungi in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.,Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology.3., July, 177–182.
Vaishnav, S. K. and Chhangani, D. L. (1981): Evaluation of bacteriological status in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media,Indian Journal of pathology and Microbiology.24 : 113–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandy, A., Mallya, P.S. & Sivarajan, K. Chronic suppurative otitis media—A bacteriological study. Indian J Otolaryngol 43, 136–138 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994107
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994107